Vue实现双向绑定的原理以及响应式数据
来源:互联网 发布:网络漫画 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/24 20:44
Vue中的数据实现响应式绑定
1、对象实现响应式:
是在初始化的时候利用definePrototype的定义set和get过滤器,在进行组件模板编译时实现water的监听搜集依赖项,当数据发生变化时在set中通过调用dep.notify进行发布通知,实现视图的更新。
2、数组实现响应式:
对于数组则是通过继承重写数组的方法splice、pop、push、shift、unshift、sort、reverse、等可以修改原数组的方式实现响应式的,但是通过length以及直接利用item[index]方式修改数组是不能实现响应式的改变dom(这种两种方式涉及到数组的内部实现)。在数据更新后为了避免过于频繁的进行dom的操作,在vue中会将更新的dom进行批量操作,而不是直接有数据更新就刷新dom,vue将需要更新的dom压入异步队列记性批量操作,提高性能。
下面具体的实现,实现原理大致如下:
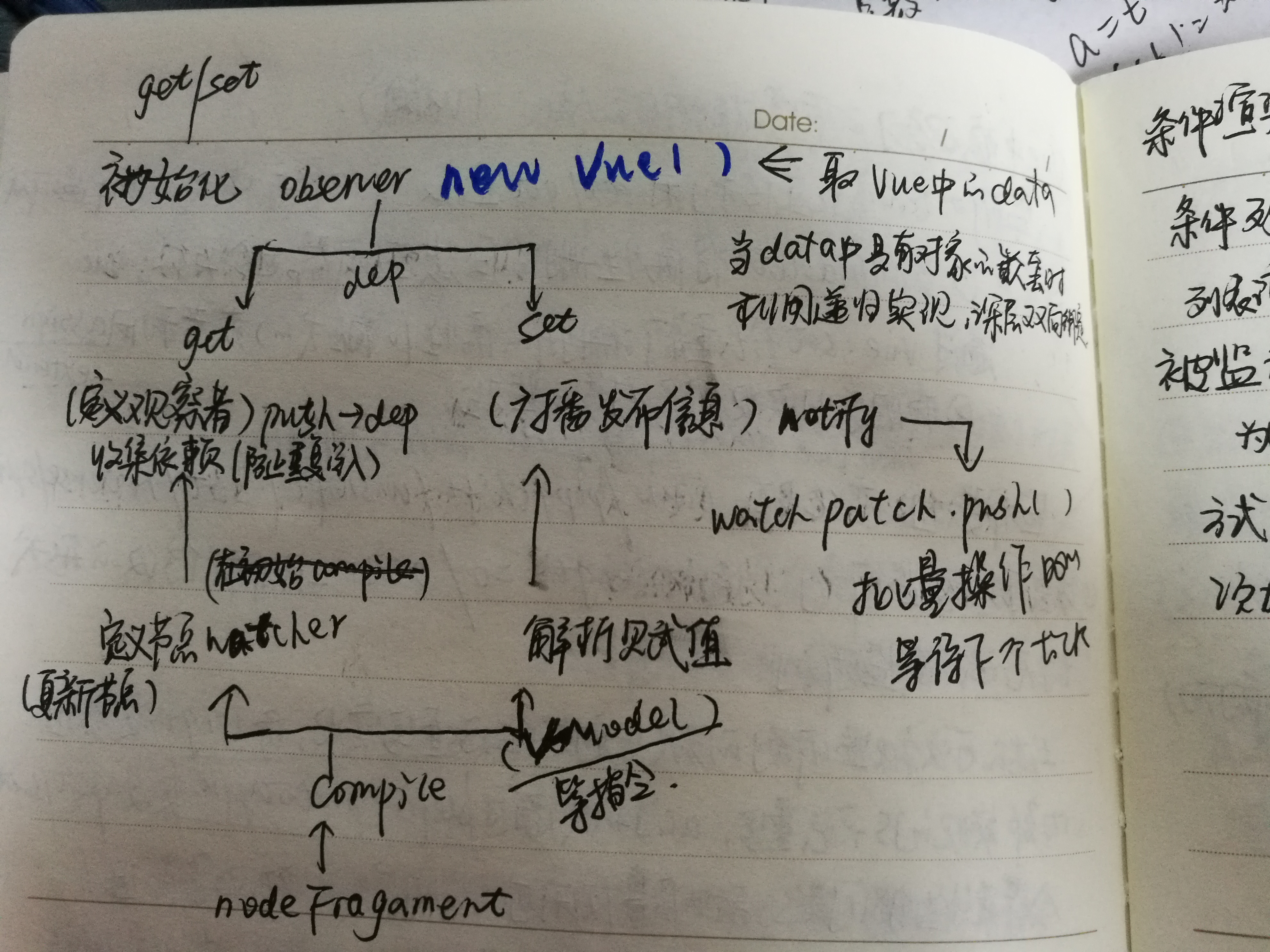
对象中实现双向数据绑定,可以直接在浏览器查看效果:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Two-way data-binding</title></head><body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="text"> {{ text }} </div> <script> function observe (obj, vm) { Object.keys(obj).forEach(function (key) { defineReactive(vm, key, obj[key]); }); } function defineReactive (obj, key, val) { var dep = new Dep(); Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { get: function () { // 添加订阅者watcher到主题对象Dep if (Dep.target) dep.addSub(Dep.target); return val }, set: function (newVal) { if (newVal === val) return val = newVal; // 作为发布者发出通知 dep.notify(); } }); } function nodeToFragment (node, vm) { var flag = document.createDocumentFragment(); var child; while (child = node.firstChild) { compile(child, vm); flag.appendChild(child); // 将子节点劫持到文档片段中 } return flag; } function compile (node, vm) { var reg = /\{\{(.*)\}\}/; // 节点类型为元素 if (node.nodeType === 1) { var attr = node.attributes; // 解析属性 for (var i = 0; i < attr.length; i++) { if (attr[i].nodeName == 'v-model') { var name = attr[i].nodeValue; // 获取v-model绑定的属性名 node.addEventListener('input', function (e) { // 给相应的data属性赋值,进而触发该属性的set方法 vm[name] = e.target.value; }); node.value = vm[name]; // 将data的值赋给该node node.removeAttribute('v-model'); } }; new Watcher(vm, node, name, 'input'); } // 节点类型为text if (node.nodeType === 3) { if (reg.test(node.nodeValue)) { var name = RegExp.$1; // 获取匹配到的字符串 name = name.trim(); new Watcher(vm, node, name, 'text'); } } } function Watcher (vm, node, name, nodeType) { Dep.target = this; this.name = name; this.node = node; this.vm = vm; this.nodeType = nodeType; this.update(); Dep.target = null; } Watcher.prototype = { update: function () { this.get(); if (this.nodeType == 'text') { this.node.nodeValue = this.value; } if (this.nodeType == 'input') { this.node.value = this.value; } }, // 获取data中的属性值 get: function () { this.value = this.vm[this.name]; // 触发相应属性的get } } function Dep () { this.subs = [] } Dep.prototype = { addSub: function(sub) { this.subs.push(sub); }, notify: function() { this.subs.forEach(function(sub) { sub.update(); }); } }; function Vue (options) { this.data = options.data; var data = this.data; observe(data, this); var id = options.el; var dom = nodeToFragment(document.getElementById(id), this); // 编译完成后,将dom返回到app中 document.getElementById(id).appendChild(dom); } var vm = new Vue({ el: 'app', data: { text: 'hello world' } }); </script></body></html>
在vue的data中定义的属性才具有响应式的效果,通过vue.name或者this.name形式定义的全局变量虽然可以在template中使用,但是其不是响应式的。同时在data中定义的对象obj,如果后面给对象定义新的属性也不是响应式的,除非通过vue提供的方法set设置,具体如下:
new vue({ data(){ return { obj:{} } }, methods:{ this.obj.name="hs"//非响应属性 this.$set(this.obj,'name','hs')//name属性将会是响应式的 }})如果data中定义的有数组元素同时在computed中也要注意具体如下面介绍。
二、computed定义的计算属性
1、在vue中$option.data中定义的数据是都是响应式的,在初始化生命周期的时候就已经实现了数据双向绑定,通常在view中只是用一个表达式语句,当绑定时的逻辑比较复杂是可以通过计算属性的方式实现。但是在computed中定义的属性只具有get方法,所以当在程序中改变属性的时候并不能实现视图的动态响应。可以通过显示的定义set的方式实现视图的刷新。
<div v-on:click="con">{{model1}}</div>JS代码
const app = new Vue({ data:function () { return { model:'hello', name:'world', } }, computed:{ model1: { get: function(){ return this.model; },set:function (val) { return this.model=val; } } }, methods:{ con:function () { this.model1="hello world"//动态修改model1属性时,视图也会跟着跟新 console.log(this.model1); } }, /* watch:{ 'model1':function (val) { console.log(val) } }*/ }).$mount('#app')
2、如果在computed中定义的属性依赖于data中定义的属性,当data中的属性动态变化时,视图中绑定的computed的值也会跟着变化
const app = new Vue({ /* router:router,*/ data:function () { return { model:'hello', name:'world', } }, computed:{ model1: { get: function(){ return a; },set:function (val) { a=val; } } }, methods:{ con:function () { this.model1="hello world" console.log(this.model1); } }, /* watch:{ 'model1':function (val) { console.log(val) } }*/ }).$mount('#app')
通过以上两种方式实现的computed的动态双向绑定实质是通过中间的层data的属性,computed中依赖的属性如果不是data中的属性则也不能实现动态的绑定 ,即当上面的get,set中的this.model换成一个全局的属性时,也不能实现动态的更新。所以实质上在vue中最为原始的响应式数据实际是在data中定义的,如果computed中定义的属性依赖于data中的属性时,其实质是其依赖data中的属性在访问时触发data中的getter方法,从而会注册监听器,所以当依赖属性变化时,computed中的属性也会跟着变化。但是在computed中定义的不具有依赖项的属性是直接挂在在vue实例上的属性其是不具有响应式的特点的。
3、watch监听data中属性的变化,可以实现和computed的同样的效果,当时当监听的属性依赖多个属性时,利用computed更为方便,如下:
(1)使用watch监听
<div id="demo">{{fullName}}</div> var vm = new Vue({ el: '#demo', data: { firstName: 'Foo', lastName: 'Bar', fullName: 'Foo Bar' }}) vm.$watch('firstName', function (val) { this.fullName = val + ' ' + this.lastName}) vm.$watch('lastName', function (val) { this.fullName = this.firstName + ' ' + val}(2)利用computed监听,更为简洁,同时computed会将结果进行缓存,当结果没有发生变化时,不会触发相应回调
var vm = new Vue({ data: { firstName: 'Foo', lastName: 'Bar' }, computed: { fullName: function () { return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName } }})
- Vue实现双向绑定的原理以及响应式数据
- vue实现数据双向绑定原理剖析
- vue.js双向数据绑定实现原理
- 【学习笔记】Vue中实现双向数据绑定的原理
- vue中数据双向绑定的实现原理
- vue双向数据绑定的原理解密
- vue双向数据绑定的原理
- Vue.js双向绑定的实现原理
- Vue.js双向绑定的实现原理
- Vue的双向绑定原理及实现
- vue双向数据绑定原理
- Vue 双向数据绑定原理
- vue如何实现数据的双向绑定
- Vue:实现双向数据绑定
- Vue双向数据绑定原理分析
- Vue.js双向数据绑定原理
- Vue双向数据绑定原理解析
- Vue 双向绑定的原理及实现Demo
- cookie和session的区别异同
- eclipse远程调试tomcat服务
- margin外边距合并问题以及解决方式
- 输入一个URL到页面呈现其中发生的过程-------http过程详解
- ORACLE在分区表的分区字段上进行更新的方法
- Vue实现双向绑定的原理以及响应式数据
- 最小公倍数和最大公约数求解方法
- Vue中过度动画效果应用
- 64位系统兼容32位工具
- vue组件之间的通信以及如何在父组件中调用子组件的方法和属性
- JS中判断对象是不是数组的方法
- JS以及CSS对页面的阻塞
- ES6中的export以及import的使用多样性
- Js中有关变量声明和函数声明提升的问题


