View 的绘制过程
来源:互联网 发布:詹姆斯对热火数据 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 15:25
1.概述
本文是 Android 开发艺术探索第4章,及如下两篇博客的学习笔记
http://www.cnblogs.com/yongdaimi/p/6164686.html
http://blog.csdn.net/a396901990/article/details/36475213
http://blog.csdn.net/a396901990/article/details/38129669
,源码是 Android N的。
view的 三大流程:measure、layout 和 draw
1.测量——onMeasure():测量 View 的宽和高,本文主要讲测量
2.布局——onLayout():决定 View 在 父容器 ViewGroup 中的位置
3.绘制——onDraw():将 View 绘制在屏幕上
ViewRoot(ViewRootImpl)是连接 WindowManager 和 DecorView 的纽带,View 的 三大流程 也是由 ViewRoot 来完成的。
ActivityThread 中 Activity 对象被创建完毕,会将 DecorView 添加到 Window 中,同时会创建 ViewRootImpl 对象,并关联 ViewRootImpl 和 DecorView对象。
//WindowManagerGlobal.addView() public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) { ... ViewRootImpl root; ... root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); ... root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView); ... }View 的绘制流程是从 ViewRootImpl.performTraversal() 开始的,performTraversal 依次调用了 performMeasure(), performLayout(), performDraw() 完成了 顶级 view 的 measure,layout,draw 三大流程,流程图如下,onMeasure() 会对所有子元素进行 测量,测量从 父容器到子元素中,完成测量。
// ViewRootImpl.java private void performTraversals() { ... // Ask host how big it wants to be performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); ... performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight); ... performDraw(); ... }2. MeasureSpec
测量过程中,系统会将 View 的 LayoutParams 根据父容器所施加的规则转换成 MeasureSpec,然后再根据 MeasureSpec 测量出 View 的 宽 / 高
其中 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 是 view 想要的大小说明, widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 需要 size 和 mode 来确定,MeasureSpec 和 size mode 的关系就封装在 MeasureSpec 里。
MeasureSpec作用就是通过二进制的方法,用一个变量携带两个数据(size,mode)
//View.java /** * A MeasureSpec encapsulates the layout requirements passed from parent to child. * Each MeasureSpec represents a requirement for either the width or the height. * A MeasureSpec is comprised of a size and a mode. There are three possible * modes: * <dl> * <dt>UNSPECIFIED</dt> * <dd> * The parent has not imposed any constraint on the child. It can be whatever size * it wants. * </dd> * * <dt>EXACTLY</dt> * <dd> * The parent has determined an exact size for the child. The child is going to be * given those bounds regardless of how big it wants to be. * </dd> * * <dt>AT_MOST</dt> * <dd> * The child can be as large as it wants up to the specified size. * </dd> * </dl> * * MeasureSpecs are implemented as ints to reduce object allocation. This class * is provided to pack and unpack the <size, mode> tuple into the int. */ public static class MeasureSpec { // 进位大小为2的30次方(int的大小为32位,所以进位30位就是要使用int的最高两位32和31位做标志位) private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30; // 3向左进位30,就是11 00000000000(11后跟30个0) private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint * on the child. It can be whatever size it wants. */ // 0向左进位30,就是00 00000000000(00后跟30个0) public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size * for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless * of how big it wants to be. */ // 01 00000000000(01后跟30个0) public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up * to the specified size. */ // 10 00000000000(10后跟30个0) public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Creates a measure specification based on the supplied size and mode. * * The mode must always be one of the following: * <ul> * <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}</li> * <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}</li> * <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST}</li> * </ul> * * <p><strong>Note:</strong> On API level 17 and lower, makeMeasureSpec's * implementation was such that the order of arguments did not matter * and overflow in either value could impact the resulting MeasureSpec. * {@link android.widget.RelativeLayout} was affected by this bug. * Apps targeting API levels greater than 17 will get the fixed, more strict * behavior.</p> * * @param size the size of the measure specification * @param mode the mode of the measure specification * @return the measure specification based on size and mode */ // measureSpec = size + mode; (注意:二进制的加法,不是十进制的加法!) // 这里设计的目的就是使用一个32位的二进制数,32和31位代表了mode的值,后30位代表size的值 public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size, @MeasureSpecMode int mode) { if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) { return size + mode; } else { return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK); } } /** * Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification. * * @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from * @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}, * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY} */ @MeasureSpecMode public static int getMode(int measureSpec) { //noinspection ResourceType // mode = measureSpec & MODE_MASK; // MODE_MASK = 11 00000000000(11后跟30个0),原理是用MODE_MASK后30位的0替换掉measureSpec后30位中的1,再保留32和31位的mode值。 // 例如10 00..00100 & 11 00..00(11后跟30个0) = 10 00..00(AT_MOST),这样就得到了mode的值 return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK); } /** * Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification. * * @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from * @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification */ public static int getSize(int measureSpec) { // 原理同上,不过这次是将MODE_MASK取反,也就是变成了00 111111(00后跟30个1),将32,31替换成0也就是去掉mode,保留后30位的size return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK); } ... }SpecMode 的三种类型:
- UNSPECIFIED :父容器不对 view 有任何限制,要多大给多大,一般用于系统内部,表示一种测量的状态。——二进制表示:00
- EXACTLY :父容器已经检验出 view 所需要的精确大小,SpecSize 就是 view 的最终大小,对应 LayoutParams 的 match_parent 和 具体数值。——二进制表示:01
- AT_MOST :View的大小 不能大于 父容器指定的 SpecSize,对应 LayoutParams 的 wrap_content。——二进制表示:10
3. MeasureSpec 和 LayoutParams
View 测量的时候,系统会将 LayoutParams 在 父容器的约束下,转换成对应的 MeasureSpec,然后再根据 MeasureSpec 来测量 view 的宽/高。也就是说 LayoutParams 和 父容器 共同决定了 MeasureSpec。
顶级View(DecorView)和普通View不同:
DecorView 的 MeasureSpec 由 窗口的大小 和 自己的 LayoutParams 决定。
普通view 的 MeasureSpec 由父容器的 MeasureSpec 和 自己的 LayoutParams 决定。
MeasureSpec 确定了,onMeasure() 就可以确定 View 的测量的宽/高了。
3.1 DecorView 的 MeasureSpec 过程
// ViewRootImpl.java private boolean measureHierarchy(final View host, final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, final Resources res, final int desiredWindowWidth, final int desiredWindowHeight) { ... childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width); childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height); performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); ... } /** * Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's * layout params. * * @param windowSize * The available width or height of the window * * @param rootDimension * The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the * window. * * @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view. */ private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) { int measureSpec; // 根据 LayoutParams 中的 宽/高 参数来分类 switch (rootDimension) { case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT: // Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize. // EXACTLY 精确模式,大小就是 窗口的大小 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY); break; case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT: // Window can resize. Set max size for root view. // AT_MOST 最大模式,大小不定,但是不能超过窗口的大小 measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST); break; default: // Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size. // 固定大小(比如 100dp),EXACTLY 精确模式,大小为 LayoutParams 指定的大小,比如 100dp measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY); break; } return measureSpec; }3.2 ViewGroup 中的 view 的 MeasureSpec 过程
// ViewGroup /** * Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into * account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding * and margins. The child must have MarginLayoutParams The heavy lifting is * done in getChildMeasureSpec. * * @param child The child to measure * @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view * @param widthUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent * horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent) * @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view * @param heightUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent * vertically (possibly by other children of the parent) */ protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed, int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) { final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); // 得到子元素的 MeasureSpec, 子元素的 MeasureSpec 与父容器的 MeasureSpec, // 子元素本身的 LayoutParams, View 的 margin, padding 有关 final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + widthUsed, lp.width); final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + heightUsed, lp.height); child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); } /** * Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to * pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec * for one dimension (height or width) of one child view. * * The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the * LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example, * if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of * EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants * to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to * layout given an exact size. * * @param spec The requirements for this view,父 view 的 MeasureSpec * @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and * margins, if applicable. view的内边距和外边距(padding 和 margin) * @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current * dimension. view 的 LayoutParams.with 和 height * @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child */ public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) { // 父 view 的模式 和 大小 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec); // 通过父 view 计算 子view = 父大小 - 边距 // 父要求的大小,子view 不一定用 int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding); // 子view 的实际大小和模式 int resultSize = 0; int resultMode = 0; // 通过父view的 MeasureSpec 和 子view的LayoutParams属性 确定子view的大小 switch (specMode) { // Parent has imposed an exact size on us // 父view是 EXACTLY 精确模式 case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: if (childDimension >= 0) { // 子view 有明确的值,用子view的值 resultSize = childDimension; resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { // Child wants to be our size. So be it. // 子view是 MATCH_PARENT,用父View的值 resultSize = size; resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) { // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be // bigger than us. // 子view自己决定大小,但不能超过父view,模式是 AT_MOST resultSize = size; resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; } break; // Parent has imposed a maximum size on us case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: if (childDimension >= 0) { // Child wants a specific size... so be it resultSize = childDimension; resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { // Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed. // Constrain child to not be bigger than us. resultSize = size; resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) { // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be // bigger than us. resultSize = size; resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; } break; // Parent asked to see how big we want to be // 当父view的模式为UNSPECIFIED时,父容器不对view有任何限制,要多大给多大 // (多见于ListView、GridView) case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: if (childDimension >= 0) { // Child wants a specific size... let him have it resultSize = childDimension; resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { // Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should // be resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size; resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED; } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) { // Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how // big it should be resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size; resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED; } break; } //noinspection ResourceType return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode); }
一个view的宽高尺寸,只有在测量之后才能得到,也就是measure方法被调用之后。大家都应该使用过View.getWidth()和View.getHeight()方法,这两个方法可以返回view的宽和高,但是它们也不是在一开始就可以得到的,比如oncreate方法中,因为这时候measure方法还没有被执行,测量还没有完成,我们可以来作一个简单的实验:自定义一个MyView,继承View类,然后在OnCreate方法中,将其new出来,通过addview方法,添加到现在的布局中。然后调用MyView对象的getWidth()和getHeight()方法,会发现得到的都是0。
4. measure 过程
Measure 过程分两种情况:
1.一个 View,通过 measure 方法完成测量
2.一个 ViewGroup,先完成自己的测量,然后遍历调用所有子view的 measure(),各子元素再递归去执行测量流程。
4.1 View的 measure 过程
// ViewRootImpl.java private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure"); try { mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); } finally { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } } // View.java /** * <p> * This is called to find out how big a view should be. The parent * supplies constraint information in the width and height parameters. * </p> * * <p> * The actual measurement work of a view is performed in * {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, called by this method. Therefore, only * {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} can and must be overridden by subclasses. * </p> * * * @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the * parent * @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the * parent * * @see #onMeasure(int, int) */ // final 方法,不能被重写 public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { ... // measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); ... } /** * <p> * Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the * measured height. This method is invoked by {@link #measure(int, int)} and * should be overridden by subclasses to provide accurate and efficient * measurement of their contents. * </p> * * <p> * <strong>CONTRACT:</strong> When overriding this method, you * <em>must</em> call {@link #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)} to store the * measured width and height of this view. Failure to do so will trigger an * <code>IllegalStateException</code>, thrown by * {@link #measure(int, int)}. Calling the superclass' * {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} is a valid use. * </p> * * <p> * The base class implementation of measure defaults to the background size, * unless a larger size is allowed by the MeasureSpec. Subclasses should * override {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to provide better measurements of * their content. * </p> * * <p> * If this method is overridden, it is the subclass's responsibility to make * sure the measured height and width are at least the view's minimum height * and width ({@link #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()} and * {@link #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()}). * </p> * * @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent. * The requirements are encoded with * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}. * @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent. * The requirements are encoded with * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}. * * @see #getMeasuredWidth() * @see #getMeasuredHeight() * @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int) * @see #getSuggestedMinimumHeight() * @see #getSuggestedMinimumWidth() * @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getMode(int) * @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getSize(int) */ // 需要被子类重写,子类决定 view 的大小 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { // getDefaultSize() 将获取的宽度/高度 作为默认值 // 再根据具体的测量值 和 选用的模式 还得到 widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec // 将 widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec 传入 setMeasuredDimension() setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)); } /** * <p>This method must be called by {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to store the * measured width and measured height. Failing to do so will trigger an * exception at measurement time.</p> * * @param measuredWidth The measured width of this view. May be a complex * bit mask as defined by {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK} and * {@link #MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL}. * @param measuredHeight The measured height of this view. May be a complex * bit mask as defined by {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK} and * {@link #MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL}. */ protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) { boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this); if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) { Insets insets = getOpticalInsets(); int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right; int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom; measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth; measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight; } setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight); } /** * Utility to return a default size. Uses the supplied size if the * MeasureSpec imposed no constraints. Will get larger if allowed * by the MeasureSpec. * * @param size Default size for this view,默认大小 * @param measureSpec Constraints imposed by the parent,测量的大小 * @return The size this view should be. */ public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) { int result = size; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); switch (specMode) { case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: // 返回参数 默认大小size,即 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() getSuggestedMinimumHeight() result = size; break; case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: // 返回测量的大小:measureSpec 中的 specSize result = specSize; break; } return result; } /** * Returns the suggested minimum width that the view should use. This * returns the maximum of the view's minimum width * and the background's minimum width * ({@link android.graphics.drawable.Drawable#getMinimumWidth()}). * <p> * When being used in {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, the caller should still * ensure the returned width is within the requirements of the parent. * * @return The suggested minimum width of the view. */ protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() { // 没有背景时,返回 mMinWidth,对应的是 android:minWidth 属性的值 // 有背景时,返回 max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth()) return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth()); } /** * Returns the suggested minimum height that the view should use. This * returns the maximum of the view's minimum height * and the background's minimum height * ({@link android.graphics.drawable.Drawable#getMinimumHeight()}). * <p> * When being used in {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, the caller should still * ensure the returned height is within the requirements of the parent. * * @return The suggested minimum height of the view. */ protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() { return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight : max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight()); }getDefaultSize() 中,view 的宽/高由 specSize 决定,所以 继承自 View 的自定义控件,需要重写 onMeasure() 并设置 wrap_content 时的自身大小,否则 wrap_content 和 match_parent 的大小是一样的。
原因:getChildMeasureSpec() 中 wrap_content 的 view 的 specMode 是 AT_MOST 模式,该模式在 getChildMeasureSpec() 返回的大小是 specSize,getChildMeasureSpec() 可知 此时的 specSize 是 parentSize,即 父容器目前可以使用的大小,父容器当前剩余空间的大小。
解决:自定义 View 重写 onMeasure() 时,需要给一个默认宽/高,在 wrap_content(specMode 是 AT_MOST) 时使用
4.2 ViewGroup 的 measure 过程
ViewGroup 是个抽象类,本身没有实现 onMeasure(),但是他的子类都有各自的实现,比如 LinearLayout , RelativeLayout 等,布局特性不同,实现也不同。
通常他们都是通过 measureChildWithMargins() 或者其他类似于measureChild() 来遍历测量子View,被 GONE 的子View将不参与测量,当所有的子View都测量完毕后,才根据父View传递过来的模式和大小来最终决定自身的大小。
// ViewGroup.java /** * Ask all of the children of this view to measure themselves, taking into * account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding. * We skip children that are in the GONE state The heavy lifting is done in * getChildMeasureSpec. * 遍历所有的子view去测量自己(跳过GONE类型View) * @param widthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view,父视图的宽详细测量值 * @param heightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view,父视图的高详细测量值 */ protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { final int size = mChildrenCount; final View[] children = mChildren; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { final View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) { measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } } } /** * Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into * account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding. * The heavy lifting is done in getChildMeasureSpec. * * @param child The child to measure * @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view * @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view */ protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec) { // 取出子元素的 LayoutParams final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams(); // getChildMeasureSpec() 创建子元素的 MeasureSpec final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width); final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height); // 将 子元素的 MeasureSpec 传递给 View 的 measure() 进行测量 child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); }View视图结构:
View视图可以是单一的一个如TextView,也可以是一个视图组(ViewGroup)如LinearLayout。
如图:对于多View的视图他的结构是树形结构,最顶层是ViewGroup,ViewGroup下可能有多个ViewGroup或View。
这个树的概念很重要,因为无论我们是在测量大小或是调整布局的时候都是从树的顶端开始一层一层,一个分支一个分支的进行(树形递归)。
measure 的作用就是为整个 View树计算实际的大小,而通过刚才对 View树的介绍知道,想计算整个 View树的大小,就需要递归的去计算每一个子视图的大小(Layout同理)。
对每一个视图通过 onMeasure() 的一系列测量流程后计算出实际的高(mMeasuredHeight)和宽(mMeasureWidth)传入 setMeasuredDimension() 完成单个 View 的测量,如果所测的视图是 ViewGroup 则可以通过 measureChild() 递归的计算其中的每一个子view。对于每个 View 的实际宽高都是由父视图和本身视图决定的。
measure 完成以后,通过 getMeasuredWidth()/Height() 可以获取 view 的测量宽/高,
需要注意的是,在某些极端情况下,系统可能需要 measure 多次才能确定最终的测量宽/高,这种情况下,onMeasure() 中拿到的测量宽/高是不准确的
比较好的习惯是:在 onLayout() 中获取 view 的测量宽/高 或 最终宽/高
在Activity的 onCreate()、onStart()、onResume() 中获取 view 的宽/高 信息,可能为0。
原因:view 的 measure 过程 和 Activity 的生命周期方法是不同步的。
解决:
1.Activity/View.onWindowFocusChanged()
Activity 焦点变更(获得或失去)都会调用该方法,该方法中,view已经初始化完毕了,宽/高已经准备好了,可以获取宽/高
2.view.post(runnable)
3.ViewTreeOnserver
4.view.measure()
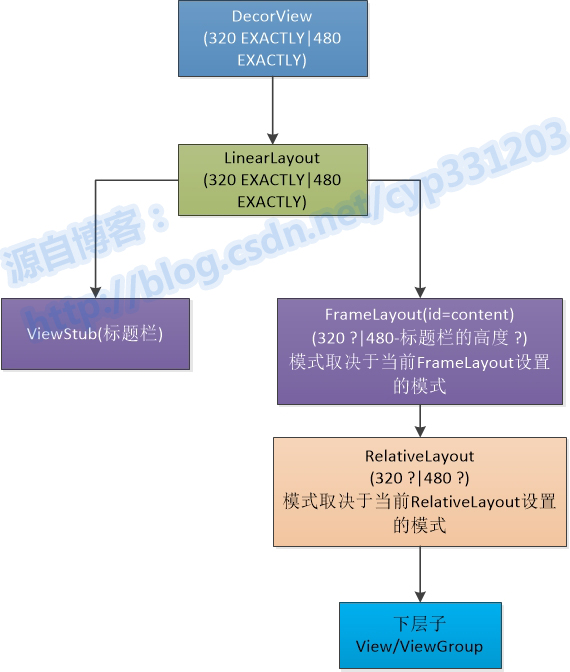
4.3 helloWorld 的 UI层级关系图
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="${relativePackage}.${activityClass}" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>为了方便起见,这里我们使用requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);去除标题栏的影响,只看层级关系。
package com.example.hello; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Window; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } }UI 层级图: 
可以发现最简单的helloworld的层级关系图是这样的,
最开始是一个 PhoneWindow 的内部类 DecorView,这个 DecorView 实际上是系统最开始加载的最底层的一个 viewGroup,它是 FrameLayout 的子类,
然后加载了一个 LinearLayout,在这个 LinearLayout 上加载了一个 id 为 content 的 FrameLayout 和一个 ViewStub,这个实际上是原本为 ActionBar 的位置,由于我们使用了 requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE),于是变成了空的 ViewStub;
然后在 id 为 content 的 FrameLayout 才加载了我们的布局 XML 文件中写的 RelativeLayout 和 TextView。
那么measure方法在系统中传递尺寸和模式,必定是从DecorView这一层开始的,我们假定手机屏幕是320*480,那么DecorView最开始是从硬件的配置文件中读取手机的尺寸,然后设置measure的参数大小为320*480,而模式是EXCACTLY,传递关系可以由下图示意:
5. layout 过程
layout 过程决定了 view 的四个顶点的坐标和实际的 view 的宽/高,完成后,可以通过 getTop()、getBottom()、getLeft() 和 getRight() 来获取 view 的四个顶点的位置,也可以通过 getWidth() getHeight() 来拿到 view 的最终的宽/高
layout 的作用是 ViewGroup 用来确定子元素的位置,当 ViewGroup 的位置确定后,在 onLayout() 中遍历所有子元素并调用 layout(),在 layout() 中也会调用 onLayout()
// View.java /** * Assign a size and position to a view and all of its * descendants * * <p>This is the second phase of the layout mechanism. * (The first is measuring). In this phase, each parent calls * layout on all of its children to position them. * This is typically done using the child measurements * that were stored in the measure pass().</p> * * <p>Derived classes should not override this method. * Derived classes with children should override * onLayout. In that method, they should * call layout on each of their children.</p> * * @param l Left position, relative to parent * @param t Top position, relative to parent * @param r Right position, relative to parent * @param b Bottom position, relative to parent */ @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"}) public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) { onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec); mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; } // 传入的参数是新的 左上右下的值 int oldL = mLeft; int oldT = mTop; int oldB = mBottom; int oldR = mRight; // setFrame() 初始化 mLeft、mRight、mTop 和 mBottom 的值 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b); if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) { // 父元素完成自己的定位,调用 onLayout() 确定子元素的位置 // View 和 ViewGroup 都没有 onLayout() 的实现,需要子类实现 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED; ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo; if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) { ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy = (ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone(); int numListeners = listenersCopy.size(); for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) { // 调用 onLayoutChange(), // 通知所有注册了OnLayoutChangeListener的类view大小和位置发生变化 listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB); } } } mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT; mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT; } // LinearLayout.java @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) { layoutVertical(l, t, r, b); } else { layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b); } } /** * Position the children during a layout pass if the orientation of this * LinearLayout is set to {@link #VERTICAL}. * * @see #getOrientation() * @see #setOrientation(int) * @see #onLayout(boolean, int, int, int, int) * @param left * @param top * @param right * @param bottom */ void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { final int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft; int childTop; int childLeft; // Where right end of child should go final int width = right - left; int childRight = width - mPaddingRight; // Space available for child int childSpace = width - paddingLeft - mPaddingRight; final int count = getVirtualChildCount(); final int majorGravity = mGravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK; final int minorGravity = mGravity & Gravity.RELATIVE_HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK; switch (majorGravity) { case Gravity.BOTTOM: // mTotalLength contains the padding already childTop = mPaddingTop + bottom - top - mTotalLength; break; // mTotalLength contains the padding already case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL: childTop = mPaddingTop + (bottom - top - mTotalLength) / 2; break; case Gravity.TOP: default: childTop = mPaddingTop; break; } // 遍历所有的子 view for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i); if (child == null) { childTop += measureNullChild(i); } else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) { final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); ... if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) { childTop += mDividerHeight; } childTop += lp.topMargin; // setChildFrame() 调用子view 的 layout(), 为子元素指定对应的位置 setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child), childWidth, childHeight); // childTop 逐渐增大,后边的子元素在靠下的位置 childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child); i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i); } } } private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) { child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height); }layout 完成父元素的定位,通过 onLayout() 调用 子view的 layout() 确定子view 的位置
5.1 getHeight 与 getMeasuredHeight
// View.java /** * Return the width of the your view. * * @return The width of your view, in pixels. */ @ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout") public final int getWidth() { return mRight - mLeft; } /** * Return the height of your view. * * @return The height of your view, in pixels. */ @ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout") public final int getHeight() { return mBottom - mTop; } protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { ... mLeft = left; mTop = top; mRight = right; mBottom = bottom; ... } /** * Like {@link #getMeasuredHeightAndState()}, but only returns the * raw width component (that is the result is masked by * {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK}). * * @return The raw measured height of this view. */ public final int getMeasuredHeight() { return mMeasuredHeight & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK; } /** * Like {@link #getMeasuredWidthAndState()}, but only returns the * raw width component (that is the result is masked by * {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK}). * * @return The raw measured width of this view. */ public final int getMeasuredWidth() { return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK; } view.getLeft()——mLeft:子 View 左边界到父 view 右边界的距离
view.getTop()——mTop:子 View 上边界到父 view 下边界的距离
view.getRight()——mRight:子 View 右边界到父 view 左边界的距离
view.getBottom()——mBottom:子 View 下边距到父 View 上边界的距离
上边的代码,getWidth() 返回的是 view 的测量宽度, getHeight() 返回的是 view 的测量高度
测量宽/高形成于 measure 过程,最终宽/高 形成于 layout 过程,大部分情况是相等的,只有特殊情况不等。
getWidth() ,和 getLeft() 等这些函数都是View相对于其父View的位置。而getMeasuredWidth() , getMeasuredHeight() 是测量后该View的实际值(有点绕,下面摘录一段jafsldkfj所写的Blog中的解释).
实际上在当屏幕可以包裹内容的时候,他们的值是相等的,
只有当view超出屏幕后,才能看出他们的区别:
getMeasuredHeight() 是实际 View 的大小,与屏幕无关,而 getHeight() 的大小此时则是屏幕的大小。
当超出屏幕后,getMeasuredHeight() 等于getHeight() 加上屏幕之外没有显示的大小
6. draw 过程
draw 的作用是将 view 绘制到屏幕上,view 的绘制遵循如下几个步骤:
(1) 绘制背景 background.draw(canvas)
(2)绘制自己(onDraw)
(3)绘制Children(dispatchDraw)
(4)绘制装饰(onDrawScrollBars)
// View.java /** * Manually render this view (and all of its children) to the given Canvas. * The view must have already done a full layout before this function is * called. When implementing a view, implement * {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} instead of overriding this method. * If you do need to override this method, call the superclass version. * * @param canvas The Canvas to which the View is rendered. */ @CallSuper public void draw(Canvas canvas) { final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags; final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE && (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState); mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN; /* * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed * in the appropriate order: * * 1. Draw the background * 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading * 3. Draw view's content * 4. Draw children * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) */ // Step 1, draw the background, if needed int saveCount; if (!dirtyOpaque) { drawBackground(canvas); } // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case) final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0; boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0; if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) { // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children // 通过 dispatchDraw() 实现绘制的传递,遍历所有子 view.draw() dispatchDraw(canvas); // Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) { mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas); } // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars) onDrawForeground(canvas); // we're done... return; } ... }- view 的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- view的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程
- View 的绘制过程
- android view的绘制过程
- Android View的绘制过程
- View的绘制过程方法
- View的绘制过程分析
- Android view的绘制过程
- android绘制view的过程
- Android View的绘制过程
- Android中View的绘制过程
- win10远程控制ubuntu16.04
- Android多渠道打包
- CSS设计美丽之绝对定位(absolute)的使用(小作品)
- org.greenrobot.eventbus.EventBusException: Subscriber class already registered to event class
- leetcode 520. Detect Capital
- View 的绘制过程
- CNN学习资料链接分享
- 05-树8 File Transfer (25分)
- zookeeper(一) 介绍,搭建,使用
- solr cache 1
- Ubuntu16.04搜狗輸入法只有懸浮窗,不能輸入中文問題
- shared_ptr之定制删除器
- POJ1692 Crossed Matchings DP
- Huffman 编解码算法实现与压缩效率分析





