HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals
来源:互联网 发布:深圳网络教育机构 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/26 05:59
Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 5024 Accepted Submission(s): 2294
Total Submission(s): 5024 Accepted Submission(s): 2294
Problem Description
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
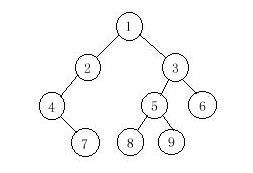
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.

Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
Output
For each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
91 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 64 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
Source
HDU 2007-Spring Programming Contest
题意:已知二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历,求后序遍历。
思路:先序遍历的第一个点便是根节点,中序遍历根节点左边的点是左子树,右边的点是右子树,分别递归左子树和右子树,再把他们当作一个整体,从中找出“根节点”(其实就是把递归前的那个“根节点”去掉后成为根节点的结点,这样,它又可以分作左子树和右子树,递归,直到找到叶子结点输出),由于递归是递归左子树,再递归右子树,再返回,其实就相当于后序遍历了。
Code Render Status : Rendered By HDOJ G++ Code Render Version 0.01 Beta#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>struct node{ int v; node *l, *r;};int a[1005], b[1005];node* bulid(int *a, int *b, int n){ for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ if(a[0] == b[i]){ node *t = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); t->l = bulid(a+1, b, i); t->r = bulid(a+i+1, b+i+1, n-i-1); t->v = b[i]; return t; } } return NULL;}void Postorder(node *s){ if(s->l != NULL) Postorder(s->l); if(s->r != NULL) Postorder(s->r); printf("%d%c", s->v, s->v==a[0]?'\n':' ');}int main(){ int n, i; while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF){ for(i = 0;i < n;i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); for(i = 0;i < n;i++) scanf("%d", &b[i]); node *root = bulid(a, b, n); Postorder(root); }} 0 0
- HDU1710:Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU1710-Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals【树的遍历】
- HDU1710——Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树)
- 数据结构之二叉树的遍历 HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals ----- 二叉树前序中序推后序
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树遍历)
- HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树重建模板609)
- HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals(DFS,二叉树的遍历)
- HDOJ1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- traversals for Binary Tree
- Android WebView页面加载优化
- Arduino IDE的编译执行过程解读
- sscanf用法总结
- NVIDIA Jetson TK1学习与开发(四):一些细节问题
- codeforces #345(div2)
- HDU1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- YTU 1439: 2.4.5 Fractions to Decimals 分数化小数
- Problem F: C语言习题 不等长字符串排序
- opencv颜色识别和操作
- Oracle12c中SQL优化(SQL TUNING)新特性之SQL计划指令
- 【bzoj1305】[CQOI2009]dance跳舞 最大流
- Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2) (D. Image Preview(二分))
- NVIDIA Jetson TK1学习与开发(五):helloworld的C版本与C++版本
- 时间复杂度


