自己动手写java 字节流输入输出流
来源:互联网 发布:香港旅游 知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/07 06:38
自己动手写java 字节流输入输出流
数据流是一串连续不断的数据的集合,就象水管里的水流,在水管的一端一点一点地供水,而在水管的另一端看到的是一股连续不断的水流。
“流是磁盘或其它外围设备中存储的数据的源点或终点。”
1) 数据流:
一组有序,有起点和终点的字节的数据序列。包括输入流和输出流。
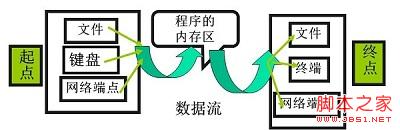
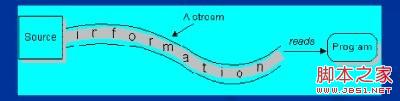
2) 输入流(Input Stream):
程序从输入流读取数据源。数据源包括外界(键盘、文件、网络…),即是将数据源读入到程序的通信通道
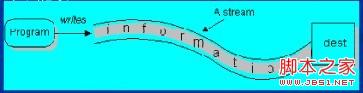
3) 输出流:
程序向输出流写入数据。将程序中的数据输出到外界(显示器、打印机、文件、网络…)的通信通道。
采用数据流的目的就是使得输出输入独立于设备。
1.输入流代码
import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;//字节数组输入流public class MyByteInputStream extends InputStream { private byte[] buf;// 存放数据流的数组 private int bufLength;// 记录buf数组长度 private int pos;// 已经存放数据的下标位置 private int readPos = 0;// 记录当前数据流读取到的位置 public MyByteInputStream(int i) { buf = new byte[32]; bufLength = 32; pos = 0; } // 构建输入流(直接存入待输入的流数据) public MyByteInputStream(byte[] b) { if (b != null && b.length > 0) { int copyLength = b.length; buf = new byte[copyLength]; System.arraycopy(b, 0, buf, 0, copyLength);// 复制数组内容 bufLength = copyLength; pos = copyLength; } else { buf = new byte[32]; bufLength = 32; pos = 0; } } /* * 若有数据则返回对应buf[readPos],否则返回-1 */ public int read() throws IOException { if (pos > 0 && readPos <= (pos - 1)) { readPos = readPos + 1; return buf[readPos - 1]; } return -1; }}
2.输出流代码
import java.io.OutputStream;public class MyByteOutStream extends OutputStream { private byte[] buf;// 输出流 private int length;// 存放输出流的长度 private int pos;// 写到的位置 public MyByteOutStream() { buf = new byte[32]; length = 32; pos = 0; } public MyByteOutStream(int size) { if (size > 0) { buf = new byte[size]; length = size; pos = 0; } else { buf = new byte[32]; length = 32; pos = 0; } } /** * 将字符b写入到字节流中,若流空间不够则扩展 * * @param b */ public void write(int b) { if (pos < length) { buf[pos] = (byte) b; pos = pos + 1; } else { // TODO:扩展字节流buf[]大小 } } /** * 将输出流copy * * @return */ public byte[] toByteArray() { if (pos > 0) { byte[] b = new byte[pos]; System.arraycopy(buf, 0, b, 0, pos); return b; } return null; }}
3.测试类
import java.io.IOException;public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String inputStr = "Test input stream!"; String outStr = "Test out strem!"; // 自定义输入流 MyByteInputStream myByteInputStream = new MyByteInputStream(inputStr.getBytes()); try { for (int i; (i = myByteInputStream.read()) != -1;) { System.out.print(Character.toString((char) i)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(""); // 自定义输出流 MyByteOutStream myByteOutStream = new MyByteOutStream(100); byte[] b = outStr.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { myByteOutStream.write(b[i]); } byte[] outb = myByteOutStream.toByteArray(); for (int i = 0; i < outb.length; i++) { System.out.print(Character.toString((char) outb[i])); } System.out.println(""); }}
ps:欢迎各位吐槽指点~
阅读全文
0 0
- 自己动手写java 字节流输入输出流
- Java字节输入输出流
- java 字节输入输出流
- java IO(输入输出) 字节流
- java输入输出流,字节流,字符流
- Java输入输出流-----字节流(1)
- java输入输出流、字符字节流
- JAVA输入输出流--字节流篇
- java输入输出流、字符字节流
- Java输入输出之字节流拷贝文件
- JAVA IO字节输入输出流实例
- JAVA输入输出(IO)之字节流
- Java-文件输入输出(字节流)
- Java-输入输出基础(字节流)
- Java-对象输入输出(字节流)
- java中字节输入输出流操作详解
- Java流式输入输出-面向字节
- java IO(输入输出) 字节缓冲流
- mysql锁隔离机制
- RTP-RTCP协议分析
- UVA1252[Twenty Questions] 状态压缩动态规划模型
- [编程题] 序列交换
- 脑弄大开之——如何抛弃数字和运算符号只用计算机和函数进行运算
- 自己动手写java 字节流输入输出流
- 内部类
- 二listview多条目加载
- Android--(2)--详解线性布局(LinearLayout)
- Git常见命令总结
- The study of calling fuction in Python(20170907)
- nefu 84 五指山(扩展ou'ji'li)
- 应用服务器的调优
- 求解斐波那契数列的第n个数



