Java 通过先序中序序列生成二叉树
来源:互联网 发布:网络p2p理财哪家好 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/01 08:22
二叉树的前序以及后续序列,以空格间隔每个元素,重构二叉树,最后输出二叉树的三种遍历方式的序列以验证。
输入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
3 2 5 4 1 7 8 6 10 9
输出:
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
3,2,5,4,1,7,8,6,10,9
3,5,4,2,8,7,10,9,6,1
分析
以上述输入为例,该树的结构为:
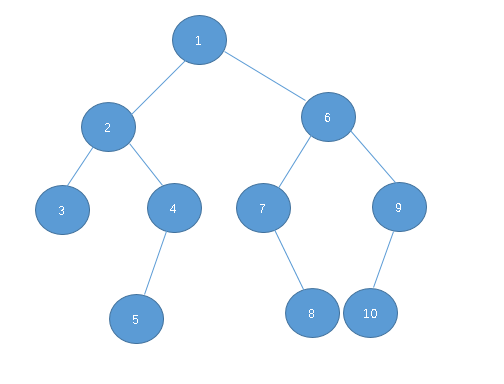
在解决这方面问题时,需要把控这几个因素:
(1)前序的第一个元素必为根节点;
(2)中序中在根节点左边的为左子树,在根节点右边的为右子树。
抓住上面两点,就可以无限递归,从而产生一个完整的二叉树。
算法演算
前序:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
中序:3 2 5 4 1 7 8 6 10 9
<默认优先处理左子树>
(1)第一次:
产生节点 1。
生成左子树
先序:2 3 4 5
中序:3 2 5 4
生成右子树
前序:6 7 8 9 10
中序:7 8 6 10 9
(2)第二次
产生节点 2(由左子树得来,故为第一次结点的左子树)。
生成左子树
前序:3
中序:3
生成右子树
先序:4 5
中序:5 4
(3)第三次
产生节点 3(同上,产生左子树)
<此处限定:当先序长度小于等于1时,直接Return>
(4)第四次(因为Return,所以处理第二次产生的右子树)
产生结点 4
生成左子树
先序:null
中序:null
生成右子树
先序:5
后续:5
<此处限定:当新生成的左(右)序列为空时,则只进行右(左)序列的处理,并将为空的节点初始化为null>
……
以此类推,即可轻松生成一棵二叉树。
实现代码
package DataStructe;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Scanner;public class TreeReBuild { /*先序(DLR)、中序(LDR)遍历对应的三个数组*/ static ArrayList<Integer> DLR=new ArrayList<Integer>(); static ArrayList<Integer> LDR=new ArrayList<Integer>(); static node root=new node(); /*二叉树的结点结构*/ static class node{ node rchild; node lchild; int data; node(int ndata) { data=ndata; rchild=null; lchild=null; } public node() { rchild=null; lchild=null; } } /*核心算法*/ static void reBuildTreeprocess(node x,ArrayList<Integer> qx,ArrayList<Integer> zx) { x.data=qx.get(0);//前序第一个元素必为根节点 if(qx.size()<=1) { return; } x.lchild=new node(); x.rchild=new node(); //两个序列的拆分索引 int rootindex = 0; int qxindex=0; /*拆分序列*/ ArrayList<Integer>newqxleft = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList<Integer>newqxright= new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList<Integer>newzxleft = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList<Integer>newzxright = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //拆分中序 for(int j=0;j<zx.size();j++) { if(zx.get(j)==x.data) { zx.remove(j); j--; rootindex=j; break; } } //生成新的中序(左) for(int j=0;j<=rootindex;j++){ newzxleft.add(zx.get(j)); } //生成新的中序(右) for(int j=rootindex+1;j<zx.size();j++) { newzxright.add(zx.get(j)); } //拆分前序,确定分离的元素索引 if(newzxright.isEmpty()) { //中序右为空,前序全为左子树 for(int i=1;i<qx.size();i++) { newqxleft.add(qx.get(i)); } x.rchild=null; reBuildTreeprocess(x.lchild, newqxleft, newzxleft); } else{ if(newzxleft.isEmpty()) { //中序左为空,前序全为右子树 for(int i=1;i<qx.size();i++) { newqxright.add(qx.get(i)); } x.lchild=null; reBuildTreeprocess(x.rchild, newqxright, newzxright); } else { //均不为空,分别生成 outer: for(int r=0;r<qx.size();r++) { for(int i=0;i<newzxright.size();i++) { if(qx.get(r)==newzxright.get(i)) { qxindex=r; break outer; } } } for(int t=1;t<qxindex;t++) { newqxleft.add(qx.get(t)); } for(int y=qxindex;y<qx.size();y++) { newqxright.add(qx.get(y)); } reBuildTreeprocess(x.lchild, newqxleft, newzxleft); reBuildTreeprocess(x.rchild, newqxright, newzxright); } } } /*先序遍历,用于测试结果*/ static void XSearch(node x) { if (x==null) { return; } System.out.print(x.data+","); if (x.lchild!=null) { XSearch(x.lchild); } if(x.rchild!=null){ XSearch(x.rchild); } } /*中续遍历,用于测试结果*/ static void ZSearch(node x) { if (x==null) { return; } if (x.lchild!=null) { ZSearch(x.lchild); } System.out.print(x.data+","); if(x.rchild!=null){ ZSearch(x.rchild); } } /*后续遍历,用于测试结果*/ static void HSearch(node x) { if (x==null) { return; } if (x.lchild!=null) { HSearch(x.lchild); } if(x.rchild!=null){ HSearch(x.rchild); } System.out.print(x.data+","); } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner getin=new Scanner(System.in); /*读入先序序列*/ String readydata=getin.nextLine(); String []DLRdata=readydata.split(" "); for(int i=0;i<DLRdata.length;i++) { int qxdata=Integer.parseInt(DLRdata[i]); DLR.add(qxdata); } /*读入中序序列*/ readydata=getin.nextLine(); String[]LDRdata=readydata.split(" "); for(int i=0;i<LDRdata.length;i++) { int zxdata=Integer.parseInt(LDRdata[i]); LDR.add(zxdata); } reBuildTreeprocess(root, DLR, LDR); XSearch(root); System.out.println(); ZSearch(root); System.out.println(); HSearch(root); System.out.println(); }}
- Java 通过先序中序序列生成二叉树
- Java先序序列构造二叉树
- 序列化二叉树(Java实现)
- 序列化二叉树java实现
- 由递增序列生成平衡的查找二叉树
- 通过有序数组生成平衡搜索二叉树
- java通过数组描述二叉树
- 通过二叉树的前序序列和后续序列构建二叉树,有问题带定位
- 由先序序列和中序序列生成一棵二叉树
- JAVA生成消息序列
- 二叉树问题---通过有序数组生成平衡搜索二叉树
- 二叉树序列化
- 二叉树序列化
- 序列化二叉树
- 序列化二叉树
- 序列化二叉树
- 序列化二叉树
- 序列化二叉树
- 通过BitSet完成对单词使用字母的统计
- 通过回车键来结束一段不定长度的数组的输入。
- 栈的Java简单实现
- Java 实现二叉树的构建以及3种遍历方法
- 每天进步一点点——五分钟理解一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)
- Java 通过先序中序序列生成二叉树
- Java 循环队列的实现
- Java 冒泡排序与快速排序的实现
- Java 线程池的实现
- 网络通信中基于套接字输入流和输出流的创建
- Java TCP通信概念及实例
- JSP/Servlet Web 学习笔记 DayOne
- JSP/Servlet Web 学习笔记 DayTwo
- Java UDP的简单实例以及知识点简述


