jdk源码解析--集合类
来源:互联网 发布:战舰建模软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/01 09:26
最近在整理JAVA 基础知识,从jdk源码入手,今天就jdk中 java.util包下集合类进行理解
先看图
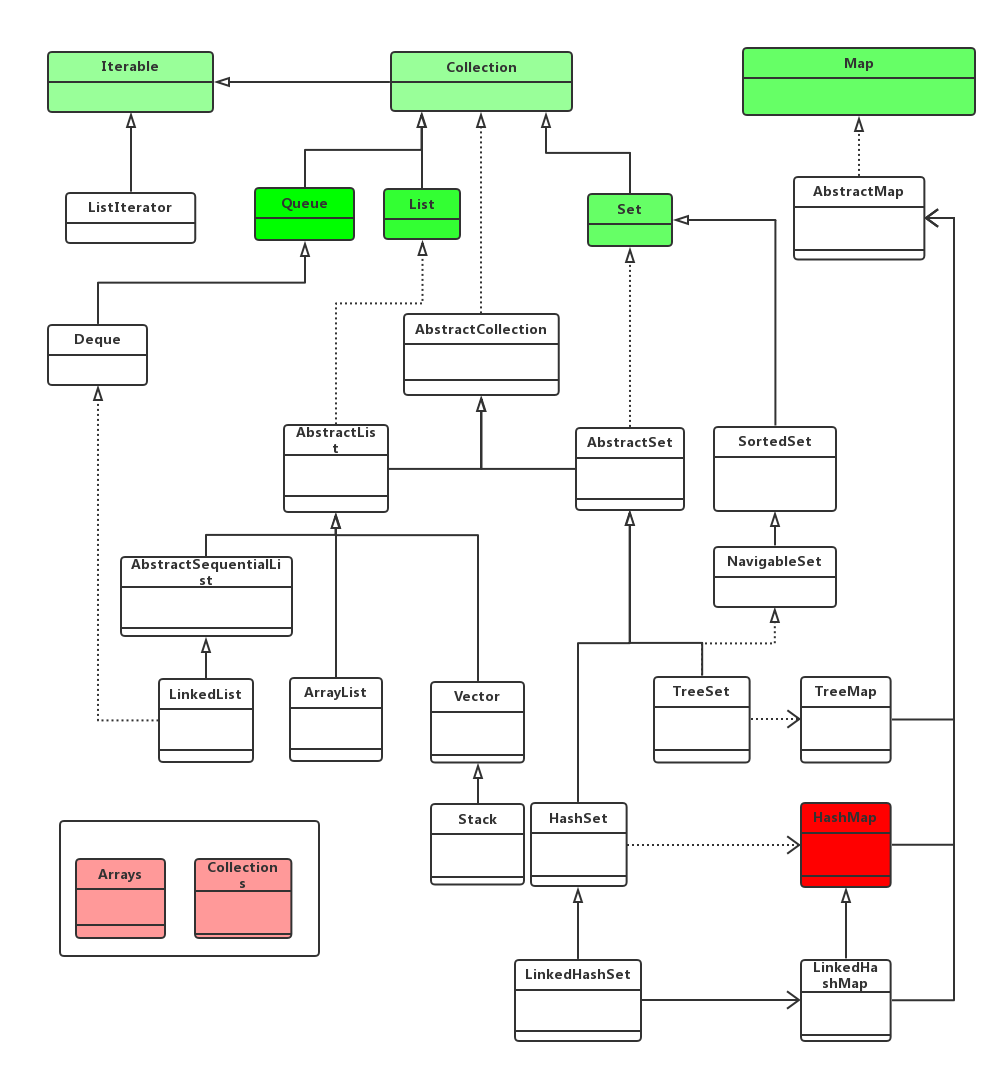
从类图结构可以了解 java.util包下的2个大类:
1、Collecton:可以理解为主要存放的是单个对象
2、Map:可以理解为主要存储key-value类型的对象
一、Collection
Collection继承了Iterate接口,Iterate用于集合内迭代器抽象接口,其子类均实现接口中方法,看下ArrayList下实现:
1 /** 2 * Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence. 3 * 4 * <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>. 5 * 6 * @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence 7 */ 8 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 9 return new Itr(); // 返回内部类实例10 }11 12 /**13 * An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr14 */15 private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {16 int cursor; // index of next element to return 指向下一个位置索引id17 int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such 指向上一个位置索引id18 int expectedModCount = modCount;19 20 public boolean hasNext() {21 return cursor != size;22 }23 24 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")25 public E next() {26 checkForComodification();27 int i = cursor;28 if (i >= size)29 throw new NoSuchElementException();30 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;31 if (i >= elementData.length)32 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();33 cursor = i + 1;34 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];35 }36 37 public void remove() {38 if (lastRet < 0)39 throw new IllegalStateException();40 checkForComodification();41 42 try {43 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);44 cursor = lastRet;45 lastRet = -1;46 expectedModCount = modCount;47 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {48 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();49 }50 }51 52 @Override53 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")54 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {55 Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);56 final int size = ArrayList.this.size;57 int i = cursor;58 if (i >= size) {59 return;60 }61 final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;62 if (i >= elementData.length) {63 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();64 }65 while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {66 consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);67 }68 // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic69 cursor = i;70 lastRet = i - 1;71 checkForComodification();72 }73 74 final void checkForComodification() {75 if (modCount != expectedModCount)76 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();77 }78 }
1、List
特点:有序结果、顺序遍历、索引、允许有重复值
(1) ArrayList
以上特点实现:
transient Object[] elementData; // List内部存储对象数组结果public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true;}// 添加对象时先识别是否越界,没有越界则数组对象当前索引值的下一个添 // 添加对象时,不识别重复,所以有序允许重复值/** * Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will * be empty after this call returns. */public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0;}// 清空List时顺序遍历值置为null
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
其中 remove方法 :
public E remove(int index) { // 按索引删除对象 rangeCheck(index); // 校验输入索引id是否越界,若越界则抛出运行时异常 IndexOutOfBoundsException modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; // 定位到索引的下一位 if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); //调用native方法实现数组位置左移 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work // 末尾元素置空 return oldValue; } public boolean remove(Object o) {// 按对象删除 if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { // 识别对象相等使用equals方法,使用时注意重写equals方法 fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /* * Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not * return the value removed. */ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; // 删除元素时,modCount值变更 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }
可以看到ArrayList中对数组进行,操作时常用到System.arraycopy
java.lang.System下
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
还有在 java.util.Arrays下数组copy方法,最终也是调用System.arraycopy方法
1 public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { 2 return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); 3 } 4 5 public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { 6 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 7 T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) 8 ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] 9 : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);10 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,11 Math.min(original.length, newLength));12 return copy;13 }
示例:
 View Code
View Code
可以看到出现异常:ConcurrentModificationException,出现该异常原因是:
“快速失败”也就是fail-fast,它是Java集合的一种错误检测机制。当创建Iterator后,在Iterator使用还没有结束时,改变(删除或增添新项)集合元素就会出现上面的错误
看看ArrayList的排序方法:sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
1 public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) { 2 final int expectedModCount = modCount; 3 Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c); 4 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { 5 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 6 } 7 modCount++; 8 } 9 10 public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,11 Comparator<? super T> c) {12 if (c == null) {13 sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);14 } else {15 rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);16 if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)17 legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c);18 else19 TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c, null, 0, 0);20 }21 }
示例:
 View Code
View Code
(2)LinkedList
1 public class LinkedList<E> 2 extends AbstractSequentialList<E> 3 implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 4 // 实现了Deque接口,可以做队列使用 5 6 /** 7 * Pointer to first node. 8 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || 9 * (first.prev == null && first.item != null)10 */11 transient Node<E> first;12 13 /**14 * Pointer to last node.15 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||16 * (last.next == null && last.item != null)17 */18 transient Node<E> last;19 20 /**21 * Constructs an empty list.22 */23 public LinkedList() {24 }25 26 // 集合对象存储结构,通过当前节点的前后节点,维护顺序集合(双向链表结构)27 private static class Node<E> {28 E item;29 Node<E> next;30 Node<E> prev;31 32 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {33 this.item = element;34 this.next = next;35 this.prev = prev;36 }37 }
以上为 LinkedList的内部存储结构,以Node存储。
在看下集合元素插入、删除及获取方法实现:
1 public boolean add(E e) { 2 linkLast(e); 3 return true; 4 } 5 6 /** 7 * Links e as last element. 8 */ 9 void linkLast(E e) {10 final Node<E> l = last; // 保存最后个节点11 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);// 新增节点12 last = newNode; // 将新节点置为最后节点13 if (l == null)14 first = newNode;15 else16 l.next = newNode;17 size++;18 modCount++;19 }20 21 public E remove() {22 return removeFirst(); // 去掉首节点23 }24 25 public E removeFirst() {26 final Node<E> f = first;27 if (f == null)28 throw new NoSuchElementException();29 return unlinkFirst(f);30 }31 32 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {33 // assert f == first && f != null;34 final E element = f.item;35 final Node<E> next = f.next;36 f.item = null;37 f.next = null; // help GC38 first = next;39 if (next == null)40 last = null;41 else42 next.prev = null;43 size--;44 modCount++;45 return element;46 }47 48 // 入栈方法49 public void push(E e) {50 addFirst(e);51 }52 // 出栈方法53 public E pop() {54 return removeFirst();55 }56 57 // 入队58 public boolean offer(E e) {59 return add(e);60 }61 public boolean add(E e) {62 linkLast(e);63 return true;64 }65 // 出队66 public E poll() {67 final Node<E> f = first;68 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);69 }70 71 //随机访问集合对象72 public E get(int index) {73 checkElementIndex(index);74 return node(index).item;75 }76 77 /**78 * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.79 */80 Node<E> node(int index) {81 // assert isElementIndex(index);82 // 识别 index id离首节点近还是尾节点近,减少遍历 83 if (index < (size >> 1)) {84 Node<E> x = first;85 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) // 0(i)86 x = x.next;87 return x;88 } else {89 Node<E> x = last;90 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) // 0(i)91 x = x.prev;92 return x;93 }94 }
通过以上源码理解 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 区别类似数据结构中 数组及链表结构区别 ,新增、删除 和 随机访问存在 效率上的差别:
ArrayList是最常用的集合,其内部实现是一个数组,ArrayList的大小是可以动态扩充的。对于元素的随机访问效率高,其访问的时间复杂度为O(1),对于数据的插入与删除,从尾部操作效率高,时间复杂度和随机访问一样是O(1),若是从头部操作则效率会比较低,因为从头部插入或删除时需要移动后面所有元素,其时间复杂度为O(n-i)(n表示元素个数,i表示元素位置)
LinkList对于随机访问效率是比较低的,因为它需要从头开始索引,所以其时间复杂度为O(i)。但是对于元素的增删,LinkList效率高,因为只需要修改前后指针即可,其时间复杂度为O(1)。
(3)Vector
与ArrayList类型,内部也是使用数据来存储对象,但是线程安全的,因为实现方法重写的时候,全部加上了同步关键字:synchronized;(一般不建议使用,性能消耗)
(4)Stack
publicclass Stack<E> extends Vector<E> { /** * Creates an empty Stack. */ public Stack() { }
2、Queue
遵循FIFO(先入先出规则),内部出栈入栈方法,主要区别在于是否是阻塞入队或出队
3、Set
public class HashSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable/** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has * default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */ public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); }// Set 集合对象存储在 Map的 key中 public boolean contains(Object o) { return map.containsKey(o); }// 添加对象到Set集合中 public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; }// 删除Set集合中对象 public boolean remove(Object o) { return map.remove(o)==PRESENT; }
实际Set集合的实现依赖于Map的实现,通过Map的 key值唯一性来实现
二、Map
1、HashMap:基于Map接口实现、允许null 键值、无序、非同步
一起看下HashMap的实现
// map 内部对象链表存储结构static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; // 下一节点 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } // 重写hashCode方法 public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } // 重写 equals方法 public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) return true; } return false; } }transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 用数组保存多条链表的首节点// 获取 key所对应的存储JNode的 value值public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; }// 识别是否存在key所对应的 Node public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return getNode(hash(key), key) != null; }
// map 内部对象链表存储结构static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; // 下一节点 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } // 重写hashCode方法 public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } // 重写 equals方法 public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) return true; } return false; } }transient Node<K,V>[] table; // 用数组保存多条链表的首节点// 获取 key所对应的存储JNode的 value值public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; }// 识别是否存在key所对应的 Node public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return getNode(hash(key), key) != null; }
// 插入 对象public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }// 调用的内部方法,final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { // tab 为map内首节点集合 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; // 先识别table是否为空,为空则初始化,hashmap内存存储延迟加载在这里体现 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; // 通过hash值以长度做按位与,识别读取元素的存储在tab中的位置 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) // 若tab所在链表首节点为空,则直接构造新节点 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { // tab所在链表首节点不为空,则遍历p所在链表或红黑树,找到可以存储的位置 Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
可以看到,在HashMap中存储的结构下, Node类型的数组保存头部节点(单链表)或根节点(红黑树),先以 Node的key的hash值与数组长度做位与运算(hash碰撞),初始
时使用单链表存储新插入对象(newNode),当链表长度超过8时,会将链表结构转为红黑树结构存储(treeifyBin方法)
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { // 找到需要转换的 单链表 e,遍历单链表,转换为TreeNode,保存前后节点关系 TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); //让桶的第一个元素指向新建的红黑树头结点,以后这个桶里的元素就是红黑树而不是链表了 if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) hd.treeify(tab); } }
先将单链表转换为 treenode,在调用 treeify方法构造红黑树
2、LinkedHashMap
继承HashMap,HashMap是无序集合,而LinkedHashMap为有序集合
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
构造LinkedHashMap.EntreyNode<K,V> 继承 HashMap.Node<K,V> 实现双向链表
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { Entry<K,V> before, after; // before 保存前置节点,after保存后置节点 Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } } /** * The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list. */ transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; // 头节点 /** * The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list. */ transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; // 尾部节点// 重写HashMap的 创建新节点方法 Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e); linkNodeLast(p); // 将新节点放到尾部节点,从而保证顺序 return p; }// link at the end of list private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail; tail = p; if (last == null) head = p; else { p.before = last; last.after = p; } }
3、TreeMap
TreeMap直接使用红黑树结构存储集合元素,根据键 做排序,排序规则按内部 comparator 对象的实例对象的排序规则,若comparator为空,则按自然排序
1 public class TreeMap<K,V> 2 extends AbstractMap<K,V> 3 implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 4 { 5 /** 6 * The comparator used to maintain order in this tree map, or 7 * null if it uses the natural ordering of its keys. 8 * 9 * @serial10 */11 private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; // 对象比较接口12 13 private transient Entry<K,V> root; // 根节点
root的实现逻辑为 TreeMap.Entrey<K,V> 继承 Map.Entrey<K,V> 实现 ,与HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>实现类似
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { K key; V value; Entry<K,V> left; Entry<K,V> right; Entry<K,V> parent; boolean color = BLACK;
所以TreeMap put和get方法就是以键先进行红黑树的查找后操作
4、HashTable
HashTable和HashMap数据结构类似,主要区别为HashTable中操作集合元素对象的方法都加上了 同步关键字(synchronized), 所以说线程安全的及集合
- jdk源码解析--集合类
- JDK集合源码解析剖析
- JDK源码解析集合篇--综述
- JdK源码阅读-集合类
- 【集合源码】HashMap源码解析(基于JDK 1.8)
- JDK源码解析集合篇--ArrayList全解析
- JDK源码解析集合篇--LinkedList全解析
- JDK源码解析集合篇--HashMap无敌全解析
- JDK源码解析之ThreadLocal类
- JDK源码解析之ThreadLocal类
- JDK源码解析之HashMap类
- JDK DualPivotQuicksort 源码解析
- JDK DualPivotQuicksort 源码解析
- JDK DualPivotQuicksort 源码解析
- JDK DualPivotQuicksort 源码解析
- jdk源码解析--set
- jdk集合源码之ArrayList
- jdk集合源码之LinkedList
- gitlab 操作命令小记(待编辑)
- 链表面试题(七)---合并两个有序链表
- 如何制作自己的开源库
- I2C设备驱动(一)--工作原理
- 如何自定义控件
- jdk源码解析--集合类
- Spring事务管理
- 面向对象选项卡(回头写个简单的小案例)
- web 学习备忘录
- HTTP与HTTPS的区别
- 欢迎使用CSDN-markdown编辑器
- 第一单元练习题
- 初识Spring
- 【23种设计模式从零学4-代理模式】



