非极大值抑制——基于人脸检测(框出最大概率值的人脸区域)
来源:互联网 发布:手机淘宝怎么改差评 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/07 10:25
非极大值抑制算法
1. 算法原理
非极大值抑制算法(Non-maximum suppression, NMS)的本质是搜索局部极大值,抑制非极大值元素。
2. 3邻域情况下NMS的实现
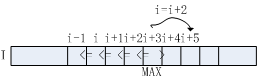
3邻域情况下的NMS即判断一维数组I[W]的元素I[i](2<=i<=W-1)是否大于其左邻元素I[i-1]和右邻元素I[i+1],算法流程如下图所示:

a. 算法流程3-5行判断当前元素是否大于其左邻与右邻元素,如符合条件,该元素即为极大值点。对于极大值点I[i],已知I[i]>I[i+1],故无需对i+1位置元素做进一步处理,直接跳至i+2位置,对应算法流程第12行。

b. 若元素I[i]不满足算法流程第3行判断条件,将其右邻I[i+1]作为极大值候选,对应算法流程第7行。采用单调递增的方式向右查找,直至找到满足I[i]>I[i+1]的元素,若i<=W-1,该点即为极大值点,对应算法流程第10-11行。
3. NMS在物体检测中的应用
物体检测中应用NMS算法的主要目的是消除多余(交叉重复)的窗口,找到最佳物体检测位置。

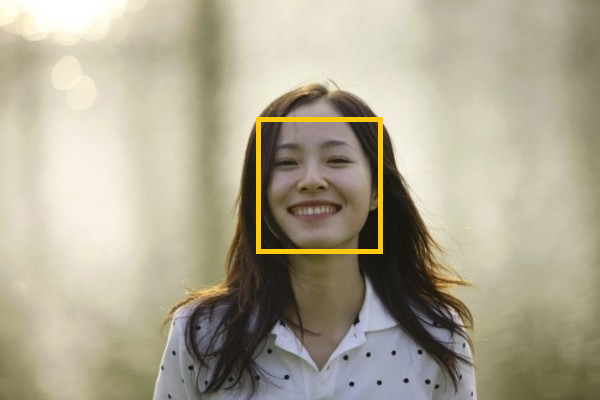
如上图所示,人脸检测中,虽然每个窗口均检测到人脸,但仅需给出一个最有可能表征人脸的窗口。
4. 算法程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
functionpickLocate = nms(boxes, overlap)% Non-maximum suppression.% In object detect algorithm, select high score detections and skip windows% covered by a previously selected detection.%% input - boxes : object detect windows.% xMin yMin xMax yMax score.% overlap : suppression threshold.% output - pickLocate : number of local maximum score.boxes = double(boxes);ifisempty(boxes) pickLocate = [];else xMin = boxes(:, 1); yMin = boxes(:, 2); xMax = boxes(:, 3); yMax = boxes(:, 4); s = boxes(:,end); % area of every detected windows. area= (xMax - xMin + 1) .* (yMax - yMin + 1); % sort detected windows based on the score. [vals, I] =sort(s); pickLocate = []; while~isempty(I) last= length(I); i= I(last); pickLocate = [pickLocate;i]; suppress = [last]; forpos = 1 : last- 1 j= I(pos); % covered area. xx1 =max(xMin(i), xMin(j)); yy1 =max(yMin(i), yMin(j)); xx2 =min(xMax(i), xMax(j)); yy2 =min(yMax(i), yMax(j)); w = xx2 - xx1 + 1; h = yy2 - yy1 + 1; if((w > 0) && (h > 0)) % compute overlap. o = w * h /min(area(i),area(j)); if(o > overlap) suppress = [suppress; pos]; end end % xx1 = max(x1(i), x1(I(1:last-1))); % yy1 = max(y1(i), y1(I(1:last-1))); % xx2 = min(x2(i), x2(I(1:last-1))); % yy2 = min(y2(i), y2(I(1:last-1))); % w = max(0.0, xx2-xx1+1); % h = max(0.0, yy2-yy1+1); % inter = w.*h; % o = inter ./ (area(i) + area(I(1:last-1)) - inter); % saving the windows which o less than threshold. % I = I(o <= overlap); end I(suppress) = []; endend分类: 物体识别
好文要顶关注我 收藏该文 ![]()
![]()
0
0
«上一篇:内部排序之直接插入排序
»下一篇:内部排序之简单选择排序
»下一篇:内部排序之简单选择排序
posted @ 2016-02-26 09:13 liekkas0626 阅读(13107) 评论(0)编辑 收藏
阅读全文
0 0
- 非极大值抑制——基于人脸检测(框出最大概率值的人脸区域)
- 人脸检测--非极大值抑制-Non-Maximum Suppression
- cs231n笔记(9+)——非极大值抑制
- NMS——非极大值抑制
- NMS——非极大值抑制
- NMS——非极大值抑制
- NMS——非极大值抑制
- NMS——非极大值抑制
- 非极大值抑制——NMS实例
- NMS——非极大值抑制
- NMS—非极大值抑制算法
- 非极大值抑制在物体检测方面的应用
- 非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)在物体检测领域的应用
- 非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)在物体检测领域的应用
- 非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)在物体检测领域的应用
- 非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)在物体检测领域的应用
- 非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)在物体检测领域的应用
- 非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)在物体检测领域的应用
- Struts2学习笔记(一)——工作原理
- kafka的c/c++高性能客户端librdkafka简介
- NAT的四种类型
- IOS UITableView实现左滑删除
- HTML表单
- 非极大值抑制——基于人脸检测(框出最大概率值的人脸区域)
- sudo时无法使用代理
- Android 跳转系统相册
- Django建教育平台(四)--Django Admin与Xadmin
- PHP学习心得
- T-SQL与PL/SQL的比较
- SpringMVC
- Oracle 数据导入/导出 IMPDP/EXPDP
- Spring事务管理——使用XML配置声明式事务


