Hadoop中sequencefile和mapfile的区别
来源:互联网 发布:天使语训软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 17:46
原文网址:http://blog.csdn.net/javaman_chen/article/details/7241087
Hadoop的HDFS和MapReduce子框架主要是针对大数据文件来设计的,在小文件的处理上不但效率低下,而且十分消耗内存资源(每一个小文件占用一个Block,每一个block的元数据都存储在namenode的内存里)。解决办法通常是选择一个容器,将这些小文件组织起来统一存储。HDFS提供了两种类型的容器,分别是SequenceFile和MapFile。
一、SequenceFile
SequenceFile的存储类似于Log文件,所不同的是Log File的每条记录的是纯文本数据,而SequenceFile的每条记录是可序列化的字符数组。
SequenceFile可通过如下API来完成新记录的添加操作:
fileWriter.append(key,value)
可以看到,每条记录以键值对的方式进行组织,但前提是Key和Value需具备序列化和反序列化的功能
Hadoop预定义了一些Key Class和Value Class,他们直接或间接实现了Writable接口,满足了该功能,包括:
Text 等同于Java中的String
IntWritable 等同于Java中的Int
BooleanWritable 等同于Java中的Boolean
.
.
在存储结构上,SequenceFile主要由一个Header后跟多条Record组成,如图所示:
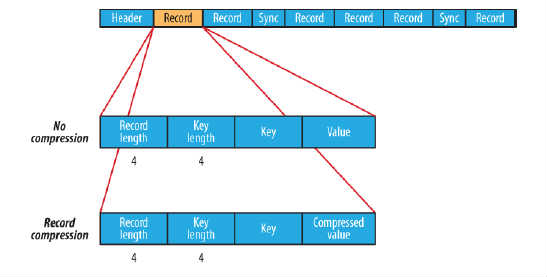
Header主要包含了Key classname,Value classname,存储压缩算法,用户自定义元数据等信息,此外,还包含了一些同步标识,用于快速定位到记录的边界。
每条Record以键值对的方式进行存储,用来表示它的字符数组可依次解析成:记录的长度、Key的长度、Key值和Value值,并且Value值的结构取决于该记录是否被压缩。
数据压缩有利于节省磁盘空间和加快网络传输,SeqeunceFile支持两种格式的数据压缩,分别是:record compression和block compression。
record compression如上图所示,是对每条记录的value进行压缩
block compression是将一连串的record组织到一起,统一压缩成一个block,如图所示:
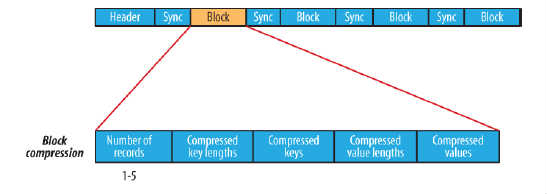
block信息主要存储了:块所包含的记录数、每条记录Key长度的集合、每条记录Key值的集合、每条记录Value长度的集合和每条记录Value值的集合
注:每个block的大小是可通过io.seqfile.compress.blocksize属性来指定的
示例:SequenceFile读/写 操作
二、MapFile
MapFile是排序后的SequenceFile,通过观察其目录结构可以看到MapFile由两部分组成,分别是data和index。
index作为文件的数据索引,主要记录了每个Record的key值,以及该Record在文件中的偏移位置。在MapFile被访问的时候,索引文件会被加载到内存,通过索引映射关系可迅速定位到指定Record所在文件位置,因此,相对SequenceFile而言,MapFile的检索效率是高效的,缺点是会消耗一部分内存来存储index数据。
需注意的是,MapFile并不会把所有Record都记录到index中去,默认情况下每隔128条记录存储一个索引映射。当然,记录间隔可人为修改,通过MapFIle.Writer的setIndexInterval()方法,或修改io.map.index.interval属性;
另外,与SequenceFile不同的是,MapFile的KeyClass一定要实现WritableComparable接口,即Key值是可比较的。
示例:MapFile读写操作
注意:使用MapFile或SequenceFile虽然可以解决HDFS中小文件的存储问题,但也有一定局限性,如:
1.文件不支持复写操作,不能向已存在的SequenceFile(MapFile)追加存储记录
2.当write流不关闭的时候,没有办法构造read流。也就是在执行文件写操作的时候,该文件是不可读取的。
个人理解:
mapfile就是为了解决sequencefile没有索引的问题而设置的,我们阅读mapfile的源码会发现。
/** A file-based map from keys to values.
*
* <p>A map is a directory containing two files, the <code>data</code> file,
* containing all keys and values in the map, and a smaller <code>index</code>
* file, containing a fraction of the keys. The fraction is determined by
* {@link Writer#getIndexInterval()}.
*
* <p>The index file is read entirely into memory. Thus key implementations
* should try to keep themselves small.
*
* <p>Map files are created by adding entries in-order. To maintain a large
* database, perform updates by copying the previous version of a database and
* merging in a sorted change list, to create a new version of the database in
* a new file. Sorting large change lists can be done with {@link
* SequenceFile.Sorter}.
*/
mapfile包含两个sequencefile文件一个存储数据一个存放索引。索引文件应该尽量保持比较小,因为操作数据文件时会把真个索引文件读取到内存。数据的添加和合并同sequencefile一致。
在来看看 write.append(key,value)
/** Append a key/value pair to the map. The key must be greater or equal
* to the previous key added to the map. */
public synchronized void append(WritableComparable key, Writable val)
throws IOException {
checkKey(key);
long pos = data.getLength();
// Only write an index if we've changed positions. In a block compressed
// file, this means we write an entry at the start of each block
if (size >= lastIndexKeyCount + indexInterval && pos > lastIndexPos) {
position.set(pos); // point to current eof
index.append(key, position);
lastIndexPos = pos;
lastIndexKeyCount = size;
}
data.append(key, val); // append key/value to data
size++;
}
我们可以看到几个信息:
①:if条件:size >= lastIndexKeyCount + indexInterval && pos > lastIndexPos,一个条件 key的个数 必须大于 key 上一次写入索引文件时key的值 + indexInterval (索引间隔,默认为128),第二个条件 ,写入位置即当前数据偏移量必须比上次写入偏移量大。这样保证了,每隔128个key值写一次索引文件。
②:添加的key值必须大于或等于先前的key,使用chek()函数来确定
③:index sequencefile的写入流 通过 index.append(key, position); 来确定索引文件的 key和value值,其中 value 是data.getLength()的值,data是通过 FSDataOutputStream输出流来确定当前数据在整个data文件中的偏移量。
待续。。。
欢迎朋友们指正。
- Hadoop中sequencefile和mapfile的区别
- Hadoop中的SequenceFile和MapFile
- Hadoop HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- Hadoop HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- Hadoop HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- Hadoop HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- 将Hadoop中SequenceFile,MapFile转换为文本文件
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- MapReduce中的SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- HDFS之SequenceFile和MapFile
- SequenceFile & MapFile
- SequenceFile & MapFile
- 2017 程序设计实习之C++部分作业题汇总
- 棋盘覆盖递归与分治算法
- opencv 图像模板匹配
- JS闭包理解以及立即执行函数
- Fiddler获取包信息
- Hadoop中sequencefile和mapfile的区别
- 配置UVCCamera驱动到内核
- Scrapy爬取百度股票时遇403错误的解决方法
- 剑指Offer面试题17 & Leetcode21
- 数据结构 — 二叉树的基本操作(递归实现)
- 串口中怎样接收一个完整数据包的解析
- java学生成绩管理系统
- 能不做自己写个类,也叫java.lang.String?
- VS2013+CUDA+TBB



