cf424c 亦或交换律 模循环节 亦或前缀和
来源:互联网 发布:php html页面生成图片 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/17 00:12
People in the Tomskaya region like magic formulas very much. You can see some of them below.
Imagine you are given a sequence of positive integer numbers p1, p2, ...,pn. Lets write down some magic formulas:
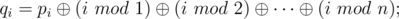
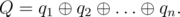
Here, "mod" means the operation of taking the residue after dividing.
The expression 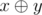 means applying the bitwisexor (excluding "OR") operation to integersx and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++ and Java it is represented by "^", in Pascal — by "xor".
means applying the bitwisexor (excluding "OR") operation to integersx and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++ and Java it is represented by "^", in Pascal — by "xor".
People in the Tomskaya region like magic formulas very much, but they don't like to calculate them! Therefore you are given the sequencep, calculate the value of Q.
The first line of the input contains the only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106). The next line containsn integers: p1, p2, ..., pn (0 ≤ pi ≤ 2·109).
The only line of output should contain a single integer — the value of Q.
31 2 3
3
1--n mod 1--n
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cmath>#include<algorithm>#include<cstring>#include<queue>using namespace std;long long esum[1000005];int main(){ int n; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { long long ans=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { long long tp; scanf("%lld",&tp); ans^=tp; } esum[0]=0; esum[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) { esum[i]=i^esum[i-1]; } for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) { int num=n/i; int res=n%i; if(num%2==1) ans^=esum[i-1]; ans^=esum[res]; } printf("%lld\n",ans); }}- cf424c 亦或交换律 模循环节 亦或前缀和
- 与或非亦或与交换
- 异或交换解析
- 异或交换数值
- Codeforces 17E Palisection Manacher ( 或 Panlindromic Tree ) + 前缀和
- 异或前缀和+DFS hdu5416 CRB and Tree
- HDU 5480 Conturbatio(并查集或前缀和)
- HDU 5416 CRB and Tree 异或前缀和
- Wannafly挑战赛1 B Xorto(前缀异或和)
- 亦或
- 【BZOJ4397】[Usaco2015 dec]Breed Counting【前缀和】【或莫队】【或线段树】【或可持久化线段树】
- 前缀异或:XOR Segment (用的是前缀和的思想,所以暂且称这个方法为前缀异或)
- a和b交换面试题(用异或解决)
- "异或"实现a和b两变量交换
- "异或"实现a和b两变量交换
- 异或交换与数组交换
- 异或交换变量内容
- 旋转交换或向量旋转
- mysql入门
- H5面试----简述一下src与href的区别
- OpenCV学习之图像域的填充
- win7 64位旗舰版系统运行regsvr32.exe提示版本不兼容
- 【LeetCode】002. Add Two Numbers
- cf424c 亦或交换律 模循环节 亦或前缀和
- 项目管理学习总结(4)——项目团队,如何展开有效沟通?
- 3、spring集成quartz
- python常用模块之random模块
- ATLCOM服务端连接点,advise返回CONNECT_E_CANNOTCONNECT的一个可能原因
- 只有程序员能听懂的笑话,你知道几个?
- 机器学习-数据挖掘面试题
- 能够正常使用的,经过测试的java+jquery+webcam调用本地摄像头拍照,然后将拍照结果上传数据库blob字段功能的实现(一)
- mac系统(macOS)编辑器关闭自动转换英文单、双引号为中文、自动拼写检查等


