JDK源码解析之LinkedList
来源:互联网 发布:java fast paxos算法 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 07:39
一、 LinkedList简介
LinkedList 跟 ArrayList一样实现了List接口,但跟ArrayList不同的是ArrayList采用的是数组作为存储元素的容器,所以ArrayList可以直接用角标获取元素,所以ArrayList查询效率较高, 但在添加和删除元素的速度比较慢,因为得移动元素。而LinkedList采用的是链表来存储元素, 因为它没有下标,所以在查询某个元素时的速度较慢,需要遍历链表,但在添加和删除元素时不用移动其他元素,所以增删速度快。
二、 LinkedList的数据结构
1. LinkedList结构图
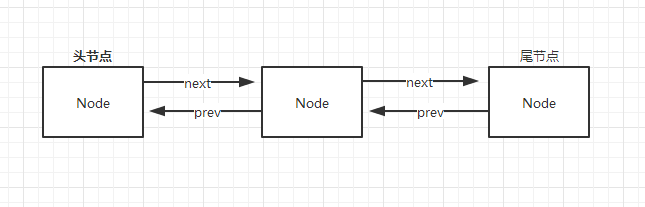
Linked中的每个节点都包含了上一个元素和下一个元素,如果该节点为头节点的话,该节点就只有下一个元素,如果该节点是尾节点的话,name该节点只有上一个元素
2. LinkedList增删图
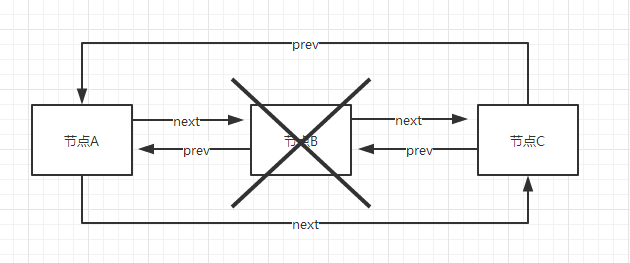
有A、B、C三个节点如上,A的next是B,B的next是C,如果要将B节点删除,只要将A节点的next节点指向C,将C节点的prev指向A即可
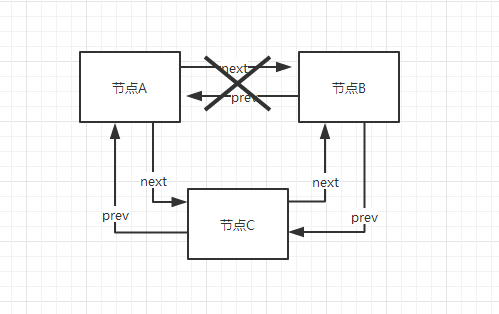
有A、B 两个节点,A的next是B,如果要在A、B之间插入节点C,则需将A的next指向C,C的prev指向A,C的next指向B,B的prev指向C
三、LinkedList源码解析
package java.util;import java.util.function.Consumer;public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{ // 链表中元素的个数 transient int size = 0; // 链表的第一个节点 transient Node<E> first; // 链表的最后一个节点 transient Node<E> last; // 空参数构造函数 public LinkedList() { } // 参数为Collection的构造函数,将另外一个集合的元素添加都链表中 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); } // 往链表头部加入一个元素 private void linkFirst(E e) {//获取当前链表的头 final Node<E> f = first;// 创建一个节点,因为该节点要放到头部, //所以该节点的上一个节点为null,而下一个节点就是原来链表的头 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);// 将新节点赋值给first first = newNode;// 如果原来节点的first为空,说明原来链表没有节点,所以尾节点也等于新节点 if (f == null) last = newNode; else // 否则将原来的头节点的上一个节点赋值为新的头节点 f.prev = newNode;// 链表中元素 + 1 size++;// 修改次数 + 1 modCount++; } // 往链表尾部加入一个元素,与上面类似 void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last;// 新添加的尾节点的上一个节点是原来链表的尾节点,而下一个节点是null final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) //说明原来链表没有节点 first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } // 在某个节点之前添加一个节点 void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null;// 获取succ节点原来的上一个节点 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;// 新加节点的上一个节点为原来succ的上一个节点,而下一个节点则为 succ final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode;// 如果succ的上一个节点为null的话说明原来链表中succ是头结点,所以新节点则成为了头节点 if (pred == null) first = newNode; else // 原来链表中succ的上一个节点的下个节点改成新的节点 pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } // 删除头节点 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { // assert f == first && f != null;// 获取头节点的元素 final E element = f.item;// 获取头节点的下一个元素 final Node<E> next = f.next;// 将要删除的头节点的元素和下一个元素置为null,下一次垃圾回收就会回收掉 f.item = null; f.next = null; // help GC//将头节点设为原来链表的第二个节点 first = next; if (next == null) //如果next为空的话说明原来链表只剩一个节点,所以last也赋值为null last = null; else // 否则新的头节点的上一个节点置为null next.prev = null; size--; modCount++;// 返回删掉的节点的元素 return element; } // 移除最后一个节点,与上类似 private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { // assert l == last && l != null; final E element = l.item; final Node<E> prev = l.prev; l.item = null; l.prev = null; // help GC last = prev; if (prev == null) first = null; else prev.next = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } // 删除某一个节点 E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item;// 获取上一个节点 final Node<E> next = x.next;// 获取下一个节点 final Node<E> prev = x.prev;// 如果上一个节点null的话,则要删除的节点为头节点,所以它的next则成为头节点 if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { // 否则的话将next赋值到prev的下一个节点 prev.next = next; x.prev = null; }// 如果next为null的话,则要删除的节点为尾节点,所以它的上一个节点则成为尾节点 if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { // 否则的话将prev赋值到next的上一个节点 next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } // 获取第一个节点的元素 public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; } // 获取最后一个节点的元素 public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; } // 移除第一个节点 public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();//调用上面的移除第一个节点方法 return unlinkFirst(f); } // 移除最后一个节点 public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); } // 往头部添加节点 public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); } //往尾部添加节点 public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); } // 判断该链表是否包含某个元素 public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; } // 获取链表的元素个数 public int size() { return size; } // 添加节点,则往尾部添加节点 public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } // 移除某个节点,成功返回true,否则false public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { //遍历链表 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { //遍历链表 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } // 将另外一个集合中的元素添加到链表的尾部 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } // 将另外一个集合中的元素添加到链表指点的某个位置 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { // 检查该位置是否>=0 并且 <= size checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); // 将集合转成数组 int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) // 如果该集合中没有元素则返回false return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { // 判断是否加在尾节点后面 succ = null; // 如果是的话,集合C中的最后一个元素将成为链表尾节点,所以它的next为null pred = last; // 并且集合C中的第一个元素的上一个节点为原链表的最后一个节点 } else { succ = node(index); // 不是的话则获取链表中index位置的节点,// 该节点将成为集合C中的最后一个元素下一个节点 pred = succ.prev; // 而该节点的上一个节点成为集合C中的第一个元素的上一个节点 } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) // 说明index位置的节点是头节点,所以集合C中的第一个元素成为头节点 first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; // 每添加一个节点就赋值给pred,用于做下个节点的头节点 pred = newNode; } // 说明集合C是添加到尾节点后面,所以集合C中的最后一个元素将成为链表尾节点 if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { // 将原来index位置的next节点成为集合C中的最后一个元素的下一个节点, pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; } // 清空链表 public void clear() { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; } // 通过给定位置获取元素 public E get(int index) {// 判断该位置是否在越界 checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } // 修改某个节点的元素 public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; } // 往某个位置添加元素 public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } // 移除掉某个位置的元素 public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); } // 判断index是否越界,相当于数组中的下标 private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size; } // 判断index是否越界 private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size; } // 下标越界异常信息 private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; } // 检查元素下标 private void checkElementIndex(int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } // 检查位置下标 private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { if (!isPositionIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } // 通过下标查找节点 Node<E> node(int index) {// size >> 1 = size / 2 取链表的中间值位置, 目的:优化查找速度 if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 如果index < 中间值 则从头部遍历 Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { // 如果 index > 中间值则从尾部遍历 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } // 获取某个元素在链表的位置,获取不到返回 -1 public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; } // 判断某个元素在链表最后一次出现的位置 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (x.item == null) return index; } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; } } return -1; } // 获取第一个节点的元素 public E peek() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } // 获取第一个节点的元素,如果为空则抛出异常 public E element() { return getFirst(); } // 获取第一个节点的元素并移除 public E poll() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } // 移除某个元素并返回 public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } // 往链表尾部添加元素 public boolean offer(E e) { return add(e); } // 往链表头部添加元素 public boolean offerFirst(E e) { addFirst(e); return true; } // 往链表尾部添加元素 public boolean offerLast(E e) { addLast(e); return true; } // 获取第一个元素 public E peekFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } // 获取最后一个元素 public E peekLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : l.item; } // 获取第一个节点的元素并移除 public E pollFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } // 获取最后一个节点的元素并移除 public E pollLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); } // 往链表头部添加元素(入栈) public void push(E e) { addFirst(e); } // 移除链表的第一个元素并返回(出栈) public E pop() { return removeFirst(); } // 移除在链表第一次的出现该元素的节点返回 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { return remove(o); } // 移除在链表最后一次的出现该元素的节点返回 public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } // 获取从某个位置开始的迭代器 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { checkPositionIndex(index); return new ListItr(index); } // 迭代器 private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { private Node<E> lastReturned; private Node<E> next; private int nextIndex; private int expectedModCount = modCount; ListItr(int index) { // assert isPositionIndex(index); next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); nextIndex = index; } // 是否有下一个元素,用于正向迭代 public boolean hasNext() { return nextIndex < size; }// 获取下一个元素 public E next() { checkForComodification(); if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; return lastReturned.item; }// 是否有上一个元素,用于反向迭代 public boolean hasPrevious() { return nextIndex > 0; }// 获取上一个元素 public E previous() { checkForComodification(); if (!hasPrevious()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; nextIndex--; return lastReturned.item; }// 获取下一个迭代的下标 public int nextIndex() { return nextIndex; }// 获取上一个迭代的下标 public int previousIndex() { return nextIndex - 1; }// 移除上一次迭代的元素 public void remove() { checkForComodification(); if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; unlink(lastReturned); if (next == lastReturned) next = lastNext; else nextIndex--; lastReturned = null; expectedModCount++; }// 修改上一次迭代的元素 public void set(E e) { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); lastReturned.item = e; }// 往上一次迭代的元素后面添加元素 public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); lastReturned = null; if (next == null) linkLast(e); else linkBefore(e, next); nextIndex++; expectedModCount++; }// 对未处理的元素执行action ,这个笔者也不是很清楚 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) { action.accept(next.item); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; } checkForComodification(); } //此方法用来判断创建迭代对象的时候List的modCount与现在List的modCount是否一样,//不一样的话就报ConcurrentModificationException异常 final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } // 链表的节点 private static class Node<E> { E item; // 当前节点存储元素 Node<E> next; // 下一个节点 Node<E> prev; // 上一个节点 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } } // 获取反向迭代器 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { return new DescendingIterator(); } // 反向迭代器 private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> { private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size()); public boolean hasNext() { return itr.hasPrevious(); } public E next() { return itr.previous(); } public void remove() { itr.remove(); } } // 克隆 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private LinkedList<E> superClone() { try { return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new InternalError(e); } } // 克隆 public Object clone() { LinkedList<E> clone = superClone(); // Put clone into "virgin" state clone.first = clone.last = null; clone.size = 0; clone.modCount = 0; // Initialize clone with our elements for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) clone.add(x.item); return clone; } // 转换成数组 public Object[] toArray() { Object[] result = new Object[size]; int i = 0; for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) result[i++] = x.item; return result; } // 转换成指定泛型类数组 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); int i = 0; Object[] result = a; for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) result[i++] = x.item; if (a.length > size) a[size] = null; return a; } // 序列化号 private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L; // 序列化时调用该方法 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException { // Write out any hidden serialization magic s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size s.writeInt(size); // Write out all elements in the proper order. for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) s.writeObject(x.item); } //反序列化时调用该方法 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // Read in any hidden serialization magic s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in size int size = s.readInt(); // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) linkLast((E)s.readObject()); } @Override public Spliterator<E> spliterator() { return new LLSpliterator<E>(this, -1, 0); } // 可分割迭代器,这个笔者不是很了解,所以没法在说明,如果知道的小伙伴可以告诉我下 static final class LLSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> { static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size; final LinkedList<E> list; // null OK unless traversed Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set int batch; // batch size for splits LLSpliterator(LinkedList<E> list, int est, int expectedModCount) { this.list = list; this.est = est; this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount; } final int getEst() { int s; // force initialization final LinkedList<E> lst; if ((s = est) < 0) { if ((lst = list) == null) s = est = 0; else { expectedModCount = lst.modCount; current = lst.first; s = est = lst.size; } } return s; } public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); } public Spliterator<E> trySplit() { Node<E> p; int s = getEst(); if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) { int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT; if (n > s) n = s; if (n > MAX_BATCH) n = MAX_BATCH; Object[] a = new Object[n]; int j = 0; do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n); current = p; batch = j; est = s - j; return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED); } return null; } public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { Node<E> p; int n; if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) { current = null; est = 0; do { E e = p.item; p = p.next; action.accept(e); } while (p != null && --n > 0); } if (list.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) { Node<E> p; if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) { --est; E e = p.item; current = p.next; action.accept(e); if (list.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); return true; } return false; } public int characteristics() { return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED; } }}阅读全文
0 0
- JDK之LinkedList源码解析
- JDK源码解析之LinkedList
- 【源码解析】JDK源码之LinkedList
- JDK源码解析之ArrayList和LinkedList
- 【JDk源码解析之二】LinkedList源码解析
- JDK源码阅读之LinkedList
- jdk集合源码之LinkedList
- jdk源码分析之LinkedList
- jdk源码剖析之LinkedList
- JDK源码走读之LinkedList
- 【JDK】:ArrayList和LinkedList源码解析
- JDK源码学习之Arraylist与LinkedList
- java源码解读之LinkedList------jdk 1.7
- JDK源码-LinkedList源码
- LinkedList源码解析 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(2)
- List源码解析之LinkedList 源码分析
- List源码解析之LinkedList 源码分析
- JDK源码解析集合篇--LinkedList全解析
- TensorFlow 实现Softmax Regression 识别数字
- java求解 集合的子集
- MainThread agent ERROR Could not determine hostname or ip address; proceeding.
- SolidWorks 2017 SP2 Premium Multilanguge Win64 1DVD
- 初次使用servlet实现对数据的增删改查
- JDK源码解析之LinkedList
- QT Basic 014 Model/View programming (模型、视图编程)
- mybatis缓存文件的配置
- Web测试方法大全
- Mac中允许任何来源的app安装
- 设计模式之观察者模式
- linux课程培训哪的好?
- 微信小程序使用百度api获取天气信息 —— 微信小程序教程系列
- struts搭建简单web工程步骤


