[源码]Elasticsearch源码2(RPC)
来源:互联网 发布:qq三国js点智力 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/01 09:21
本文讨论了ES中的远程调用RPC部分的源码实现。
一、前言
1.1 关于ES RPC
ES的分布式通信这块,主要是支持了RPC和REST两种模式(不支持大的package/stream的数据传输)。
集群Node之间的通信,数据的传输,java客户端的请求调用(TransportClient)使用的均是RPC(TCP)。
1.2 关于Netty
ES是基于netty开发的rpc模块(http同样基于netty),采用常规的基于注册/回调方式进行事件驱动的reactor/proactor模式(单线程调度,线程池处理)。
题外话,ES作为分布式系统把每个行为都抽象成了Action对象,且采用注册回调的方式进行通信,它的调用基本都是异步的,所有调用全部依赖ES
自己实现的线程池。话说这么多异步事件是不是可以直接抽象成Actor呢。(akka,或者quasar的纤程模型替代不知是否可以)。
二、ES RPC 源码分析
2.1 一个简单例子说明过程
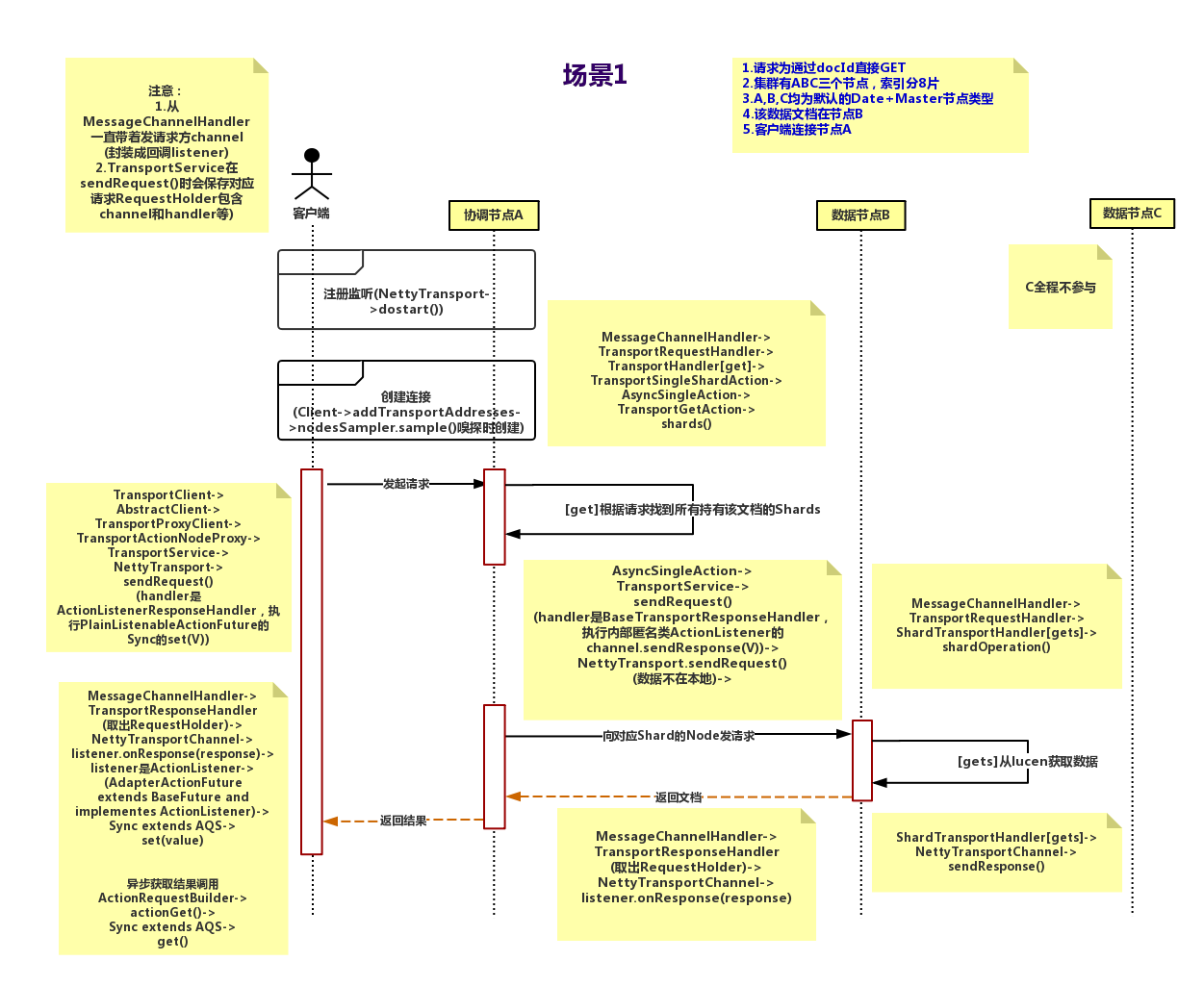
首先上时序图,举最简单的例子引入话题,一次通过es的java Client Api进行Get请求调用(Tcp方式)。
场景1:Client 连接节点A并发送请求,数据在节点B。
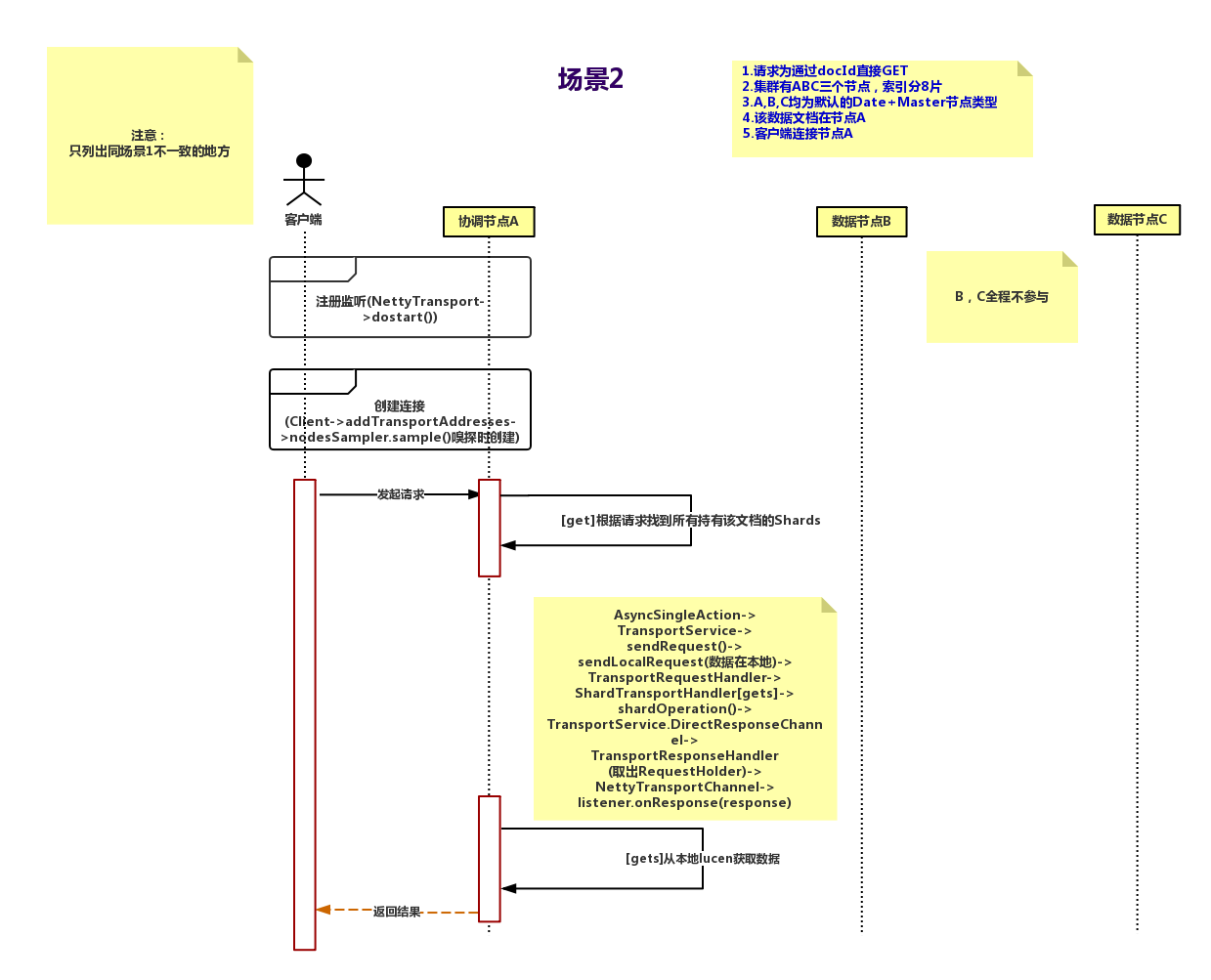
场景2:场景1简化版,Client 连接节点A并发送请求,数据就在A直接返回。
关于RPC,这里有一篇文章写的很好你应该知道的RPC原理
2.2 ES中的RPC,源码部分
由于是基于Netty,那么我们直接看源码
首先看发送请求
TransportService(Es通信过程中存请求上下文,以及RPC方法映射,即request对应action的地方),
的 clientHandlers就是异步回调池(根据requestId拿到回调执行),存放的就是requestId以及对应的
TransportResponseHandler,与code1的request是一一对应的。code1,code3 Connection连接是根据node从transport获取的。
code2发送请求最终会执行sendRequestInternal()
code4 client线程每次通过socket调用一次远程接口前,生成一个唯一的ID,即requestID
(requestID必需保证在一个Socket连接里面是唯一的),一般常常使用AtomicLong从0开始累计数字生成唯一ID。code5 构造超时回调。
code6 todo
code7 把线程上下文和callback封装
code8 将处理结果的回调对象callback,存放到全局ConcurrentHashMap里面put(requestID, callback);
code9 放入定时线程池中(类似于ScheduledThreadPool),到时间会调用handleException(e)回调给该connection超时异常。
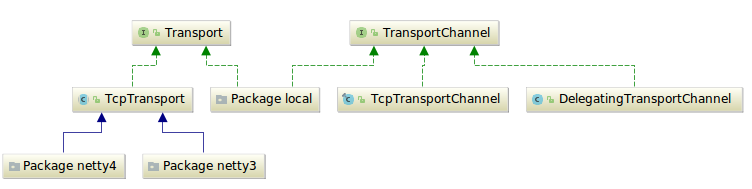
public class TransportService extends AbstractLifecycleComponent { public final <T extends TransportResponse> void sendRequest(final DiscoveryNode node, final String action, final TransportRequest request, final TransportRequestOptions options, TransportResponseHandler<T> handler) { try { Transport.Connection connection = getConnection(node);//code1 sendRequest(connection, action, request, options, handler);//code2 } catch (NodeNotConnectedException ex) { // the caller might not handle this so we invoke the handler handler.handleException(ex); } } public Transport.Connection getConnection(DiscoveryNode node) {//code3 if (isLocalNode(node)) { return localNodeConnection; } else { return transport.getConnection(node); } } private <T extends TransportResponse> void sendRequestInternal(final Transport.Connection connection, final String action, final TransportRequest request, final TransportRequestOptions options, TransportResponseHandler<T> handler) { if (connection == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("can't send request to a null connection"); } DiscoveryNode node = connection.getNode(); final long requestId = transport.newRequestId(); //code4 final TimeoutHandler timeoutHandler; try { if (options.timeout() == null) { timeoutHandler = null; } else { timeoutHandler = new TimeoutHandler(requestId); //code5 } Supplier<ThreadContext.StoredContext> storedContextSupplier = threadPool.getThreadContext().newRestorableContext(true); //code6 TransportResponseHandler<T> responseHandler = new ContextRestoreResponseHandler<>(storedContextSupplier, handler); //code7 clientHandlers.put(requestId, new RequestHolder<>(responseHandler, connection, action, timeoutHandler)); //code8 if (lifecycle.stoppedOrClosed()) { // if we are not started the exception handling will remove the RequestHolder again and calls the handler to notify // the caller. It will only notify if the toStop code hasn't done the work yet. throw new TransportException("TransportService is closed stopped can't send request"); } if (timeoutHandler != null) { assert options.timeout() != null; timeoutHandler.future = threadPool.schedule(options.timeout(), ThreadPool.Names.GENERIC, timeoutHandler);//code9 } connection.sendRequest(requestId, action, request, options); // local node optimization happens upstream code10 } catch (final Exception e) { // usually happen either because we failed to connect to the node // or because we failed serializing the message final RequestHolder holderToNotify = clientHandlers.remove(requestId); // If holderToNotify == null then handler has already been taken care of. if (holderToNotify != null) { holderToNotify.cancelTimeout(); // callback that an exception happened, but on a different thread since we don't // want handlers to worry about stack overflows final SendRequestTransportException sendRequestException = new SendRequestTransportException(node, action, e); threadPool.executor(ThreadPool.Names.GENERIC).execute(new AbstractRunnable() { @Override public void onRejection(Exception e) { // if we get rejected during node shutdown we don't wanna bubble it up logger.debug( (Supplier<?>) () -> new ParameterizedMessage( "failed to notify response handler on rejection, action: {}", holderToNotify.action()), e); } @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { logger.warn( (Supplier<?>) () -> new ParameterizedMessage( "failed to notify response handler on exception, action: {}", holderToNotify.action()), e); } @Override protected void doRun() throws Exception { holderToNotify.handler().handleException(sendRequestException); } }); } else { logger.debug("Exception while sending request, handler likely already notified due to timeout", e); } } }}TcpTransport是Netty4Transport和Netty3Transport的父类,利用范型抽象出了Channel所有涉及Channel的均由
子类去实现,其负责封装所有发送请求的逻辑。NodeChannels存入transport容器中(TcpTransport),可执行发送逻辑。
TcpTransportChannel可执行响应逻辑。
发送会根据场景选择channel(recovery,bulk,reg,state,ping分别对应不同的channel[],个数也不同,其创建的过程
涉及到节点发现的过程,另文细说),响应就是发给对应的channel。最终执行消息传输的都是Transport(TcpTransport)。真正的发送逻辑是sendRequestToChannel(),最终执行code12发送消息。
public abstract class TcpTransport<Channel> extends AbstractLifecycleComponent implements Transport { protected final ConcurrentMap<DiscoveryNode, NodeChannels> connectedNodes = newConcurrentMap(); private final Set<NodeChannels> openConnections = newConcurrentSet(); public final class NodeChannels implements Connection { @Override public void sendRequest(long requestId, String action, TransportRequest request, TransportRequestOptions options) throws IOException, TransportException { if (closed.get()) { throw new NodeNotConnectedException(node, "connection already closed"); } Channel channel = channel(options.type()); sendRequestToChannel(this.node, channel, requestId, action, request, options, getVersion(), (byte)0);//code11 } } private void sendRequestToChannel(DiscoveryNode node, final Channel targetChannel, final long requestId, final String action, final TransportRequest request, TransportRequestOptions options, Version channelVersion, byte status) throws IOException, TransportException { if (compress) { options = TransportRequestOptions.builder(options).withCompress(true).build(); } status = TransportStatus.setRequest(status); ReleasableBytesStreamOutput bStream = new ReleasableBytesStreamOutput(bigArrays); // we wrap this in a release once since if the onRequestSent callback throws an exception // we might release things twice and this should be prevented final Releasable toRelease = Releasables.releaseOnce(() -> Releasables.close(bStream.bytes())); boolean addedReleaseListener = false; StreamOutput stream = bStream; try { // only compress if asked, and, the request is not bytes, since then only // the header part is compressed, and the "body" can't be extracted as compressed if (options.compress() && canCompress(request)) { status = TransportStatus.setCompress(status); stream = CompressorFactory.COMPRESSOR.streamOutput(stream); } // we pick the smallest of the 2, to support both backward and forward compatibility // note, this is the only place we need to do this, since from here on, we use the serialized version // as the version to use also when the node receiving this request will send the response with Version version = Version.min(getCurrentVersion(), channelVersion); stream.setVersion(version); threadPool.getThreadContext().writeTo(stream); stream.writeString(action); BytesReference message = buildMessage(requestId, status, node.getVersion(), request, stream, bStream); final TransportRequestOptions finalOptions = options; Runnable onRequestSent = () -> { // this might be called in a different thread try { toRelease.close(); } finally { transportServiceAdapter.onRequestSent(node, requestId, action, request, finalOptions); } }; addedReleaseListener = internalSendMessage(targetChannel, message, onRequestSent); } finally { IOUtils.close(stream); if (!addedReleaseListener) { toRelease.close(); } } } /** * sends a message view the given channel, using the given callbacks. * * @return true if the message was successfully sent or false when an error occurred and the error hanlding logic was activated * */ private boolean internalSendMessage(Channel targetChannel, BytesReference message, Runnable onRequestSent) throws IOException { boolean success; try { sendMessage(targetChannel, message, onRequestSent); success = true; } catch (IOException ex) { // passing exception handling to deal with this and raise disconnect events and decide the right logging level onException(targetChannel, ex); success = false; } return success; }} public class Netty4Transport extends TcpTransport<Channel> { @Override protected void sendMessage(Channel channel, BytesReference reference, Runnable sendListener) { final ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(Netty4Utils.toByteBuf(reference));//code12 future.addListener(f -> sendListener.run()); }}发送响应
- 服务端接收到请求并处理后,将response结果(此结果中包含了前面的requestID)发送给客户端
接收消息
客户端socket连接上专门监听消息的线程收到消息,分析结果,取到requestID。
messageReceived是比较常见的解析数据包的过程,es自己通过XContent实现的序列化协议,所以代码可读性稍差,作者
自己通过mssagepack重写了这部分,详见别文。然叫首先交由TransportService.Adapter 从前面的ConcurrentHashMap里面get(requestID)出callback对象,
取消超时任务再交由线程池执行回调code13。code13执行的过程其实就是执行发送消息时的幂名内部类(也叫回调),
通常是交由channel去做异步通知(相当于非本地节点还在监听response),或者是Aqs释放本地阻塞(本地是调用发起方,见[源码]Elasticsearch源码1(通信机制之Future))。
public abstract class TcpTransport<Channel> extends AbstractLifecycleComponent implements Transport { /** * This method handles the message receive part for both request and responses */ public final void messageReceived(BytesReference reference, Channel channel, String profileName, InetSocketAddress remoteAddress, int messageLengthBytes) throws IOException { final int totalMessageSize = messageLengthBytes + TcpHeader.MARKER_BYTES_SIZE + TcpHeader.MESSAGE_LENGTH_SIZE; transportServiceAdapter.addBytesReceived(totalMessageSize); // we have additional bytes to read, outside of the header boolean hasMessageBytesToRead = (totalMessageSize - TcpHeader.HEADER_SIZE) > 0; StreamInput streamIn = reference.streamInput(); boolean success = false; try (ThreadContext.StoredContext tCtx = threadPool.getThreadContext().stashContext()) { long requestId = streamIn.readLong(); byte status = streamIn.readByte(); Version version = Version.fromId(streamIn.readInt()); if (TransportStatus.isCompress(status) && hasMessageBytesToRead && streamIn.available() > 0) { Compressor compressor; try { final int bytesConsumed = TcpHeader.REQUEST_ID_SIZE + TcpHeader.STATUS_SIZE + TcpHeader.VERSION_ID_SIZE; compressor = CompressorFactory.compressor(reference.slice(bytesConsumed, reference.length() - bytesConsumed)); } catch (NotCompressedException ex) { int maxToRead = Math.min(reference.length(), 10); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("stream marked as compressed, but no compressor found, first [").append(maxToRead) .append("] content bytes out of [").append(reference.length()) .append("] readable bytes with message size [").append(messageLengthBytes).append("] ").append("] are ["); for (int i = 0; i < maxToRead; i++) { sb.append(reference.get(i)).append(","); } sb.append("]"); throw new IllegalStateException(sb.toString()); } streamIn = compressor.streamInput(streamIn); } if (version.onOrAfter(Version.CURRENT.minimumCompatibilityVersion()) == false || version.major != Version.CURRENT.major) { throw new IllegalStateException("Received message from unsupported version: [" + version + "] minimal compatible version is: [" +Version.CURRENT.minimumCompatibilityVersion() + "]"); } streamIn = new NamedWriteableAwareStreamInput(streamIn, namedWriteableRegistry); streamIn.setVersion(version); threadPool.getThreadContext().readHeaders(streamIn); if (TransportStatus.isRequest(status)) { handleRequest(channel, profileName, streamIn, requestId, messageLengthBytes, version, remoteAddress, status); } else { final TransportResponseHandler<?> handler; if (TransportStatus.isHandshake(status)) { handler = pendingHandshakes.remove(requestId); } else { TransportResponseHandler theHandler = transportServiceAdapter.onResponseReceived(requestId); if (theHandler == null && TransportStatus.isError(status)) { handler = pendingHandshakes.remove(requestId); } else { handler = theHandler; } } // ignore if its null, the adapter logs it if (handler != null) { if (TransportStatus.isError(status)) { handlerResponseError(streamIn, handler); } else { handleResponse(remoteAddress, streamIn, handler); } // Check the entire message has been read final int nextByte = streamIn.read(); // calling read() is useful to make sure the message is fully read, even if there is an EOS marker if (nextByte != -1) { throw new IllegalStateException("Message not fully read (response) for requestId [" + requestId + "], handler [" + handler + "], error [" + TransportStatus.isError(status) + "]; resetting"); } } } success = true; } finally { if (success) { IOUtils.close(streamIn); } else { IOUtils.closeWhileHandlingException(streamIn); } } } private void handleResponse(InetSocketAddress remoteAddress, final StreamInput stream, final TransportResponseHandler handler) { final TransportResponse response = handler.newInstance(); response.remoteAddress(new InetSocketTransportAddress(remoteAddress)); try { response.readFrom(stream); } catch (Exception e) { handleException(handler, new TransportSerializationException( "Failed to deserialize response of type [" + response.getClass().getName() + "]", e)); return; } threadPool.executor(handler.executor()).execute(new AbstractRunnable() { @Override public void onFailure(Exception e) { handleException(handler, new ResponseHandlerFailureTransportException(e)); } @Override protected void doRun() throws Exception { handler.handleResponse(response); //code13 }}); }} public class TransportService extends AbstractLifecycleComponent { protected class Adapter implements TransportServiceAdapter { @Override public TransportResponseHandler onResponseReceived(final long requestId) { RequestHolder holder = clientHandlers.remove(requestId); if (holder == null) { checkForTimeout(requestId); return null; } holder.cancelTimeout(); if (traceEnabled() && shouldTraceAction(holder.action())) { traceReceivedResponse(requestId, holder.connection().getNode(), holder.action()); } return holder.handler(); } } }- [源码]Elasticsearch源码2(RPC)
- elasticsearch源码分析之Rest/RPC 接口解析(八)
- ElasticSearch源码
- Hadoop RPC 源码阅读2
- JavaScript RPC Client 源码
- JavaScript RPC Server 源码
- Hadoop RPC源码分析
- Hadoop RPC源码分析
- rpc源码分析
- Hadoop源码学习:RPC
- Hadoop RPC 源码解析
- HDFS RPC源码分析
- Hadoop RPC源码分析
- Spark RPC源码剖析
- linux下源码安装elasticsearch-5.5.2
- elasticsearch源码解析---AllocationDecider
- elasticsearch源码分析---TransportClient
- ElasticSearch Bulk 源码解析
- 线段树 1(基础 单点更新)
- 云客Drupal8源码分析之插件系统(中)
- zoj 3950 how many nines
- java的继承与多态
- 机器学习
- [源码]Elasticsearch源码2(RPC)
- Node Express获取参数的几种方法
- Android图片处理总结五:Bitmap方法总结
- OpenCV中的Haar+Adaboost(一):Haar特征详细介绍
- puppet
- 打工的第一个半天
- OpenCV中的Haar+Adaboost(二):积分图和45°旋转积分图
- 浅谈Android中的Handler机制
- eclipse查看文件所在硬盘的路径


