CF #420 B. Okabe and Banana Trees
来源:互联网 发布:mac os破解版 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/29 19:28
Okabe needs bananas for one of his experiments for some strange reason. So he decides to go to the forest and cut banana trees.
Consider the point (x, y) in the 2D plane such that x and y are integers and 0 ≤ x, y. There is a tree in such a point, and it has x + y bananas. There are no trees nor bananas in other points. Now, Okabe draws a line with equation 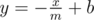 . Okabe can select a single rectangle with axis aligned sides with all points on or under the line and cut all the trees in all points that are inside or on the border of this rectangle and take their bananas. Okabe's rectangle can be degenerate; that is, it can be a line segment or even a point.
. Okabe can select a single rectangle with axis aligned sides with all points on or under the line and cut all the trees in all points that are inside or on the border of this rectangle and take their bananas. Okabe's rectangle can be degenerate; that is, it can be a line segment or even a point.
Help Okabe and find the maximum number of bananas he can get if he chooses the rectangle wisely.
Okabe is sure that the answer does not exceed 1018. You can trust him.
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers m and b (1 ≤ m ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ b ≤ 10000).
Print the maximum number of bananas Okabe can get from the trees he cuts.
1 5
30
2 3
25
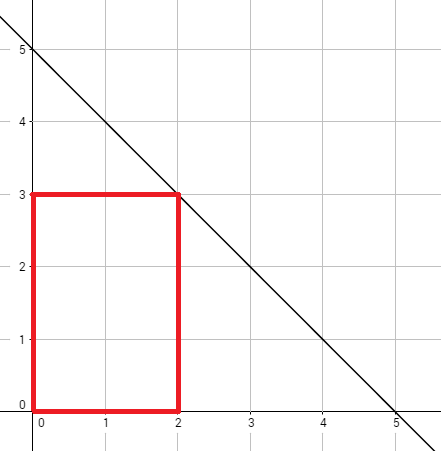
The graph above corresponds to sample test 1. The optimal rectangle is shown in red and has 30 bananas.
题意:画一条直线,取最大矩形,使得矩形的做表加和最大。
思路:暴力取线上每个点,求和。
过程:题目中给的数据范围太大,不能用循环,用算法直接算出结果。
1+2+3+~~n = n * (n+1)/2;
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int m, b;long long f(long long y){ long long sum = 0; if(!(y%2)) sum = (y+1) * (y/2); else sum = ((y+1) * (y/2) )+ (y/2) + 1; return sum;}// y = -x/m + bint main(){ while(cin >> m >> b){ long long maxx = 0; for(long long x = 0; x <= m*b; x ++){ long long y = -(x / m) + b; if(!(x%m)){ long long yy = f(y); long long sum = yy * (x+1) + f(x)*(y+1); if(sum > maxx) { maxx = sum;// cout << "**" << f(x) << " " << f(y) << endl; } } } cout << maxx << endl; }}注:可以将公式合起来,减少代码量。
- CF #420 B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- CF#420 B. Okabe and Banana Trees 思维|暴力|几何
- codeforces -420-B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- CF#420 Div.2 B. Okabe and Banana Trees(数学)
- #420 B. Okabe and Banana Trees(Div.2)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces Round #420 B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces 821 B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- codeforces 821 B Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces 821B-Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces#420 Okabe and Banana Trees
- CF821B-Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces821B Okabe and Banana Trees
- Okabe and Banana Trees CodeForces
- Codeforces 821B Okabe and Banana Trees 题解
- Codefroces 821B Okabe and Banana Trees(暴力)
- #420 Div.2 B. Okabe and Banana Trees——数学&暴力
- Okabe and Banana Trees 思路题
- Java结构语句和方法函数
- SVN 安装教程总结
- (一)栈与队列
- redis 配置文件注释
- SVN的安装以及错误应对
- CF #420 B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- 关于精度处理(浮点误差)的总结
- 李嘉诚汕头大学2017毕业演讲
- 2009国家公务员面试过关点点通
- CSS3学习
- Java虚拟机
- 使用Authenticator和send静态方法发送邮件
- PYTHON爬虫学习——urllib库之Debuglog与URLError实战练习
- springmvc拦截器


