基于Spring Boot的天气预报服务
来源:互联网 发布:zbrush mac 中文版 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 07:20
本文,我们将基于 Spring Boot 技术来实现一个微服务天气预报服务接口——micro-weather-basic。micro-weather-basic 的作用是实现简单的天气预报功能,可以根据不同的城市,查询该城市的实时天气情况。
开发环境- Gradle 4.0
- Spring Boot 1.5.6
- Apache HttpClient 1.5.3
理论上,天气的数据是天气预报的实现基础。本应用与实际的天气数据无关,理论上,可以兼容多种数据来源。但为求简单,我们在网上找了一个免费、可用的天气数据接口。
- 天气数据来源为中华万年历。例如:
- 通过城市名字获得天气数据 :http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=深圳
- 通过城市id获得天气数据:http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?citykey=101280601
- 城市ID列表。每个城市都有一个唯一的ID作为标识。见 http://cj.weather.com.cn/support/Detail.aspx?id=51837fba1b35fe0f8411b6df 或者 http://mobile.weather.com.cn/js/citylist.xml。
调用天气服务接口示例,我们以“深圳”城市为例,可用看到如下天气数据返回。
{ "data": { "yesterday": { "date": "1日星期五", "high": "高温 33℃", "fx": "无持续风向", "low": "低温 26℃", "fl": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>", "type": "多云" }, "city": "深圳", "aqi": "72", "forecast": [ { "date": "2日星期六", "high": "高温 32℃", "fengli": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>", "low": "低温 26℃", "fengxiang": "无持续风向", "type": "阵雨" }, { "date": "3日星期天", "high": "高温 29℃", "fengli": "<![CDATA[5-6级]]>", "low": "低温 26℃", "fengxiang": "无持续风向", "type": "大雨" }, { "date": "4日星期一", "high": "高温 29℃", "fengli": "<![CDATA[3-4级]]>", "low": "低温 26℃", "fengxiang": "西南风", "type": "暴雨" }, { "date": "5日星期二", "high": "高温 31℃", "fengli": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>", "low": "低温 27℃", "fengxiang": "无持续风向", "type": "阵雨" }, { "date": "6日星期三", "high": "高温 32℃", "fengli": "<![CDATA[<3级]]>", "low": "低温 27℃", "fengxiang": "无持续风向", "type": "阵雨" } ], "ganmao": "风较大,阴冷潮湿,较易发生感冒,体质较弱的朋友请注意适当防护。", "wendu": "29" }, "status": 1000, "desc": "OK"}我们通过观察数据,来了解每个返回字段的含义。
- "city": 城市名称
- "aqi": 空气指数,
- "wendu": 实时温度
- "date": 日期,包含未来5天
- "high":最高温度
- "low": 最低温度
- "fengli": 风力
- "fengxiang": 风向
- "type": 天气类型
以上数据,是我们需要的天气数据的核心数据,但是,同时也要关注下面两个字段:
- "status": 接口调用的返回状态,返回值“1000”,意味着数据是接口正常
- "desc": 接口状态的描述,“OK”代表接口正常
重点关注返回值不是“1000”的情况,说明,这个接口调用异常了。
初始化一个 Spring Boot 项目初始化一个 Spring Boot 项目 micro-weather-basic,该项目可以直接在我们之前章节课程中的 basic-gradle 项目基础进行修改。同时,为了优化项目的构建速度,我们对Maven中央仓库地址和 Gradle Wrapper 地址做了调整。其中细节暂且不表,读者可以自行参阅源码,或者学习笔者所著的《Spring Boot 教程》(https://github.com/waylau/spring-boot-tutorial)。其原理,我也整理到我的博客中了:
- https://waylau.com/change-gradle-wrapper-distribution-url-to-local-file/
- https://waylau.com/use-maven-mirrors/
添加 Apache HttpClient 的依赖,来作为我们Web请求的客户端。
// 依赖关系dependencies { //... // 添加 Apache HttpClient 依赖 compile('org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.3') //...}创建com.waylau.spring.cloud.vo包,用于相关值对象。创建天气信息类 Weather
public class Weather implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String city; private String aqi; private String wendu; private String ganmao; private Yesterday yesterday; private List<Forecast> forecast; public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getAqi() { return aqi; } public void setAqi(String aqi) { this.aqi = aqi; } public String getWendu() { return wendu; } public void setWendu(String wendu) { this.wendu = wendu; } public String getGanmao() { return ganmao; } public void setGanmao(String ganmao) { this.ganmao = ganmao; } public Yesterday getYesterday() { return yesterday; } public void setYesterday(Yesterday yesterday) { this.yesterday = yesterday; } public List<Forecast> getForecast() { return forecast; } public void setForecast(List<Forecast> forecast) { this.forecast = forecast; }}昨日天气信息:
public class Yesterday implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String date; private String high; private String fx; private String low; private String fl; private String type; public Yesterday() { } public String getDate() { return date; } public void setDate(String date) { this.date = date; } public String getHigh() { return high; } public void setHigh(String high) { this.high = high; } public String getFx() { return fx; } public void setFx(String fx) { this.fx = fx; } public String getLow() { return low; } public void setLow(String low) { this.low = low; } public String getFl() { return fl; } public void setFl(String fl) { this.fl = fl; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; }}未来天气信息:
public class Forecast implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String date; private String high; private String fengxiang; private String low; private String fengli; private String type; public String getDate() { return date; } public void setDate(String date) { this.date = date; } public String getHigh() { return high; } public void setHigh(String high) { this.high = high; } public String getFengxiang() { return fengxiang; } public void setFengxiang(String fengxiang) { this.fengxiang = fengxiang; } public String getLow() { return low; } public void setLow(String low) { this.low = low; } public String getFengli() { return fengli; } public void setFengli(String fengli) { this.fengli = fengli; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public Forecast() { }}WeatherResponse 作为整个消息的返回对象
public class WeatherResponse implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Weather data; // 消息数据 private String status; // 消息状态 private String desc; // 消息描述 public Weather getData() { return data; } public void setData(Weather data) { this.data = data; } public String getStatus() { return status; } public void setStatus(String status) { this.status = status; } public String getDesc() { return desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; }}定义了获取服务的两个接口方法
public interface WeatherDataService { /** * 根据城市ID查询天气数据 * @param cityId * @return */ WeatherResponse getDataByCityId(String cityId); /** * 根据城市名称查询天气数据 * @param cityId * @return */ WeatherResponse getDataByCityName(String cityName);}其实现为:
@Servicepublic class WeatherDataServiceImpl implements WeatherDataService { @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; private final String WEATHER_API = "http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini"; @Override public WeatherResponse getDataByCityId(String cityId) { String uri = WEATHER_API + "?citykey=" + cityId; return this.doGetWeatherData(uri); } @Override public WeatherResponse getDataByCityName(String cityName) { String uri = WEATHER_API + "?city=" + cityName; return this.doGetWeatherData(uri); } private WeatherResponse doGetWeatherData(String uri) { ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(uri, String.class); String strBody = null; if (response.getStatusCodeValue() == 200) { strBody = response.getBody(); } ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); WeatherResponse weather = null; try { weather = mapper.readValue(strBody, WeatherResponse.class); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return weather; }}返回的天气信息采用了 Jackson 来进行反序列化成为 WeatherResponse 对象。
控制器层控制器层暴露了RESTful API 地址。
@RestController@RequestMapping("/weather") public class WeatherController { @Autowired private WeatherDataService weatherDataService; @GetMapping("/cityId/{cityId}") public WeatherResponse getReportByCityId(@PathVariable("cityId") String cityId) { return weatherDataService.getDataByCityId(cityId); } @GetMapping("/cityName/{cityName}") public WeatherResponse getReportByCityName(@PathVariable("cityName") String cityName) { return weatherDataService.getDataByCityName(cityName); }}@RestController自动会将返回的数据,序列化成 JSON数据格式。
RestConfiguration 是 RestTemplate 的配置类。
@Configurationpublic class RestConfiguration { @Autowired private RestTemplateBuilder builder; @Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate() { return builder.build(); }}解决乱码:访问API//实例化这个bean这样搞@BeanpublicRestTemplate getRestTemplate(){StringHttpMessageConverter m =newStringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));returnnewRestTemplateBuilder().additionalMessageConverters(m).build();}
运行项目之后,访问项目的 API :
- http://localhost:8080/weather/cityId/101280601
- http://localhost:8080/weather/cityName/惠州
能看到如下的数据返回
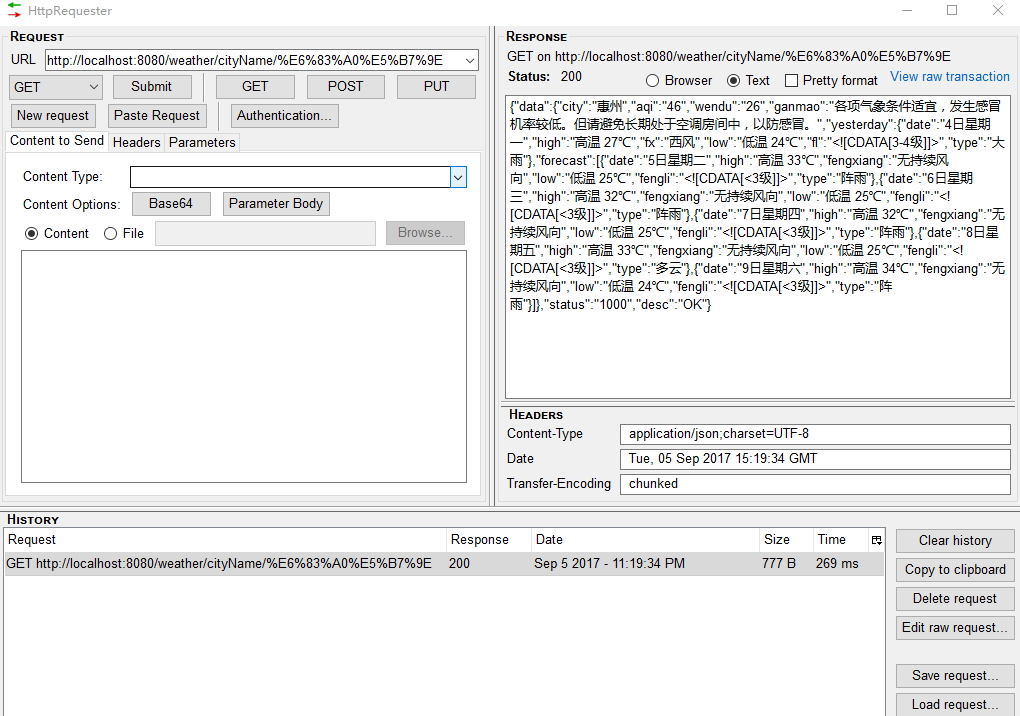
本章节的源码,见 https://github.com/waylau/spring-cloud-tutorial/ samples目录下的micro-weather-basic。
- https://waylau.com/spring-boot-weather-report/
作者: 老卫
链接:http://www.imooc.com/article/20253
来源:慕课网
本文原创发布于慕课网 ,转载请注明出处,谢谢合作!
- 基于Spring Boot的天气预报服务
- 基于Spring Boot的天气预报服务
- 用Kotlin写一个基于Spring Boot的RESTful服务
- 用Kotlin写一个基于Spring Boot的RESTful服务
- mock测试spring boot的CRUD服务
- Springboot-启动 Spring Boot服务的方式
- 基于注解的spring boot整合Druid
- 基于Spring Boot和Kotlin的联合开发
- 基于Spring Boot的各种功能实现
- spring boot 服务管理
- 用于Blog的天气预报服务
- 基于Spring boot的Spring data jpa连接MySQL数据库
- spring boot学习三:基于jsp的spring mvc示例
- Android 基于百度的天气预报
- 基于Spring技术应用的远程服务
- 创建基于Spring Clould的服务提供者
- Spring boot 集成邮件服务
- spring boot发送短信服务
- 《逻辑思维》小笔记
- 用Python 根据文件名查找数据文件
- HDU 3917 Road constructions(最大权闭合图)
- 我绝不相信一个马上就要生孩子的产妇会跳楼
- 业务侧读取配置文件信息
- 基于Spring Boot的天气预报服务
- Kendo UI Grid
- 关于一个应用进程打开另外一个应用进程的TASK和PROCESS 说明
- android监听软键盘隐藏
- python学习 原始字符串操作符 print
- MFC 双缓冲多重绘图去除闪烁的万能函数模板
- angularjs ng-submit
- oracle数据库表和表数据以及事物,视图
- 软考信息安全工程师备考指南


