Spark 之 RDD
来源:互联网 发布:国产电视推荐 知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/09 14:52
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sysmedia/article/details/70052486
Spark RDD/Core 编程 API入门系列 之rdd案例(map、filter、flatMap、groupByKey、reduceByKey、join、cogroupy等)(四)
摘要:
RDD:弹性分布式数据集,是一种特殊集合 ‚ 支持多种来源 ‚ 有容错机制 ‚ 可以被缓存 ‚ 支持并行操作,一个RDD代表一个分区里的数据集
RDD有两种操作算子:
Transformation(转换):Transformation属于延迟计算,当一个RDD转换成另一个RDD时并没有立即进行转换,仅仅是记住 了数据集的逻辑操作
Ation(执行):触发Spark作业的运行,真正触发转换算子的计算
本系列主要讲解Spark中常用的函数操作:
1.RDD基本转换
2.键-值RDD转换
3.Action操作篇
Ation(执行):触发Spark作业的运行,真正触发转换算子的计算
本系列主要讲解Spark中常用的函数操作:
1.RDD基本转换
2.键-值RDD转换
3.Action操作篇
本节所讲函数
1.mapValus
2.flatMapValues
3.comineByKey
4.foldByKey
5.reduceByKey
6.groupByKey
7.sortByKey
8.cogroup
9.join
10.LeftOutJoin
11.RightOutJoin
1.mapValus(fun):对[K,V]型数据中的V值map操作
(例1):对每个的的年龄加2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
object MapValues { def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("map") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val list = List(("mobin",22),("kpop",20),("lufei",23)) val rdd = sc.parallelize(list) val mapValuesRDD = rdd.mapValues(_+2) mapValuesRDD.foreach(println) }}输出:
(mobin,24)(kpop,22)(lufei,25)
(RDD依赖图:红色块表示一个RDD区,黑色块表示该分区集合,下同)


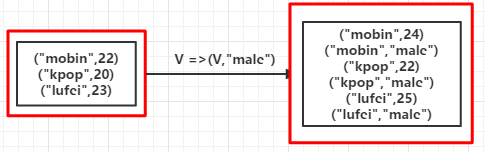
2.flatMapValues(fun):对[K,V]型数据中的V值flatmap操作
(例2):
1
2
3
4
//省略<br>val list = List(("mobin",22),("kpop",20),("lufei",23))val rdd = sc.parallelize(list)val mapValuesRDD = rdd.flatMapValues(x => Seq(x,"male"))mapValuesRDD.foreach(println)输出:
(mobin,22)(mobin,male)(kpop,20)(kpop,male)(lufei,23)(lufei,male)
如果是mapValues会输出:
(mobin,List(22, male))(kpop,List(20, male))(lufei,List(23, male))
(RDD依赖图)

3.comineByKey(createCombiner,mergeValue,mergeCombiners,partitioner,mapSideCombine)
comineByKey(createCombiner,mergeValue,mergeCombiners,numPartitions)
comineByKey(createCombiner,mergeValue,mergeCombiners)
createCombiner:在第一次遇到Key时创建组合器函数,将RDD数据集中的V类型值转换C类型值(V => C),
如例3:
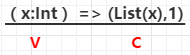

mergeValue:合并值函数,再次遇到相同的Key时,将createCombiner道理的C类型值与这次传入的V类型值合并成一个C类型值(C,V)=>C,
如例3:


mergeCombiners:合并组合器函数,将C类型值两两合并成一个C类型值
如例3:


partitioner:使用已有的或自定义的分区函数,默认是HashPartitioner
mapSideCombine:是否在map端进行Combine操作,默认为true
注意前三个函数的参数类型要对应;第一次遇到Key时调用createCombiner,再次遇到相同的Key时调用mergeValue合并值
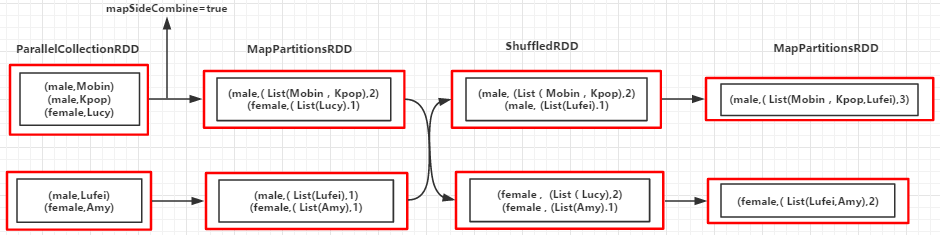
(例3):统计男性和女生的个数,并以(性别,(名字,名字....),个数)的形式输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
object CombineByKey { def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("combinByKey") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val people = List(("male", "Mobin"), ("male", "Kpop"), ("female", "Lucy"), ("male", "Lufei"), ("female", "Amy")) val rdd = sc.parallelize(people) val combinByKeyRDD = rdd.combineByKey( (x: String) => (List(x), 1), (peo: (List[String], Int), x : String) => (x :: peo._1, peo._2 + 1), (sex1: (List[String], Int), sex2: (List[String], Int)) => (sex1._1 ::: sex2._1, sex1._2 + sex2._2)) combinByKeyRDD.foreach(println) sc.stop() }}输出:
(male,(List(Lufei, Kpop, Mobin),3))(female,(List(Amy, Lucy),2))
过程分解:
Partition1:K="male" --> ("male","Mobin") --> createCombiner("Mobin") => peo1 = ( List("Mobin") , 1 )K="male" --> ("male","Kpop") --> mergeValue(peo1,"Kpop") => peo2 = ( "Kpop" :: peo1_1 , 1 + 1 ) //Key相同调用mergeValue函数对值进行合并K="female" --> ("female","Lucy") --> createCombiner("Lucy") => peo3 = ( List("Lucy") , 1 ) Partition2:K="male" --> ("male","Lufei") --> createCombiner("Lufei") => peo4 = ( List("Lufei") , 1 )K="female" --> ("female","Amy") --> createCombiner("Amy") => peo5 = ( List("Amy") , 1 ) Merger Partition:K="male" --> mergeCombiners(peo2,peo4) => (List(Lufei,Kpop,Mobin))K="female" --> mergeCombiners(peo3,peo5) => (List(Amy,Lucy))
(RDD依赖图)

4.foldByKey(zeroValue)(func)
foldByKey(zeroValue,partitioner)(func)
foldByKey(zeroValue,numPartitiones)(func)
foldByKey函数是通过调用CombineByKey函数实现的
zeroVale:对V进行初始化,实际上是通过CombineByKey的createCombiner实现的 V => (zeroValue,V),再通过func函数映射成新的值,即func(zeroValue,V),如例4可看作对每个V先进行 V=> 2 + V
func: Value将通过func函数按Key值进行合并(实际上是通过CombineByKey的mergeValue,mergeCombiners函数实现的,只不过在这里,这两个函数是相同的)
例4:
1
2
3
4
5
//省略 val people = List(("Mobin", 2), ("Mobin", 1), ("Lucy", 2), ("Amy", 1), ("Lucy", 3)) val rdd = sc.parallelize(people) val foldByKeyRDD = rdd.foldByKey(2)(_+_) foldByKeyRDD.foreach(println)输出:
(Amy,2)(Mobin,4)(Lucy,6)
先对每个V都加2,再对相同Key的value值相加。
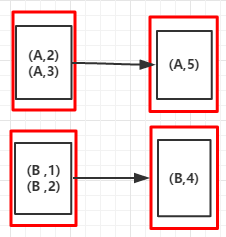
5.reduceByKey(func,numPartitions):按Key进行分组,使用给定的func函数聚合value值, numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例5
1
2
3
4
5
6
//省略val arr = List(("A",3),("A",2),("B",1),("B",3))val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr)val reduceByKeyRDD = rdd.reduceByKey(_ +_)reduceByKeyRDD.foreach(println)sc.stop输出:
(A,5)(A,4)
(RDD依赖图)

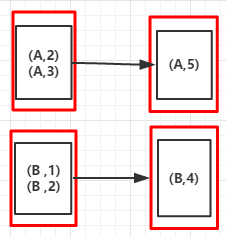
6.groupByKey(numPartitions):按Key进行分组,返回[K,Iterable[V]],numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例6:
1
2
3
4
5
6
//省略val arr = List(("A",1),("B",2),("A",2),("B",3))val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr)val groupByKeyRDD = rdd.groupByKey()groupByKeyRDD.foreach(println)sc.stop输出:
(B,CompactBuffer(2, 3))(A,CompactBuffer(1, 2))
以上foldByKey,reduceByKey,groupByKey函数最终都是通过调用combineByKey函数实现的
7.sortByKey(accending,numPartitions):返回以Key排序的(K,V)键值对组成的RDD,accending为true时表示升序,为false时表示降序,numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例7:
1
2
3
4
5
6
//省略scval arr = List(("A",1),("B",2),("A",2),("B",3))val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr)val sortByKeyRDD = rdd.sortByKey()sortByKeyRDD.foreach(println)sc.stop输出:
(A,1)(A,2)(B,2)(B,3)
8.cogroup(otherDataSet,numPartitions):对两个RDD(如:(K,V)和(K,W))相同Key的元素先分别做聚合,最后返回(K,Iterator<V>,Iterator<W>)形式的RDD,numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例8:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//省略val arr = List(("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("A", 2), ("B", 3))val arr1 = List(("A", "A1"), ("B", "B1"), ("A", "A2"), ("B", "B2"))val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(arr, 3)val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(arr1, 3)val groupByKeyRDD = rdd1.cogroup(rdd2)groupByKeyRDD.foreach(println)sc.stop输出:
(B,(CompactBuffer(2, 3),CompactBuffer(B1, B2)))(A,(CompactBuffer(1, 2),CompactBuffer(A1, A2)))
(RDD依赖图)

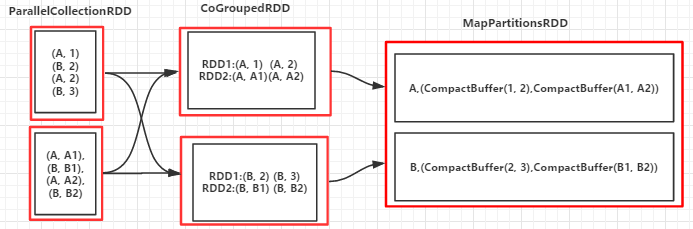
9.join(otherDataSet,numPartitions):对两个RDD先进行cogroup操作形成新的RDD,再对每个Key下的元素进行笛卡尔积,numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//省略val arr = List(("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("A", 2), ("B", 3))val arr1 = List(("A", "A1"), ("B", "B1"), ("A", "A2"), ("B", "B2"))val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr, 3)val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(arr1, 3)val groupByKeyRDD = rdd.join(rdd1)groupByKeyRDD.foreach(println)输出:
(B,(2,B1))(B,(2,B2))(B,(3,B1))(B,(3,B2)) (A,(1,A1))(A,(1,A2))(A,(2,A1))(A,(2,A2)
(RDD依赖图)

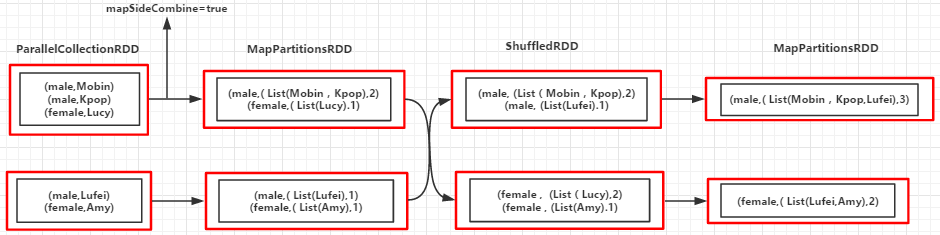
10.LeftOutJoin(otherDataSet,numPartitions):左外连接,包含左RDD的所有数据,如果右边没有与之匹配的用None表示,numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例10:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//省略val arr = List(("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("A", 2), ("B", 3),("C",1))val arr1 = List(("A", "A1"), ("B", "B1"), ("A", "A2"), ("B", "B2"))val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr, 3)val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(arr1, 3)val leftOutJoinRDD = rdd.leftOuterJoin(rdd1)leftOutJoinRDD .foreach(println)sc.stop输出:
(B,(2,Some(B1)))(B,(2,Some(B2)))(B,(3,Some(B1)))(B,(3,Some(B2))) (C,(1,None)) (A,(1,Some(A1)))(A,(1,Some(A2)))(A,(2,Some(A1)))(A,(2,Some(A2)))
11.RightOutJoin(otherDataSet, numPartitions):右外连接,包含右RDD的所有数据,如果左边没有与之匹配的用None表示,numPartitions设置分区数,提高作业并行度
例11:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//省略val arr = List(("A", 1), ("B", 2), ("A", 2), ("B", 3))val arr1 = List(("A", "A1"), ("B", "B1"), ("A", "A2"), ("B", "B2"),("C","C1"))val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr, 3)val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(arr1, 3)val rightOutJoinRDD = rdd.rightOuterJoin(rdd1)rightOutJoinRDD.foreach(println)sc.stop输出:
(B,(Some(2),B1))(B,(Some(2),B2))(B,(Some(3),B1))(B,(Some(3),B2)) (C,(None,C1)) (A,(Some(1),A1))(A,(Some(1),A2))(A,(Some(2),A1))(A,(Some(2),A2))
以上例子源码地址:https://github.com/Mobin-F/SparkExample/tree/master/src/main/scala/com/mobin/SparkRDDFun/TransFormation/RDDBase
声明:
大数据中,最重要的算子操作是:join !!!
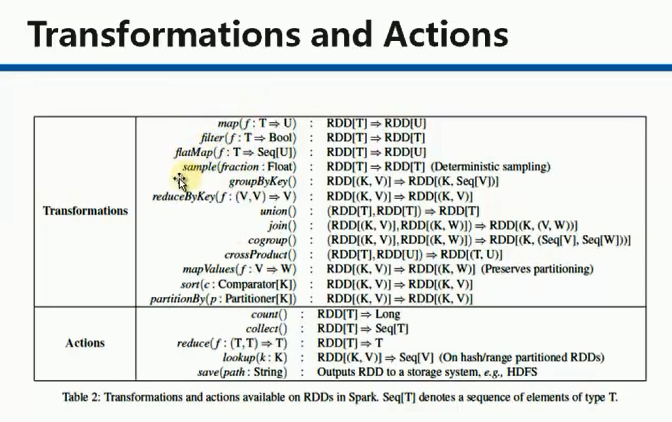
典型的transformation和action

val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD
map适用于 
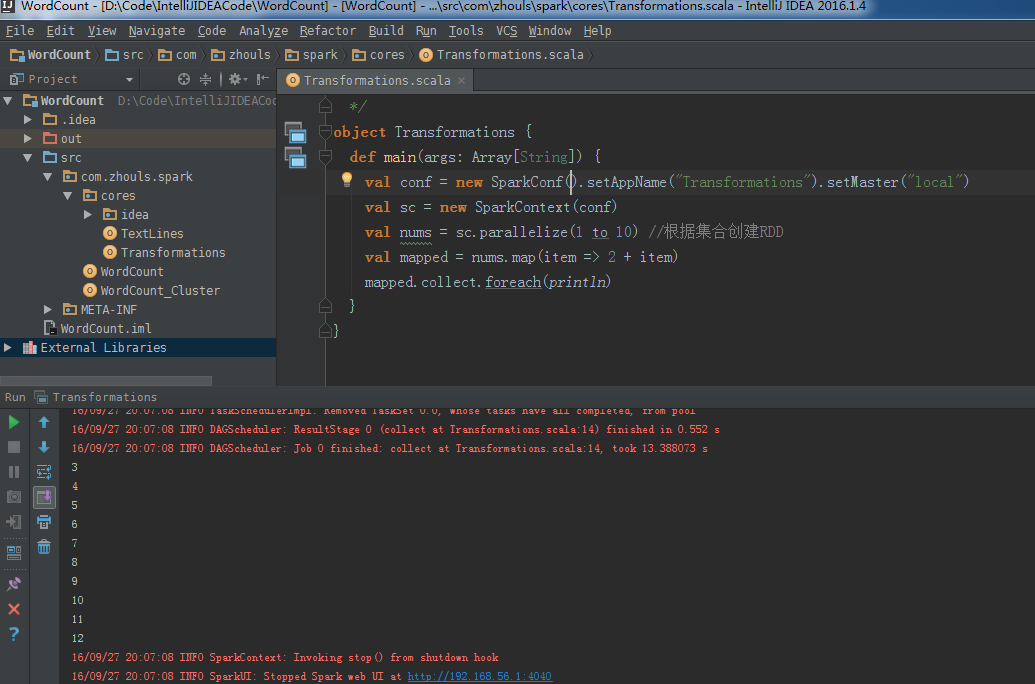
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 + item) mapped.collect.foreach(println) }}map源码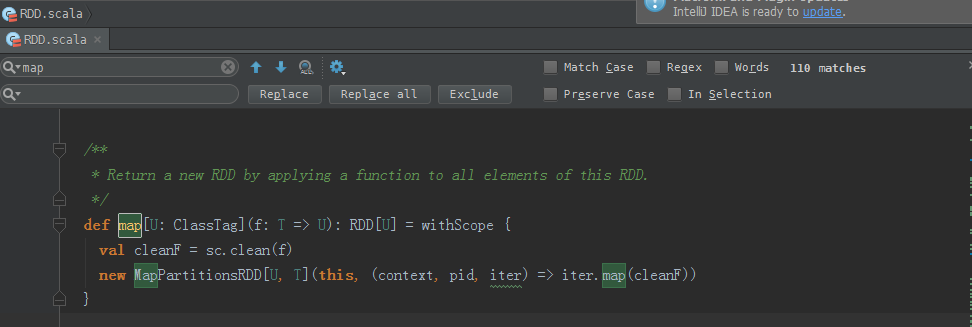
/** * Return a new RDD by applying a function to all elements of this RDD. */def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U] = withScope { val cleanF = sc.clean(f) new MapPartitionsRDD[U, T](this, (context, pid, iter) => iter.map(cleanF))}
filter适用于 
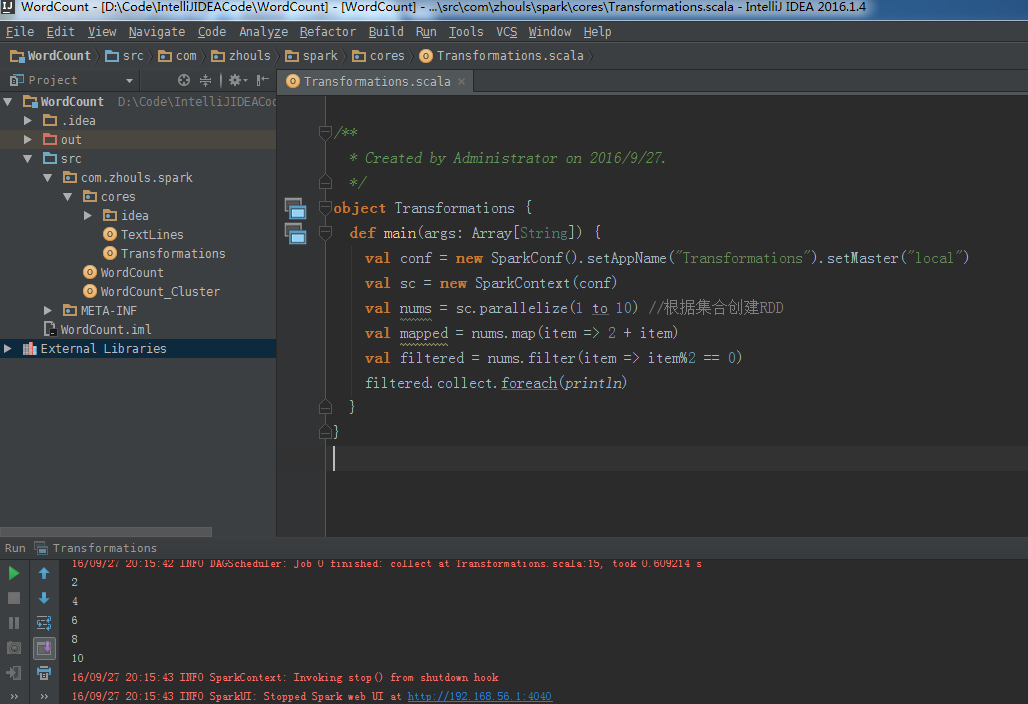
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 + item) val filtered = nums.filter(item => item%2 == 0) filtered.collect.foreach(println) }}filter源码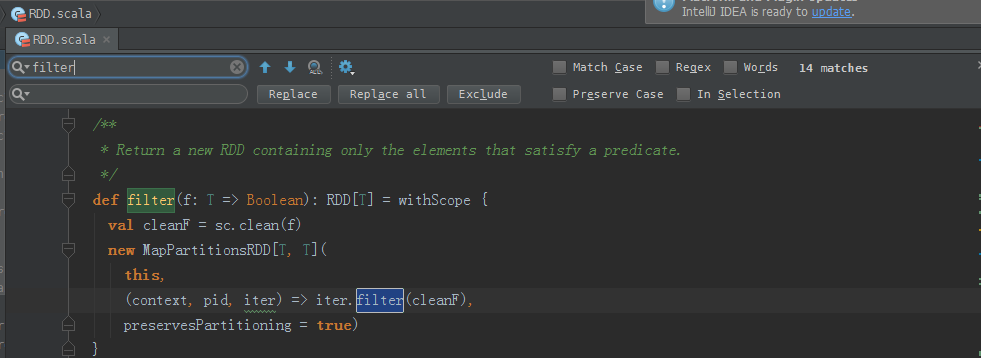
/** * Return a new RDD containing only the elements that satisfy a predicate. */def filter(f: T => Boolean): RDD[T] = withScope { val cleanF = sc.clean(f) new MapPartitionsRDD[T, T]( this, (context, pid, iter) => iter.filter(cleanF), preservesPartitioning = true)}flatMap适用于 
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 + item)// mapped.collect.foreach(println) val filtered = nums.filter(item => item%2 == 0)// filtered.collect.foreach(println) val bigData = Array("Scala Spark","Java Hadoop","Java Tachyon") val bigDataString = sc.parallelize(bigData) val words = bigDataString.flatMap(line => line.split(" ")) words.collect.foreach(println) sc.stop() }}
flatMap源码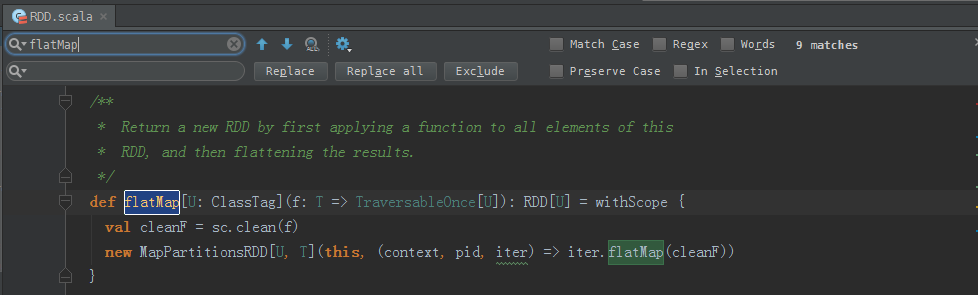
/** * Return a new RDD by first applying a function to all elements of this * RDD, and then flattening the results. */def flatMap[U: ClassTag](f: T => TraversableOnce[U]): RDD[U] = withScope { val cleanF = sc.clean(f) new MapPartitionsRDD[U, T](this, (context, pid, iter) => iter.flatMap(cleanF))}
成为大牛,必写的写法 ->
groupByKey适用于
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val sc = sparkContext("Transformations Operations") //创建SparkContext// mapTransformation(sc)//map案例// filterTransformation(sc)//filter案例// flatMapTransformation(sc)//flatMap案例 groupByKeyTransformation(sc) sc.stop() //停止sparkContext,释放相关的Driver对象,释放资源 } def sparkContext(name:String)={ val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc } def mapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 * item) //map适用于任何类型的元素且对其作用的集合中的每一个元素循环遍历并调用其作为参数的函数对每一个遍历的元素进行具体化处理 mapped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def filterTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 20) //根据集合创建RDD val filtered = nums.filter(item => item%2 == 0)//根据filter中作为参数的函数Boolean来判断符合条件的元素,并基于这些元素构成新的MapPartitionsRDD。 filtered.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def flatMapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val bigData = Array("Scala Spark","Java Hadoop","Java Tachyon")//实例化字符串类型的Array val bigDataString = sc.parallelize(bigData)//创建以字符串为元素类型的MapPartitionsRDD val words = bigDataString.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))//首先是通过传入的作为参数的函数来作用于RDD的每个字符串进行单词切分(是以集合的方式存在的),然后把切分后的结果合并成一个大的集合,是{Scala Spark Java Hadoop Java Tachyon} words.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def groupByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val data = Array(Tuple2(100,"Spark"),Tuple2(100,"Tachyon"),Tuple2(70,"Hadoop"),Tuple2(80,"Kafka"),Tuple2(80,"HBase")) val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(data) val grouped = dataRDD.groupByKey() grouped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } }groupByKey源码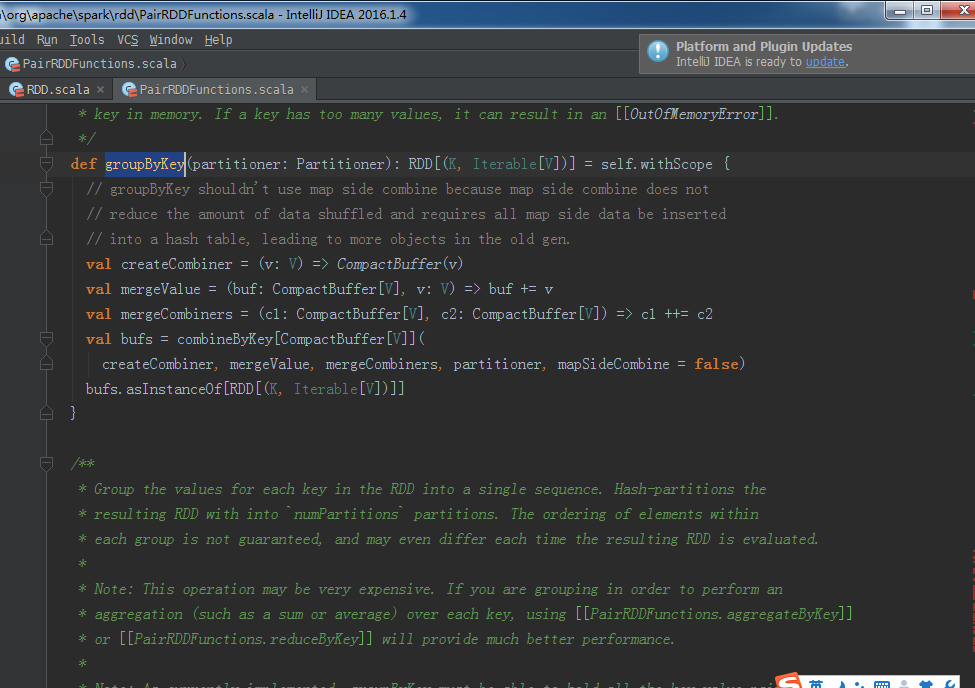
** * Group the values for each key in the RDD into a single sequence. Allows controlling the * partitioning of the resulting key-value pair RDD by passing a Partitioner. * The ordering of elements within each group is not guaranteed, and may even differ * each time the resulting RDD is evaluated. * * Note: This operation may be very expensive. If you are grouping in order to perform an * aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using [[PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey]] * or [[PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey]] will provide much better performance. * * Note: As currently implemented, groupByKey must be able to hold all the key-value pairs for any * key in memory. If a key has too many values, it can result in an [[OutOfMemoryError]]. */def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope { // groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not // reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted // into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen. val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v) val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2 val bufs = combineByKey[CompactBuffer[V]]( createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false) bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]}/** * Group the values for each key in the RDD into a single sequence. Hash-partitions the * resulting RDD with into `numPartitions` partitions. The ordering of elements within * each group is not guaranteed, and may even differ each time the resulting RDD is evaluated. * * Note: This operation may be very expensive. If you are grouping in order to perform an * aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using [[PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey]] * or [[PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey]] will provide much better performance. * * Note: As currently implemented, groupByKey must be able to hold all the key-value pairs for any * key in memory. If a key has too many values, it can result in an [[OutOfMemoryError]]. */def groupByKey(numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope { groupByKey(new HashPartitioner(numPartitions))}
reduceByKey适用于
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val sc = sparkContext("Transformations Operations") //创建SparkContext// mapTransformation(sc)//map案例// filterTransformation(sc)//filter案例// flatMapTransformation(sc)//flatMap案例// groupByKeyTransformation(sc)//groupByKey案例 reduceByKeyTransformation(sc)//reduceByKey案例 sc.stop() //停止sparkContext,释放相关的Driver对象,释放资源 } def sparkContext(name:String)={ val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc } def mapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 * item) //map适用于任何类型的元素且对其作用的集合中的每一个元素循环遍历并调用其作为参数的函数对每一个遍历的元素进行具体化处理 mapped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def filterTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 20) //根据集合创建RDD val filtered = nums.filter(item => item%2 == 0)//根据filter中作为参数的函数Boolean来判断符合条件的元素,并基于这些元素构成新的MapPartitionsRDD。 filtered.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def flatMapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val bigData = Array("Scala Spark","Java Hadoop","Java Tachyon")//实例化字符串类型的Array val bigDataString = sc.parallelize(bigData)//创建以字符串为元素类型的MapPartitionsRDD val words = bigDataString.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))//首先是通过传入的作为参数的函数来作用于RDD的每个字符串进行单词切分(是以集合的方式存在的),然后把切分后的结果合并成一个大的集合,是{Scala Spark Java Hadoop Java Tachyon} words.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def groupByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val data = Array(Tuple2(100,"Spark"),Tuple2(100,"Tachyon"),Tuple2(70,"Hadoop"),Tuple2(80,"Kafka"),Tuple2(80,"HBase"))//准备数据 val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(data)//根据集合创建RDD val grouped = dataRDD.groupByKey()//按照相同的key对value进行分组,分组后的value是一个集合 grouped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def reduceByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val lines = sc.textFile("D://SoftWare//spark-1.6.2-bin-hadoop2.6//README.md") val words = lines.flatMap{ line => line.split(" ")} val pairs = words.map { word => (word,1) } val wordCountsOdered = pairs.reduceByKey(_+_)//对相同的key,进行value的累计(包括local和reducer级别同时reduce) wordCountsOdered.collect.foreach(wordNumberPair => println(wordNumberPair._1 + ":" + wordNumberPair._2))//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } }reduceByKey源码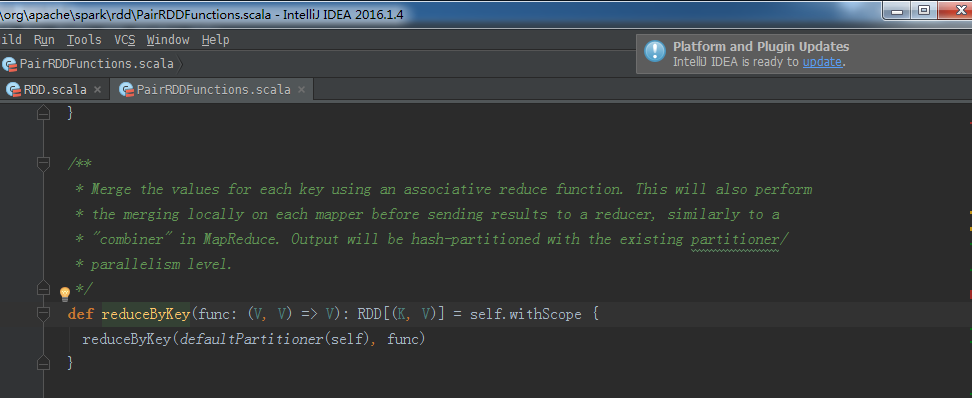
/** * Merge the values for each key using an associative reduce function. This will also perform * the merging locally on each mapper before sending results to a reducer, similarly to a * "combiner" in MapReduce. Output will be hash-partitioned with the existing partitioner/ * parallelism level. */def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope { reduceByKey(defaultPartitioner(self), func)}join适用于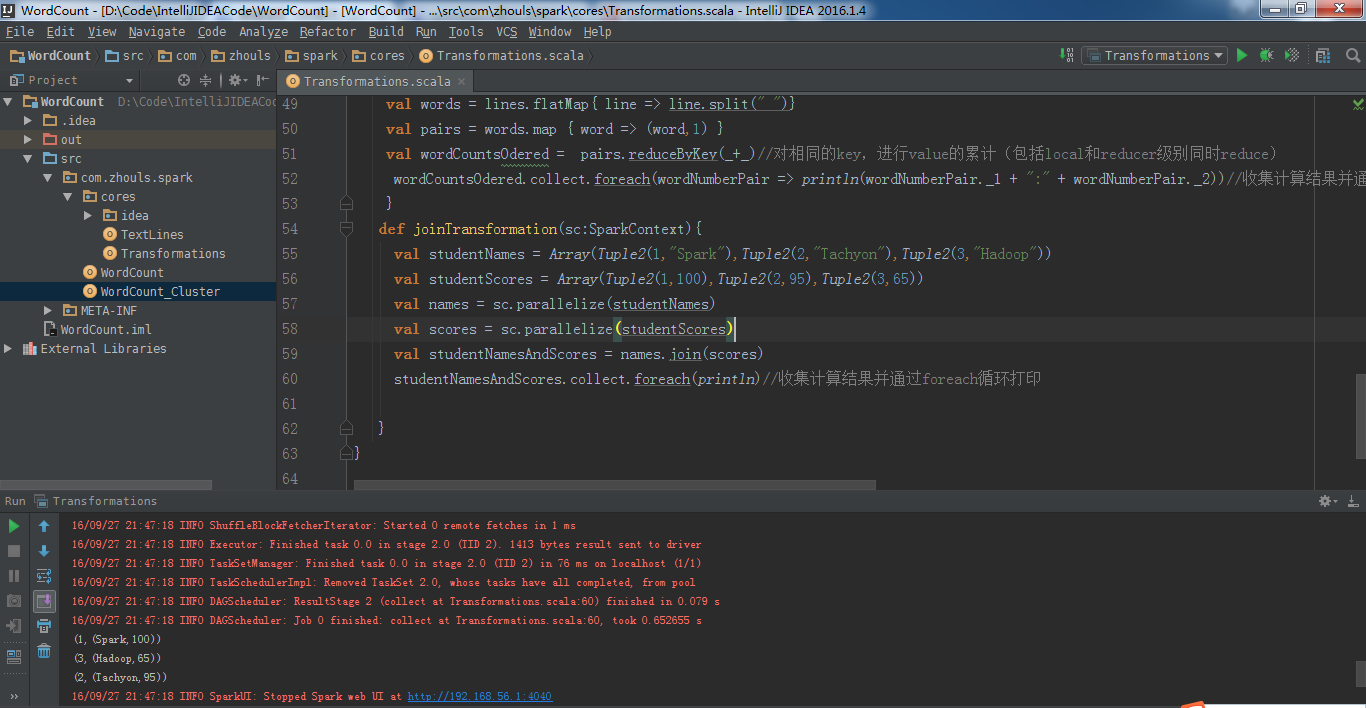
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val sc = sparkContext("Transformations Operations") //创建SparkContext// mapTransformation(sc)//map案例// filterTransformation(sc)//filter案例// flatMapTransformation(sc)//flatMap案例// groupByKeyTransformation(sc)//groupByKey案例// reduceByKeyTransformation(sc)//reduceByKey案例 joinTransformation(sc)//join案例 sc.stop() //停止sparkContext,释放相关的Driver对象,释放资源 } def sparkContext(name:String)={ val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc } def mapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 * item) //map适用于任何类型的元素且对其作用的集合中的每一个元素循环遍历并调用其作为参数的函数对每一个遍历的元素进行具体化处理 mapped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def filterTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 20) //根据集合创建RDD val filtered = nums.filter(item => item%2 == 0)//根据filter中作为参数的函数Boolean来判断符合条件的元素,并基于这些元素构成新的MapPartitionsRDD。 filtered.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def flatMapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val bigData = Array("Scala Spark","Java Hadoop","Java Tachyon")//实例化字符串类型的Array val bigDataString = sc.parallelize(bigData)//创建以字符串为元素类型的MapPartitionsRDD val words = bigDataString.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))//首先是通过传入的作为参数的函数来作用于RDD的每个字符串进行单词切分(是以集合的方式存在的),然后把切分后的结果合并成一个大的集合,是{Scala Spark Java Hadoop Java Tachyon} words.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def groupByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val data = Array(Tuple2(100,"Spark"),Tuple2(100,"Tachyon"),Tuple2(70,"Hadoop"),Tuple2(80,"Kafka"),Tuple2(80,"HBase"))//准备数据 val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(data)//根据集合创建RDD val grouped = dataRDD.groupByKey()//按照相同的key对value进行分组,分组后的value是一个集合 grouped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def reduceByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val lines = sc.textFile("D://SoftWare//spark-1.6.2-bin-hadoop2.6//README.md") val words = lines.flatMap{ line => line.split(" ")} val pairs = words.map { word => (word,1) } val wordCountsOdered = pairs.reduceByKey(_+_)//对相同的key,进行value的累计(包括local和reducer级别同时reduce) wordCountsOdered.collect.foreach(wordNumberPair => println(wordNumberPair._1 + ":" + wordNumberPair._2))//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def joinTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val studentNames = Array(Tuple2(1,"Spark"),Tuple2(2,"Tachyon"),Tuple2(3,"Hadoop")) val studentScores = Array(Tuple2(1,100),Tuple2(2,95),Tuple2(3,65)) val names = sc.parallelize(studentNames) val scores = sc.parallelize(studentScores) val studentNamesAndScores = names.join(scores) studentNamesAndScores.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 }}join源码
/** * Cartesian join with another [[DataFrame]]. * * Note that cartesian joins are very expensive without an extra filter that can be pushed down. * * @param right Right side of the join operation. * @group dfops * @since 1.3.0 */def join(right: DataFrame): DataFrame = { Join(logicalPlan, right.logicalPlan, joinType = Inner, None)}/** * Inner equi-join with another [[DataFrame]] using the given column. * * Different from other join functions, the join column will only appear once in the output, * i.e. similar to SQL's `JOIN USING` syntax. * * {{{ * // Joining df1 and df2 using the column "user_id" * df1.join(df2, "user_id") * }}} * * Note that if you perform a self-join using this function without aliasing the input * [[DataFrame]]s, you will NOT be able to reference any columns after the join, since * there is no way to disambiguate which side of the join you would like to reference. * * @param right Right side of the join operation. * @param usingColumn Name of the column to join on. This column must exist on both sides. * @group dfops * @since 1.4.0 */def join(right: DataFrame, usingColumn: String): DataFrame = { join(right, Seq(usingColumn))}/** * Inner equi-join with another [[DataFrame]] using the given columns. * * Different from other join functions, the join columns will only appear once in the output, * i.e. similar to SQL's `JOIN USING` syntax. * * {{{ * // Joining df1 and df2 using the columns "user_id" and "user_name" * df1.join(df2, Seq("user_id", "user_name")) * }}} * * Note that if you perform a self-join using this function without aliasing the input * [[DataFrame]]s, you will NOT be able to reference any columns after the join, since * there is no way to disambiguate which side of the join you would like to reference. * * @param right Right side of the join operation. * @param usingColumns Names of the columns to join on. This columns must exist on both sides. * @group dfops * @since 1.4.0 */def join(right: DataFrame, usingColumns: Seq[String]): DataFrame = { // Analyze the self join. The assumption is that the analyzer will disambiguate left vs right // by creating a new instance for one of the branch. val joined = sqlContext.executePlan( Join(logicalPlan, right.logicalPlan, joinType = Inner, None)).analyzed.asInstanceOf[Join] // Project only one of the join columns. val joinedCols = usingColumns.map(col => joined.right.resolve(col)) val condition = usingColumns.map { col => catalyst.expressions.EqualTo(joined.left.resolve(col), joined.right.resolve(col)) }.reduceLeftOption[catalyst.expressions.BinaryExpression] { (cond, eqTo) => catalyst.expressions.And(cond, eqTo) } Project( joined.output.filterNot(joinedCols.contains(_)), Join( joined.left, joined.right, joinType = Inner, condition) )}/** * Inner join with another [[DataFrame]], using the given join expression. * * {{{ * // The following two are equivalent: * df1.join(df2, $"df1Key" === $"df2Key") * df1.join(df2).where($"df1Key" === $"df2Key") * }}} * @group dfops * @since 1.3.0 */def join(right: DataFrame, joinExprs: Column): DataFrame = join(right, joinExprs, "inner")/** * Join with another [[DataFrame]], using the given join expression. The following performs * a full outer join between `df1` and `df2`. * * {{{ * // Scala: * import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._ * df1.join(df2, $"df1Key" === $"df2Key", "outer") * * // Java: * import static org.apache.spark.sql.functions.*; * df1.join(df2, col("df1Key").equalTo(col("df2Key")), "outer"); * }}} * * @param right Right side of the join. * @param joinExprs Join expression. * @param joinType One of: `inner`, `outer`, `left_outer`, `right_outer`, `leftsemi`. * @group dfops * @since 1.3.0 */def join(right: DataFrame, joinExprs: Column, joinType: String): DataFrame = { // Note that in this function, we introduce a hack in the case of self-join to automatically // resolve ambiguous join conditions into ones that might make sense [SPARK-6231]. // Consider this case: df.join(df, df("key") === df("key")) // Since df("key") === df("key") is a trivially true condition, this actually becomes a // cartesian join. However, most likely users expect to perform a self join using "key". // With that assumption, this hack turns the trivially true condition into equality on join // keys that are resolved to both sides. // Trigger analysis so in the case of self-join, the analyzer will clone the plan. // After the cloning, left and right side will have distinct expression ids. val plan = Join(logicalPlan, right.logicalPlan, JoinType(joinType), Some(joinExprs.expr)) .queryExecution.analyzed.asInstanceOf[Join] // If auto self join alias is disabled, return the plan. if (!sqlContext.conf.dataFrameSelfJoinAutoResolveAmbiguity) { return plan } // If left/right have no output set intersection, return the plan. val lanalyzed = this.logicalPlan.queryExecution.analyzed val ranalyzed = right.logicalPlan.queryExecution.analyzed if (lanalyzed.outputSet.intersect(ranalyzed.outputSet).isEmpty) { return plan } // Otherwise, find the trivially true predicates and automatically resolves them to both sides. // By the time we get here, since we have already run analysis, all attributes should've been // resolved and become AttributeReference. val cond = plan.condition.map { _.transform { case catalyst.expressions.EqualTo(a: AttributeReference, b: AttributeReference) if a.sameRef(b) => catalyst.expressions.EqualTo(plan.left.resolve(a.name), plan.right.resolve(b.name)) }} plan.copy(condition = cond)}cogroup的scala版,适用于
package com.zhouls.spark.coresimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/9/27. */object Transformations { def main(args: Array[String]) { val sc = sparkContext("Transformations Operations") //创建SparkContext// mapTransformation(sc)//map案例// filterTransformation(sc)//filter案例// flatMapTransformation(sc)//flatMap案例// groupByKeyTransformation(sc)//groupByKey案例// reduceByKeyTransformation(sc)//reduceByKey案例// joinTransformation(sc)//join案例 cogroupTransformation(sc)//cogroup案例 sc.stop() //停止sparkContext,释放相关的Driver对象,释放资源 } def sparkContext(name:String)={ val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Transformations").setMaster("local") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) sc } def mapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //根据集合创建RDD val mapped = nums.map(item => 2 * item) //map适用于任何类型的元素且对其作用的集合中的每一个元素循环遍历并调用其作为参数的函数对每一个遍历的元素进行具体化处理 mapped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def filterTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val nums = sc.parallelize(1 to 20) //根据集合创建RDD val filtered = nums.filter(item => item%2 == 0)//根据filter中作为参数的函数Boolean来判断符合条件的元素,并基于这些元素构成新的MapPartitionsRDD。 filtered.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def flatMapTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val bigData = Array("Scala Spark","Java Hadoop","Java Tachyon")//实例化字符串类型的Array val bigDataString = sc.parallelize(bigData)//创建以字符串为元素类型的MapPartitionsRDD val words = bigDataString.flatMap(line => line.split(" "))//首先是通过传入的作为参数的函数来作用于RDD的每个字符串进行单词切分(是以集合的方式存在的),然后把切分后的结果合并成一个大的集合,是{Scala Spark Java Hadoop Java Tachyon} words.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def groupByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val data = Array(Tuple2(100,"Spark"),Tuple2(100,"Tachyon"),Tuple2(70,"Hadoop"),Tuple2(80,"Kafka"),Tuple2(80,"HBase"))//准备数据 val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(data)//根据集合创建RDD val grouped = dataRDD.groupByKey()//按照相同的key对value进行分组,分组后的value是一个集合 grouped.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def reduceByKeyTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val lines = sc.textFile("D://SoftWare//spark-1.6.2-bin-hadoop2.6//README.md") val words = lines.flatMap{ line => line.split(" ")} val pairs = words.map { word => (word,1) } val wordCountsOdered = pairs.reduceByKey(_+_)//对相同的key,进行value的累计(包括local和reducer级别同时reduce) wordCountsOdered.collect.foreach(wordNumberPair => println(wordNumberPair._1 + ":" + wordNumberPair._2))//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def joinTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val studentNames = Array(Tuple2(1,"Spark"),Tuple2(2,"Tachyon"),Tuple2(3,"Hadoop")) val studentScores = Array(Tuple2(1,100),Tuple2(2,95),Tuple2(3,65)) val names = sc.parallelize(studentNames) val scores = sc.parallelize(studentScores) val studentNamesAndScores = names.join(scores) studentNamesAndScores.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 } def cogroupTransformation(sc:SparkContext){ val namesLists = Array(Tuple2(1,"xiaoming"),Tuple2(2,"xiaozhou"),Tuple2(3,"xiaoliu")) val scoresLists = Array(Tuple2(1,100),Tuple2(2,95),Tuple2(3,85),Tuple2(1,75),Tuple2(2,65),Tuple2(3,55)) val names = sc.parallelize(namesLists) val scores = sc.parallelize(scoresLists) val namesListsAndScores = names.cogroup(scores) namesListsAndScores.collect.foreach(println)//收集计算结果并通过foreach循环打印 }}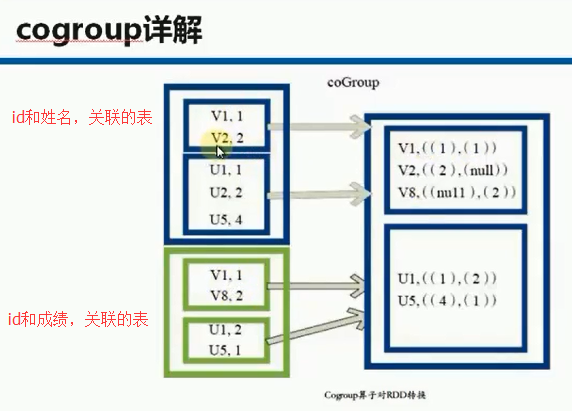
cogroup源码
/** * For each key k in `this` or `other1` or `other2` or `other3`, * return a resulting RDD that contains a tuple with the list of values * for that key in `this`, `other1`, `other2` and `other3`. */def cogroup[W1, W2, W3](other1: RDD[(K, W1)], other2: RDD[(K, W2)], other3: RDD[(K, W3)], partitioner: Partitioner) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W1], Iterable[W2], Iterable[W3]))] = self.withScope { if (partitioner.isInstanceOf[HashPartitioner] && keyClass.isArray) { throw new SparkException("Default partitioner cannot partition array keys.") } val cg = new CoGroupedRDD[K](Seq(self, other1, other2, other3), partitioner) cg.mapValues { case Array(vs, w1s, w2s, w3s) => (vs.asInstanceOf[Iterable[V]], w1s.asInstanceOf[Iterable[W1]], w2s.asInstanceOf[Iterable[W2]], w3s.asInstanceOf[Iterable[W3]]) }}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other`, return a resulting RDD that contains a tuple with the * list of values for that key in `this` as well as `other`. */def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)], partitioner: Partitioner) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))] = self.withScope { if (partitioner.isInstanceOf[HashPartitioner] && keyClass.isArray) { throw new SparkException("Default partitioner cannot partition array keys.") } val cg = new CoGroupedRDD[K](Seq(self, other), partitioner) cg.mapValues { case Array(vs, w1s) => (vs.asInstanceOf[Iterable[V]], w1s.asInstanceOf[Iterable[W]]) }}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other1` or `other2`, return a resulting RDD that contains a * tuple with the list of values for that key in `this`, `other1` and `other2`. */def cogroup[W1, W2](other1: RDD[(K, W1)], other2: RDD[(K, W2)], partitioner: Partitioner) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W1], Iterable[W2]))] = self.withScope { if (partitioner.isInstanceOf[HashPartitioner] && keyClass.isArray) { throw new SparkException("Default partitioner cannot partition array keys.") } val cg = new CoGroupedRDD[K](Seq(self, other1, other2), partitioner) cg.mapValues { case Array(vs, w1s, w2s) => (vs.asInstanceOf[Iterable[V]], w1s.asInstanceOf[Iterable[W1]], w2s.asInstanceOf[Iterable[W2]]) }}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other1` or `other2` or `other3`, * return a resulting RDD that contains a tuple with the list of values * for that key in `this`, `other1`, `other2` and `other3`. */def cogroup[W1, W2, W3](other1: RDD[(K, W1)], other2: RDD[(K, W2)], other3: RDD[(K, W3)]) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W1], Iterable[W2], Iterable[W3]))] = self.withScope { cogroup(other1, other2, other3, defaultPartitioner(self, other1, other2, other3))}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other`, return a resulting RDD that contains a tuple with the * list of values for that key in `this` as well as `other`. */def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))] = self.withScope { cogroup(other, defaultPartitioner(self, other))}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other1` or `other2`, return a resulting RDD that contains a * tuple with the list of values for that key in `this`, `other1` and `other2`. */def cogroup[W1, W2](other1: RDD[(K, W1)], other2: RDD[(K, W2)]) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W1], Iterable[W2]))] = self.withScope { cogroup(other1, other2, defaultPartitioner(self, other1, other2))}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other`, return a resulting RDD that contains a tuple with the * list of values for that key in `this` as well as `other`. */def cogroup[W]( other: RDD[(K, W)], numPartitions: Int): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))] = self.withScope { cogroup(other, new HashPartitioner(numPartitions))}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other1` or `other2`, return a resulting RDD that contains a * tuple with the list of values for that key in `this`, `other1` and `other2`. */def cogroup[W1, W2](other1: RDD[(K, W1)], other2: RDD[(K, W2)], numPartitions: Int) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W1], Iterable[W2]))] = self.withScope { cogroup(other1, other2, new HashPartitioner(numPartitions))}/** * For each key k in `this` or `other1` or `other2` or `other3`, * return a resulting RDD that contains a tuple with the list of values * for that key in `this`, `other1`, `other2` and `other3`. */def cogroup[W1, W2, W3](other1: RDD[(K, W1)], other2: RDD[(K, W2)], other3: RDD[(K, W3)], numPartitions: Int) : RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W1], Iterable[W2], Iterable[W3]))] = self.withScope { cogroup(other1, other2, other3, new HashPartitioner(numPartitions))}cogroup的java版,适用于,转自http://blog.csdn.net/kimyoungvon/article/details/51417910
另推荐一篇好的博客,https://www.iteblog.com/archives/1280
感谢!
作者:好记性不如烂笔头!
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zlslch/
阅读全文
0 0
- spark之RDD
- spark之RDD
- Spark之RDD编程
- Spark之RDD基础
- spark之RDD
- Spark RDD之Partition
- Spark RDD之Dependency
- Spark RDD之Partitioner
- Spark之RDD
- spark之RDD
- Spark 之 RDD
- Spark RDD之Partition
- Spark RDD之入门理解
- spark之RDD(四)
- spark之RDD基本转换
- Spark之键值RDD转换
- Spark源码解析之RDD
- Spark 之RDD API大全
- GPS——通过编程获取GPS经纬度信息
- 一文看懂数字货币、数字资产、虚拟货币、电子货币的区别
- what引导的宾语从句
- 机器学习笔记——正则化线性回归
- 进程池和线程池
- Spark 之 RDD
- Weird Rounding
- POJ-2236-Wireless Network [并查集]
- [LeetCode]437. Path Sum III(求二叉树中路径和等于sum的数量)
- lightoj1138Trailing Zeroes (III) 二分
- 九个步骤让你成为PHP专家
- 今年暑假不AC
- 剑指offer-扑克牌顺子
- CSS文本与字体



