Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Tree —— 缩点 + 树上最长路
来源:互联网 发布:长者风靡网络的原因 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 09:32
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/E
Anton is growing a tree in his garden. In case you forgot, the tree is a connected acyclic undirected graph.
There are n vertices in the tree, each of them is painted black or white. Anton doesn't like multicolored trees, so he wants to change the tree such that all vertices have the same color (black or white).
To change the colors Anton can use only operations of one type. We denote it as paint(v), where v is some vertex of the tree. This operation changes the color of all vertices u such that all vertices on the shortest path from v to u have the same color (including v and u). For example, consider the tree
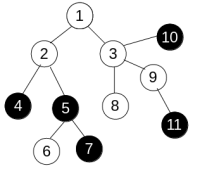
and apply operation paint(3) to get the following:
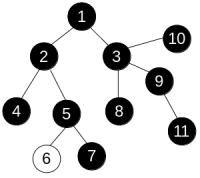
Anton is interested in the minimum number of operation he needs to perform in order to make the colors of all vertices equal.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n integers colori (0 ≤ colori ≤ 1) — colors of the vertices. colori = 0 means that the i-th vertex is initially painted white, while colori = 1 means it's initially painted black.
Then follow n - 1 line, each of them contains a pair of integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi) — indices of vertices connected by the corresponding edge. It's guaranteed that all pairs (ui, vi) are distinct, i.e. there are no multiple edges.
Print one integer — the minimum number of operations Anton has to apply in order to make all vertices of the tree black or all vertices of the tree white.
110 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 11 21 32 42 55 65 73 83 93 109 11
2
40 0 0 01 22 33 4
0
In the first sample, the tree is the same as on the picture. If we first apply operation paint(3) and then apply paint(6), the tree will become completely black, so the answer is 2.
In the second sample, the tree is already white, so there is no need to apply any operations and the answer is 0.
题解:
1.缩点:将颜色相同的连通块缩成一个点。当然并不是实际将其缩成一点,而是当前点与上一个点的颜色相同,则“不作为”, 即无视这个点。经过缩点之后,这棵树的结点颜色为黑白交替,如下图。
2.无环无向图的最长路:首先取随便一个点作为起点,然后dfs跑一遍。取得路径最长的那条路的终点,并以此作为起点,再跑一遍dfs,取最长的路径len,最终答案即为len/2,向下取整。
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const double eps = 1e-6;const int INF = 2e9;const LL LNF = 9e18;const int mod = 1e9+7;const int maxn = 2e5+10;int n, c[maxn];vector<int>son[maxn];pair<int,int> dfs(int u, int fa, int cnt){ pair<int,int> tmp = make_pair(cnt, u); for(int i = 0; i<son[u].size(); i++) { int v = son[u][i]; if(v==fa) continue; //由于无环,所以只要避免其走“回头路”即可,无需vis数组 tmp = max( tmp, dfs(v,u,cnt+(c[u]!=c[v])) ); //如果颜色相同,则cnt+0,就跳过了当前点 } return tmp;}int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++) scanf("%d",&c[i]); for(int i = 1; i<n; i++) { int u, v; scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); son[u].push_back(v); son[v].push_back(u); } pair<int,int> tmp; tmp = dfs(1,-1,1); tmp = dfs(tmp.second, -1, 1); cout<< tmp.first/2 <<endl;}- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Tree —— 缩点 + 树上最长路
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2)E. Anton and Tree(dfs缩点,想法题)
- [排列组合]Codeforces Round #324 (Div. 2)E - Anton and Ira
- 【codeforces 734E】Anton and Tree【缩点+DP】
- Codeforces Round #264 (Div. 2) E. Caisa and Tree 树上操作暴力
- Codeforces Round #417 (Div. 2) E. Sagheer and Apple Tree (树上尼姆博弈)
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Making Potions —— 二分
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) D. Anton and Chess —— 基础题
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Making Potions
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) Anton and Chess
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) D. Anton and Chess
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) F. Anton and School
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Making Potions
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2)-D. Anton and Chess
- Codeforces Round #324 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Ira(贪心)
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) -- E. Anton and Permutation(分块xjb 搞)
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Permutation(分块+二分)
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2)E. Anton and Permutation(分块)
- STL-顺序容器-向量vector
- 禁用firfox的表单自动填充
- React继ES6后更新部分
- javascript学习笔记(二)
- 第四届“图灵杯”NEUQ-ACM程序设计竞赛(团队赛)-网络同步赛A(组合数学)
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Tree —— 缩点 + 树上最长路
- HTML标签
- MongoDB复制集入门
- Elastic Search初识之吐槽
- mysqldump 参数介绍
- MOOC清华《程序设计基础》第1章第2题:求周长
- Android中TimePickerDialog的使用
- ionic中的在线视频播放功能
- hdu 2093



