Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
来源:互联网 发布:怎么看iphone的mac地址 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/04 18:55
概述
上一篇我们介绍了如何将$.ajax和Vue.js结合在一起使用,并实现了一个简单的跨域CURD示例。Vue.js是数据驱动的,这使得我们并不需要直接操作DOM,如果我们不需要使用jQuery的DOM选择器,就没有必要引入jQuery。vue-resource是Vue.js的一款插件,它可以通过XMLHttpRequest或JSONP发起请求并处理响应。也就是说,$.ajax能做的事情,vue-resource插件一样也能做到,而且vue-resource的API更为简洁。另外,vue-resource还提供了非常有用的inteceptor功能,使用inteceptor可以在请求前和请求后附加一些行为,比如使用inteceptor在ajax请求时显示loading界面。
本文的主要内容如下:
- 介绍vue-resource的特点
- 介绍vue-resource的基本使用方法
- 基于this.$http的增删查改示例
- 基于this.$resource的增删查改示例
- 基于inteceptor实现请求等待时的loading画面
- 基于inteceptor实现请求错误时的提示画面
本文11个示例的源码:http://xiazai.jb51.net/201701/yuanma/vue-resource_jb51.rar
vue-resource特点
vue-resource插件具有以下特点:
1. 体积小
vue-resource非常小巧,在压缩以后只有大约12KB,服务端启用gzip压缩后只有4.5KB大小,这远比jQuery的体积要小得多。
2. 支持主流的浏览器
和Vue.js一样,vue-resource除了不支持IE 9以下的浏览器,其他主流的浏览器都支持。
3. 支持Promise API和URI Templates
Promise是ES6的特性,Promise的中文含义为“先知”,Promise对象用于异步计算。
URI Templates表示URI模板,有些类似于ASP.NET MVC的路由模板。
4. 支持拦截器
拦截器是全局的,拦截器可以在请求发送前和发送请求后做一些处理。
拦截器在一些场景下会非常有用,比如请求发送前在headers中设置access_token,或者在请求失败时,提供共通的处理方式。
vue-resource使用
引入vue-resource
<script src="js/vue.js"></script><script src="js/vue-resource.js"></script>基本语法
引入vue-resource后,可以基于全局的Vue对象使用http,也可以基于某个Vue实例使用http。
// 基于全局Vue对象使用httpVue.http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);Vue.http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);// 在一个Vue实例内使用$httpthis.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);this.$http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);在发送请求后,使用then方法来处理响应结果,then方法有两个参数,第一个参数是响应成功时的回调函数,第二个参数是响应失败时的回调函数。
then方法的回调函数也有两种写法,第一种是传统的函数写法,第二种是更为简洁的ES 6的Lambda写法:
// 传统写法this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(function(response){ // 响应成功回调}, function(response){ // 响应错误回调});// Lambda写法this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then((response) => { // 响应成功回调}, (response) => { // 响应错误回调});PS:做过.NET开发的人想必对Lambda写法有一种熟悉的感觉。
支持的HTTP方法
vue-resource的请求API是按照REST风格设计的,它提供了7种请求API:
- get(url, [options])
- head(url, [options])
- delete(url, [options])
- jsonp(url, [options])
- post(url, [body], [options])
- put(url, [body], [options])
- patch(url, [body], [options])
除了jsonp以外,另外6种的API名称是标准的HTTP方法。当服务端使用REST API时,客户端的编码风格和服务端的编码风格近乎一致,这可以减少前端和后端开发人员的沟通成本。
客户端请求方法 服务端处理方法
options对象
发送请求时的options选项对象包含以下属性:
参数 类型 描述
string请求的URLmethodstring请求的HTTP方法,例如:'GET', 'POST'或其他HTTP方法bodyObject, FormData stringrequest bodyparamsObject请求的URL参数对象headersObjectrequest headertimeoutnumber单位为毫秒的请求超时时间 (0 表示无超时时间)beforefunction(request)请求发送前的处理函数,类似于jQuery的beforeSend函数progressfunction(event)ProgressEvent回调处理函数credentialsboolean表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证emulateHTTPboolean发送PUT, PATCH, DELETE请求时以HTTP POST的方式发送,并设置请求头的X-HTTP-Method-OverrideemulateJSONboolean将request body以application/x-www-form-urlencoded content type发送emulateHTTP的作用
如果Web服务器无法处理PUT, PATCH和DELETE这种REST风格的请求,你可以启用enulateHTTP现象。启用该选项后,请求会以普通的POST方法发出,并且HTTP头信息的X-HTTP-Method-Override属性会设置为实际的HTTP方法。
Vue.http.options.emulateHTTP =true;emulateJSON的作用
如果Web服务器无法处理编码为application/json的请求,你可以启用emulateJSON选项。启用该选项后,请求会以application/x-www-form-urlencoded作为MIME type,就像普通的HTML表单一样。
Vue.http.options.emulateJSON =true;response对象
response对象包含以下属性:
方法 类型 描述
string以string形式返回response bodyjson()Object以JSON对象形式返回response bodyblob()Blob以二进制形式返回response body属性类型描述okboolean响应的HTTP状态码在200~299之间时,该属性为truestatusnumber响应的HTTP状态码statusTextstring响应的状态文本headersObject响应头注意:本文的vue-resource版本为v0.9.3,如果你使用的是v0.9.0以前的版本,response对象是没有json(), blob(), text()这些方法的。
CURD示例
提示:以下示例仍然沿用上一篇的组件和WebAPI,组件的代码和页面HTML代码我就不再贴出来了。
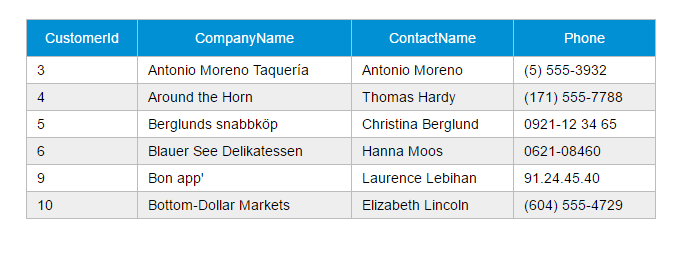
GET请求
var demo = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { gridColumns: ['customerId','companyName', 'contactName', 'phone'], gridData: [], apiUrl:'http://211.149.193.19:8080/api/customers' }, ready:function() { this.getCustomers() }, methods: { getCustomers:function() { this.$http.get(this.apiUrl) .then((response) => { this.$set('gridData', response.data) }) .catch(function(response) { console.log(response) }) } }})这段程序的then方法只提供了successCallback,而省略了errorCallback。
catch方法用于捕捉程序的异常,catch方法和errorCallback是不同的,errorCallback只在响应失败时调用,而catch则是在整个请求到响应过程中,只要程序出错了就会被调用。
在then方法的回调函数内,你也可以直接使用this,this仍然是指向Vue实例的:
getCustomers: function() { this.$http.get(this.apiUrl) .then((response) => { this.$set('gridData', response.data) }) .catch(function(response) { console.log(response) })}为了减少作用域链的搜索,建议使用一个局部变量来接收this。
JSONP请求
getCustomers: function() { this.$http.jsonp(this.apiUrl).then(function(response){ this.$set('gridData', response.data) })}POST请求
var demo = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { show:false, gridColumns: [{ name:'customerId', isKey:true }, { name:'companyName' }, { name:'contactName' }, { name:'phone' }], gridData: [], apiUrl:'http://211.149.193.19:8080/api/customers', item: {} }, ready:function() { this.getCustomers() }, methods: { closeDialog:function() { this.show =false }, getCustomers:function() { varvm = this vm.$http.get(vm.apiUrl) .then((response) => { vm.$set('gridData', response.data) }) }, createCustomer:function() { varvm = this vm.$http.post(vm.apiUrl, vm.item) .then((response) => { vm.$set('item', {}) vm.getCustomers() }) this.show =false } }})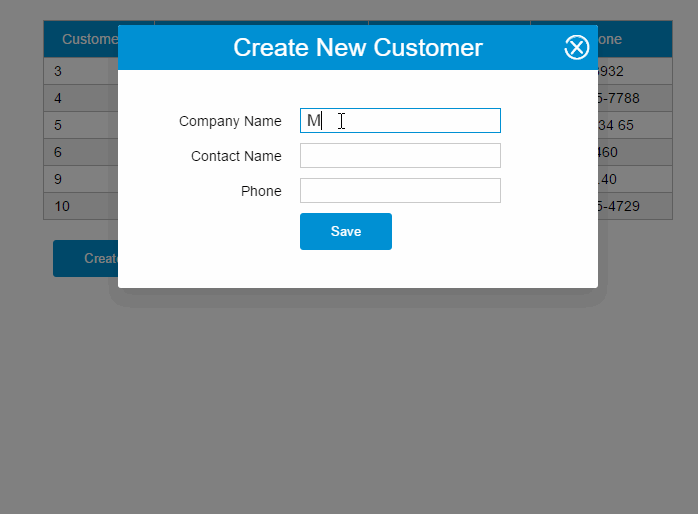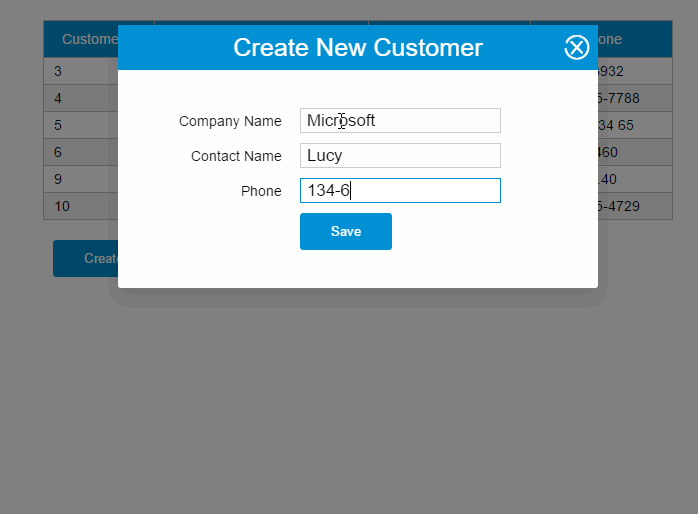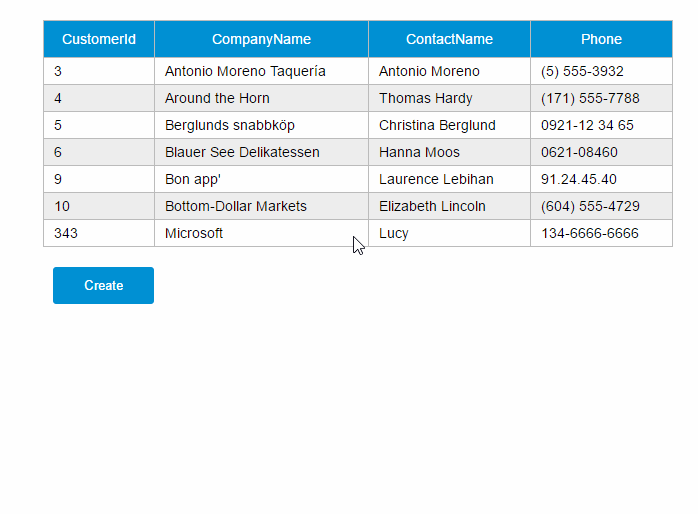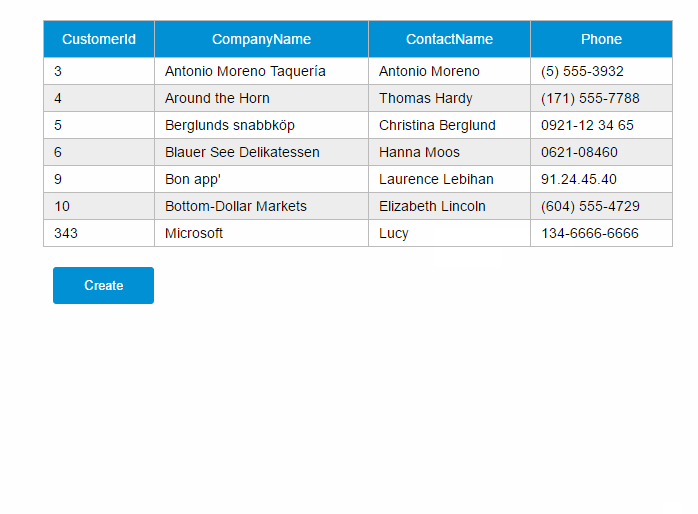
PUT请求
updateCustomer: function() { varvm = this vm.$http.put(this.apiUrl +'/' + vm.item.customerId, vm.item) .then((response) => { vm.getCustomers() })}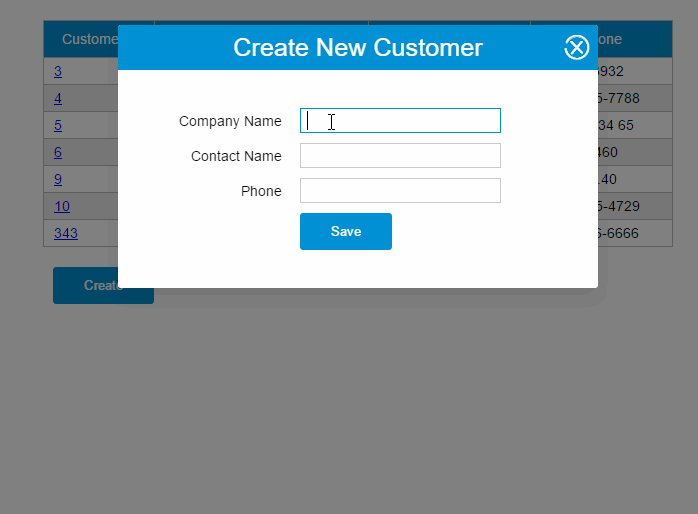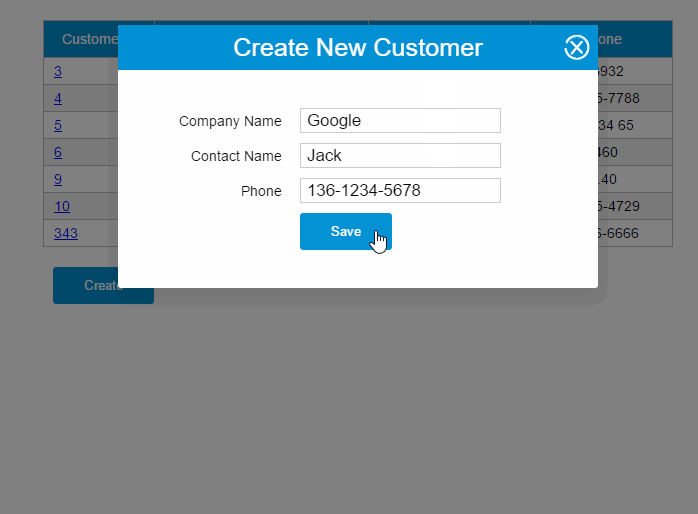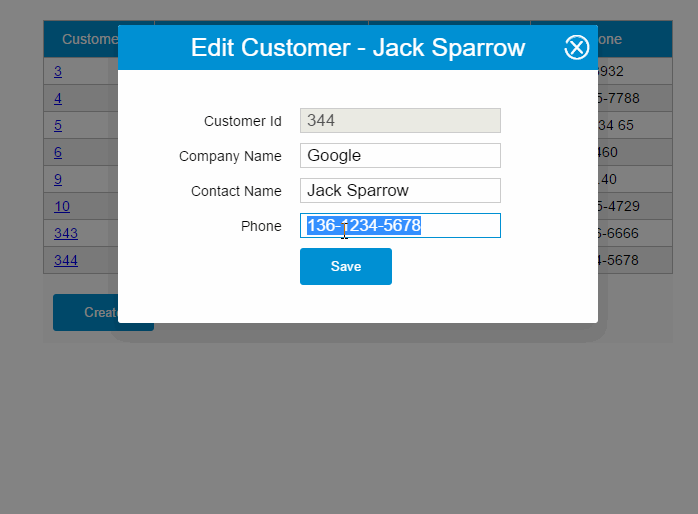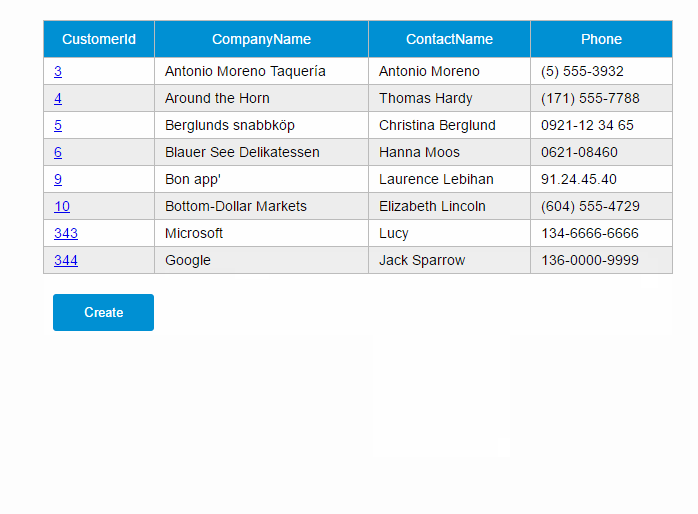
Delete请求
deleteCustomer: function(customer){ varvm = this vm.$http.delete(this.apiUrl +'/' + customer.customerId) .then((response) => { vm.getCustomers() })}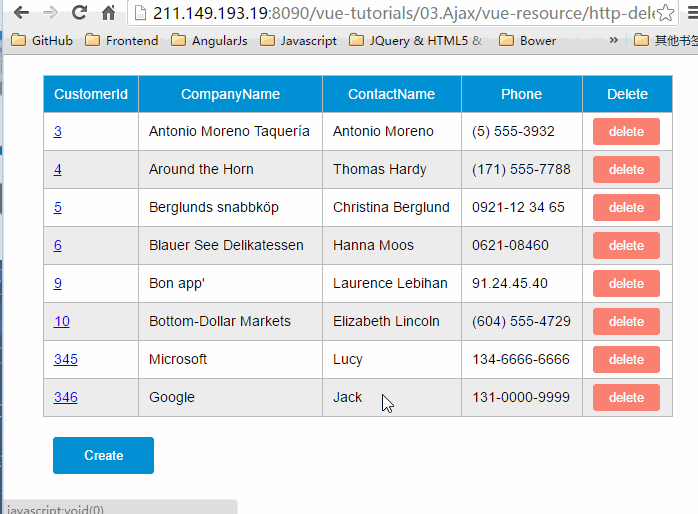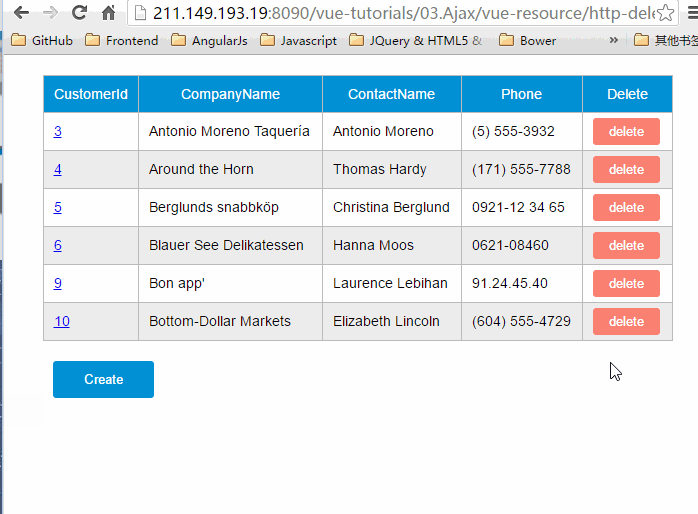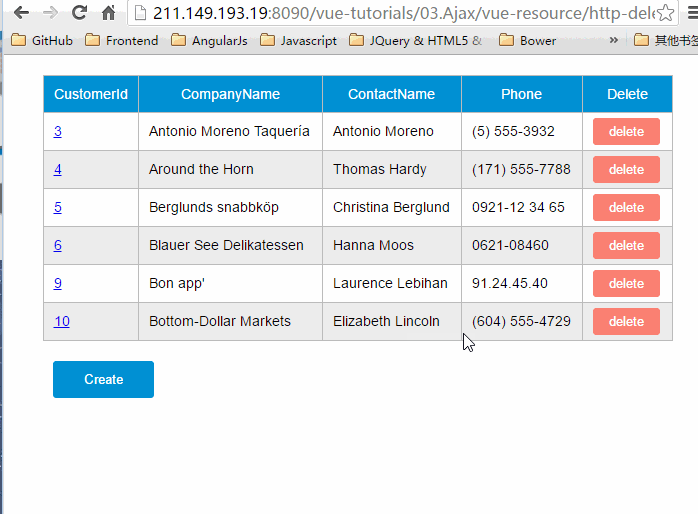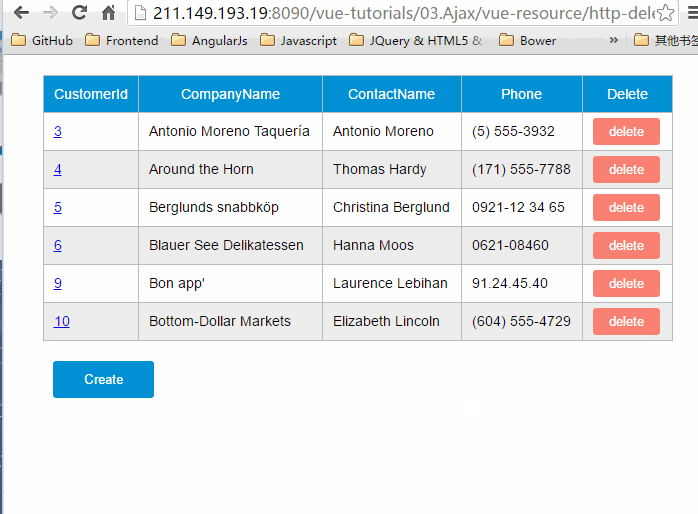
使用resource服务
vue-resource提供了另外一种方式访问HTTP——resource服务,resource服务包含以下几种默认的action:
get: {method: 'GET'},save: {method: 'POST'},query: {method: 'GET'},update: {method: 'PUT'},remove: {method: 'DELETE'},delete: {method:'DELETE'}resource对象也有两种访问方式:
- 全局访问:Vue.resource
- 实例访问:this.$resource
resource可以结合URI Template一起使用,以下示例的apiUrl都设置为{/id}了:
apiUrl: 'http://211.149.193.19:8080/api/customers{/id}'
GET请求
使用get方法发送GET请求,下面这个请求没有指定{/id}。
getCustomers: function() { varresource = this.$resource(this.apiUrl) vm =this resource.get() .then((response) => { vm.$set('gridData', response.data) }) .catch(function(response) { console.log(response) })}POST请求
使用save方法发送POST请求,下面这个请求没有指定{/id}。
createCustomer: function() { varresource = this.$resource(this.apiUrl) vm =this resource.save(vm.apiUrl, vm.item) .then((response) => { vm.$set('item', {}) vm.getCustomers() }) this.show =false}PUT请求
使用update方法发送PUT请求,下面这个请求指定了{/id}。
updateCustomer: function() { varresource = this.$resource(this.apiUrl) vm =this resource.update({ id: vm.item.customerId}, vm.item) .then((response) => { vm.getCustomers() })}{/id}相当于一个占位符,当传入实际的参数时该占位符会被替换。
例如,{ id: vm.item.customerId}中的vm.item.customerId为12,那么发送的请求URL为:
http://211.149.193.19:8080/api/customers/12
DELETE请求
使用remove或delete方法发送DELETE请求,下面这个请求指定了{/id}。
deleteCustomer: function(customer){ varresource = this.$resource(this.apiUrl) vm =this resource.remove({ id: customer.customerId}) .then((response) => { vm.getCustomers() })}使用inteceptor
拦截器可以在请求发送前和发送请求后做一些处理。
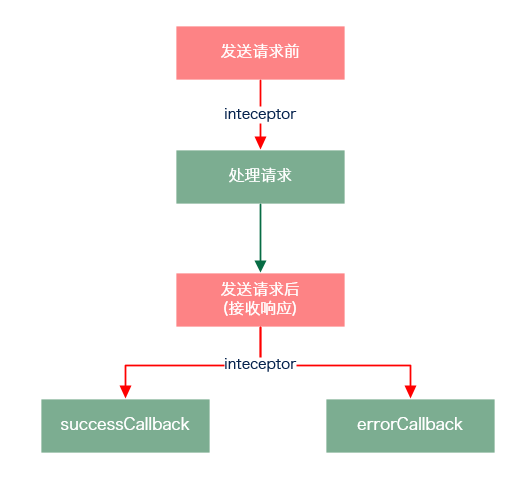
基本用法
Vue.http.interceptors.push((request, next) => { // ... // 请求发送前的处理逻辑 // ... next((response) => { // ... // 请求发送后的处理逻辑 // ... // 根据请求的状态,response参数会返回给successCallback或errorCallback returnresponse })})在response返回给successCallback或errorCallback之前,你可以修改response中的内容,或做一些处理。
例如,响应的状态码如果是404,你可以显示友好的404界面。
如果不想使用Lambda函数写法,可以用平民写法:
Vue.http.interceptors.push(function(request, next) { // ... // 请求发送前的处理逻辑 // ... next(function(response) { // ... // 请求发送后的处理逻辑 // ... // 根据请求的状态,response参数会返回给successCallback或errorCallback returnresponse })})示例1
之前的CURD示例有一处用户体验不太好,用户在使用一些功能的时候如果网络较慢,画面又没有给出反馈,用户是不知道他的操作是成功还是失败的,他也不知道是否该继续等待。
通过inteceptor,我们可以为所有的请求处理加一个loading:请求发送前显示loading,接收响应后隐藏loading。
具体步骤如下:
1.添加一个loading组件
<templateid="loading-template"> <divclass="loading-overlay"> <divclass="sk-three-bounce"> <divclass="sk-child sk-bounce1"></div> <divclass="sk-child sk-bounce2"></div> <divclass="sk-child sk-bounce3"></div> </div> </div></template>2.将loading组件作为另外一个Vue实例的子组件
var help = new Vue({ el:'#help', data: { showLoading:false }, components: { 'loading': { template:'#loading-template', } }})3.将该Vue实例挂载到某个HTML元素
<divid="help"> <loadingv-show="showLoading"></loading></div>4.添加inteceptor
Vue.http.interceptors.push((request, next) => { loading.show =true next((response) => { loading.show =false returnresponse });});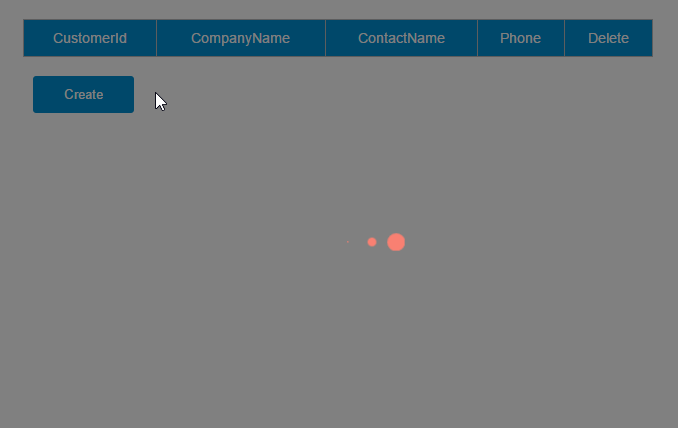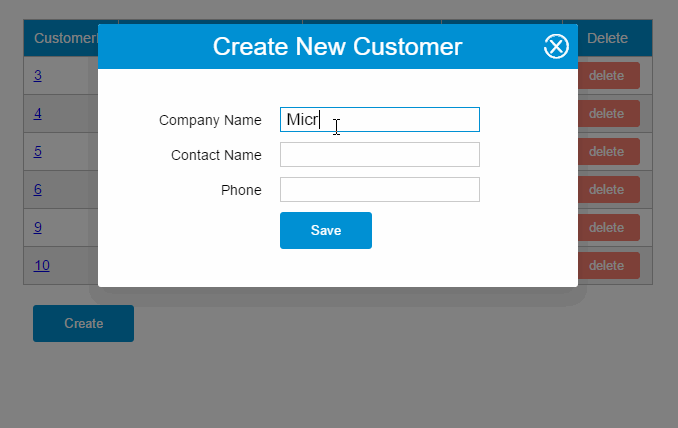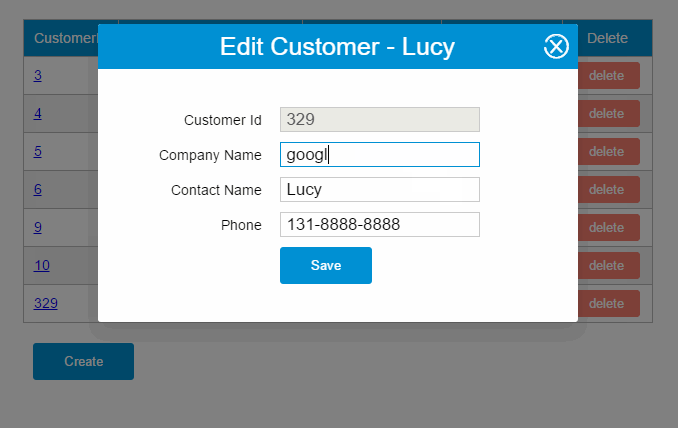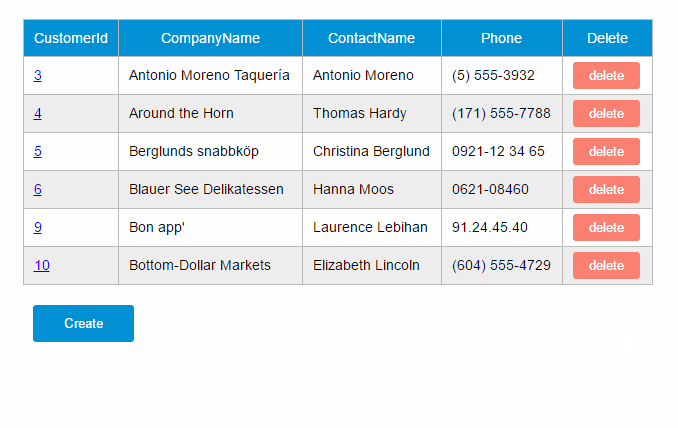
示例2
当用户在画面上停留时间太久时,画面数据可能已经不是最新的了,这时如果用户删除或修改某一条数据,如果这条数据已经被其他用户删除了,服务器会反馈一个404的错误,但由于我们的put和delete请求没有处理errorCallback,所以用户是不知道他的操作是成功还是失败了。
你问我为什么不在每个请求里面处理errorCallback,这是因为我比较懒。这个问题,同样也可以通过inteceptor解决。
1. 继续沿用上面的loading组件,在#help元素下加一个对话框
<divid="help"> <loadingv-show="showLoading"></loading> <modal-dialog:show="showDialog"> <headerclass="dialog-header"slot="header"> <h1class="dialog-title">Server Error</h1> </header> <divclass="dialog-body"slot="body"> <pclass="error">Oops,server has got some errors, error code: {{errorCode}}.</p> </div> </modal-dialog></div>2.给help实例的data选项添加两个属性
var help = new Vue({ el:'#help', data: { showLoading:false, showDialog:false, errorCode:'' }, components: { 'loading': { template:'#loading-template', } } })3.修改inteceptor
Vue.http.interceptors.push((request, next) => { help.showLoading =true next((response) => { if(!response.ok){ help.errorCode = response.status help.showDialog =true } help.showLoading =false returnresponse });});
总结
vue-resource是一个非常轻量的用于处理HTTP请求的插件,它提供了两种方式来处理HTTP请求:
- 使用Vue.http或this.$http
- 使用Vue.resource或this.$resource
这两种方式本质上没有什么区别,阅读vue-resource的源码,你可以发现第2种方式是基于第1种方式实现的。
inteceptor可以在请求前和请求后附加一些行为,这意味着除了请求处理的过程,请求的其他环节都可以由我们来控制。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/keepfool/p/5657065.html
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略【5】
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- vue-resource全攻略
- Vue.js vue-resoucre的使用与解析 全攻略
- Vue1.0接口请求之vue-resource全攻略
- vue axios全攻略
- vue axios全攻略
- vue axios全攻略
- Vue生态——vue-resource
- vue-resource.js
- 【Vue】—Vue.js入门教程
- Vue.js系列之vue-resource
- Ascii
- MFC单文档图像处理代码--句柄图像实现
- 题目1036:Old Bill
- VMware的三种网络连接方式区别
- springboot中关于JPA的坑
- Vue.js——vue-resource全攻略
- 聊一聊数据仓库中的元数据管理系统
- jedis连接redis
- Eclipse中如何自定义类、方法等的注释
- 人形时钟,和仓鼠flash
- android studio 插件 gradle view 查看gradle依赖树
- 学密码学一定得学程序
- JDK中的Timer和TimerTask详解
- Android的Application的oncreate()多次被调用原因并解决方案


