Master基于ZooKeeper的High Availability源码实现
来源:互联网 发布:杭州java培训班包住 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/28 06:24
如果Spark的部署方式选择Standalone,一个采用Master/Slaves的典型架构,那么Master是有SPOF(单点故障,Single Point of Failure)。Spark可以选用ZooKeeper来实现HA。
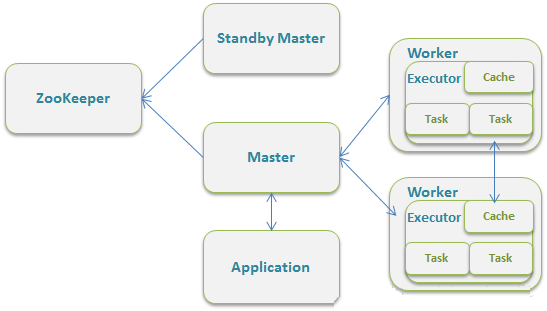
ZooKeeper提供了一个Leader Election机制,利用这个机制可以保证虽然集群存在多个Master但是只有一个是Active的,其他的都是Standby,当Active的Master出现故障时,另外的一个Standby Master会被选举出来。由于集群的信息,包括Worker, Driver和Application的信息都已经持久化到文件系统,因此在切换的过程中只会影响新Job的提交,对于正在进行的Job没有任何的影响。加入ZooKeeper的集群整体架构如下图所示。
1. Master的重启策略
Master在启动时,会根据启动参数来决定不同的Master故障重启策略:
1.ZOOKEEPER实现HA
2.FILESYSTEM:实现Master无数据丢失重启,集群的运行时数据会保存到本地/网络文件系统上
3.丢弃所有原来的数据重启
Master::preStart()可以看出这三种不同逻辑的实现。
override def preStart() { logInfo("Starting Spark master at " + masterUrl) ... //persistenceEngine是持久化Worker,Driver和Application信息的,这样在Master重新启动时不会影响 //已经提交Job的运行 persistenceEngine = RECOVERY_MODE match { case "ZOOKEEPER" => logInfo("Persisting recovery state to ZooKeeper") new ZooKeeperPersistenceEngine(SerializationExtension(context.system), conf) case "FILESYSTEM" => logInfo("Persisting recovery state to directory: " + RECOVERY_DIR) new FileSystemPersistenceEngine(RECOVERY_DIR, SerializationExtension(context.system)) case _ => new BlackHolePersistenceEngine() } //leaderElectionAgent负责Leader的选取。 leaderElectionAgent = RECOVERY_MODE match { case "ZOOKEEPER" => context.actorOf(Props(classOf[ZooKeeperLeaderElectionAgent], self, masterUrl, conf)) case _ => // 仅仅有一个Master的集群,那么当前的Master就是Active的 context.actorOf(Props(classOf[MonarchyLeaderAgent], self)) } } RECOVERY_MODE是一个字符串,可以从spark-env.sh中去设置。
val RECOVERY_MODE = conf.get("spark.deploy.recoveryMode", "NONE") 如果不设置spark.deploy.recoveryMode的话,那么集群的所有运行数据在Master重启是都会丢失,这个结论是从BlackHolePersistenceEngine的实现得出的。
private[spark] class BlackHolePersistenceEngine extends PersistenceEngine { override def addApplication(app: ApplicationInfo) {} override def removeApplication(app: ApplicationInfo) {} override def addWorker(worker: WorkerInfo) {} override def removeWorker(worker: WorkerInfo) {} override def addDriver(driver: DriverInfo) {} override def removeDriver(driver: DriverInfo) {} override def readPersistedData() = (Nil, Nil, Nil) } 它把所有的接口实现为空。PersistenceEngine是一个trait。作为对比,可以看一下ZooKeeper的实现。
class ZooKeeperPersistenceEngine(serialization: Serialization, conf: SparkConf) extends PersistenceEngine with Logging { val WORKING_DIR = conf.get("spark.deploy.zookeeper.dir", "/spark") + "/master_status" val zk: CuratorFramework = SparkCuratorUtil.newClient(conf) SparkCuratorUtil.mkdir(zk, WORKING_DIR) // 将app的信息序列化到文件WORKING_DIR/app_{app.id}中 override def addApplication(app: ApplicationInfo) { serializeIntoFile(WORKING_DIR + "/app_" + app.id, app) } override def removeApplication(app: ApplicationInfo) { zk.delete().forPath(WORKING_DIR + "/app_" + app.id) } Spark使用的并不是ZooKeeper的API,而是使用的org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFramework 和 org.apache.curator.framework.recipes.leader.{LeaderLatchListener, LeaderLatch} 。Curator在ZooKeeper上做了一层很友好的封装。
2. 集群启动参数的配置
简单总结一下参数的设置,通过上述代码的分析,我们知道为了使用ZooKeeper至少应该设置一下参数(实际上,仅仅需要设置这些参数。通过设置spark-env.sh:
spark.deploy.recoveryMode=ZOOKEEPER spark.deploy.zookeeper.url=zk_server_1:2181,zk_server_2:2181 spark.deploy.zookeeper.dir=/dir // OR 通过一下方式设置 export SPARK_DAEMON_JAVA_OPTS="-Dspark.deploy.recoveryMode=ZOOKEEPER " export SPARK_DAEMON_JAVA_OPTS="${SPARK_DAEMON_JAVA_OPTS} -Dspark.deploy.zookeeper.url=zk_server1:2181,zk_server_2:2181"各个参数的意义:

3. CuratorFramework简介
CuratorFramework极大的简化了ZooKeeper的使用,它提供了high-level的API,并且基于ZooKeeper添加了很多特性,包括
1.自动连接管理:连接到ZooKeeper的Client有可能会连接中断,Curator处理了这种情况,对于Client来说自动重连是透明的。
2.简洁的API:简化了原生态的ZooKeeper的方法,事件等;提供了一个简单易用的接口。
3.Recipe的实现(更多介绍请点击Recipes):
1)Leader的选择
2)共享锁
3)缓存和监控
4)分布式的队列
5)分布式的优先队列
CuratorFrameworks通过CuratorFrameworkFactory来创建线程安全的ZooKeeper的实例。
CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient()提供了一个简单的方式来创建ZooKeeper的实例,可以传入不同的参数来对实例进行完全的控制。获取实例后,必须通过start()来启动这个实例,在结束时,需要调用close()。
/** * Create a new client * * * @param connectString list of servers to connect to * @param sessionTimeoutMs session timeout * @param connectionTimeoutMs connection timeout * @param retryPolicy retry policy to use * @return client */ public static CuratorFramework newClient(String connectString, int sessionTimeoutMs, int connectionTimeoutMs, RetryPolicy retryPolicy) { return builder(). connectString(connectString). sessionTimeoutMs(sessionTimeoutMs). connectionTimeoutMs(connectionTimeoutMs). retryPolicy(retryPolicy). build(); } 需要关注的还有两个Recipe:org.apache.curator.framework.recipes.leader.{LeaderLatchListener, LeaderLatch}。
首先看一下LeaderlatchListener,它在LeaderLatch状态变化的时候被通知:
1.在该节点被选为Leader的时候,接口isLeader()会被调用
2.在节点被剥夺Leader的时候,接口notLeader()会被调用
由于通知是异步的,因此有可能在接口被调用的时候,这个状态是准确的,需要确认一下LeaderLatch的hasLeadership()是否的确是true/false。这一点在接下来Spark的实现中可以得到体现。
/** * LeaderLatchListener can be used to be notified asynchronously about when the state of the LeaderLatch has changed. * * Note that just because you are in the middle of one of these method calls, it does not necessarily mean that * hasLeadership() is the corresponding true/false value. It is possible for the state to change behind the scenes * before these methods get called. The contract is that if that happens, you should see another call to the other * method pretty quickly. */ public interface LeaderLatchListener { /** * This is called when the LeaderLatch's state goes from hasLeadership = false to hasLeadership = true. * * Note that it is possible that by the time this method call happens, hasLeadership has fallen back to false. If * this occurs, you can expect {@link #notLeader()} to also be called. */ public void isLeader(); /** * This is called when the LeaderLatch's state goes from hasLeadership = true to hasLeadership = false. * * Note that it is possible that by the time this method call happens, hasLeadership has become true. If * this occurs, you can expect {@link #isLeader()} to also be called. */ public void notLeader(); } LeaderLatch负责在众多连接到ZooKeeper Cluster的竞争者中选择一个Leader。Leader的选择机制可以看ZooKeeper的具体实现,LeaderLatch这是完成了很好的封装。我们只需要要知道在初始化它的实例后,需要通过
public class LeaderLatch implements Closeable { private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); private final CuratorFramework client; private final String latchPath; private final String id; private final AtomicReference<State> state = new AtomicReference<State>(State.LATENT); private final AtomicBoolean hasLeadership = new AtomicBoolean(false); private final AtomicReference<String> ourPath = new AtomicReference<String>(); private final ListenerContainer<LeaderLatchListener> listeners = new ListenerContainer<LeaderLatchListener>(); private final CloseMode closeMode; private final AtomicReference<Future<?>> startTask = new AtomicReference<Future<?>>(); . . . /** * Attaches a listener to this LeaderLatch * <p/> * Attaching the same listener multiple times is a noop from the second time on. * <p/> * All methods for the listener are run using the provided Executor. It is common to pass in a single-threaded * executor so that you can be certain that listener methods are called in sequence, but if you are fine with * them being called out of order you are welcome to use multiple threads. * * @param listener the listener to attach */ public void addListener(LeaderLatchListener listener) { listeners.addListener(listener); } 通过addListener可以将我们实现的Listener添加到LeaderLatch。在Listener里,我们在两个接口里实现了被选为Leader或者被剥夺Leader角色时的逻辑即可。
4. ZooKeeperLeaderElectionAgent的实现
实际上因为有Curator的存在,Spark实现Master的HA就变得非常简单了,ZooKeeperLeaderElectionAgent实现了接口LeaderLatchListener,在isLeader()确认所属的Master被选为Leader后,向Master发送消息ElectedLeader,Master会将自己的状态改为ALIVE。当noLeader()被调用时,它会向Master发送消息RevokedLeadership时,Master会关闭。
private[spark] class ZooKeeperLeaderElectionAgent(val masterActor: ActorRef, masterUrl: String, conf: SparkConf) extends LeaderElectionAgent with LeaderLatchListener with Logging { val WORKING_DIR = conf.get("spark.deploy.zookeeper.dir", "/spark") + "/leader_election" // zk是通过CuratorFrameworkFactory创建的ZooKeeper实例 private var zk: CuratorFramework = _ // leaderLatch:Curator负责选出Leader。 private var leaderLatch: LeaderLatch = _ private var status = LeadershipStatus.NOT_LEADER override def preStart() { logInfo("Starting ZooKeeper LeaderElection agent") zk = SparkCuratorUtil.newClient(conf) leaderLatch = new LeaderLatch(zk, WORKING_DIR) leaderLatch.addListener(this) leaderLatch.start() } 在prestart中,启动了leaderLatch来处理选举ZK中的Leader。就如在上节分析的,主要的逻辑在isLeader和noLeader中。
override def isLeader() { synchronized { // could have lost leadership by now. //现在leadership可能已经被剥夺了。。详情参见Curator的实现。 if (!leaderLatch.hasLeadership) { return } logInfo("We have gained leadership") updateLeadershipStatus(true) } } override def notLeader() { synchronized { // 现在可能赋予leadership了。详情参见Curator的实现。 if (leaderLatch.hasLeadership) { return } logInfo("We have lost leadership") updateLeadershipStatus(false) } } updateLeadershipStatus的逻辑很简单,就是向Master发送消息。
def updateLeadershipStatus(isLeader: Boolean) { if (isLeader && status == LeadershipStatus.NOT_LEADER) { status = LeadershipStatus.LEADER masterActor ! ElectedLeader } else if (!isLeader && status == LeadershipStatus.LEADER) { status = LeadershipStatus.NOT_LEADER masterActor ! RevokedLeadership } } 5. 设计理念
为了解决Standalone模式下的Master的SPOF,Spark采用了ZooKeeper提供的选举功能。Spark并没有采用ZooKeeper原生的Java API,而是采用了Curator,一个对ZooKeeper进行了封装的框架。采用了Curator后,Spark不用管理与ZooKeeper的连接,这些对于Spark来说都是透明的。Spark仅仅使用了100行代码,就实现了Master的HA。当然了,Spark是站在的巨人的肩膀上。谁又会去重复发明轮子呢?
- Master基于ZooKeeper的High Availability源码实现
- Spark技术内幕:Master基于ZooKeeper的High Availability(HA)源码实现
- Spark技术内幕:Master基于ZooKeeper的High Availability(HA)源码实现
- Spark技术内幕:Master基于ZooKeeper的High Availability(HA)源码实现
- Spark Master High Availability(HA)高可用配置的2种实现
- Spark:Master High Availability(HA)高可用配置的2种实现
- Hadoop2的HA安装(high availability):JournalNode+ zookeeper
- <转>Hadoop2的HA安装(high availability):JournalNode+ zookeeper
- Spark技术内幕:Master基于ZooKeeper的HighAvailability(HA)源码实现
- Kubernetes Master High Availability 高级实践
- CloudStack High Availability源码分析
- Kafka的High Availability机制
- Mesos单点Master集群部署和High Availability集群部署
- MySQL High Availability总结(二) 配置Master
- VMware中High Availability (HA),的含义
- 用zookeeper实现简单的master选举
- MySQL High Availability总结(一)源码安装MariaDB
- Zookeeper 实现 master 选举
- 详谈Android apk打包:关于APK数字签名详解介绍
- iOS 在XCode中upload 成功,但是在itunes connect 一直看不到
- 【云计算基础技术提高班之一】体系化认识RPC
- tensorflow 中 variable_scope 与name_scope函数解析
- 浏览器的内核和Javascript引擎
- Master基于ZooKeeper的High Availability源码实现
- leveldb-expand接口设计V2
- 找幸运数
- 融云客服-断点报connect mLibHandler is null, connect waiting for bind service
- c++对象的定义和构造函数
- Java的反射机制的作用
- CodeForces 810C
- Python小程序分享02——简单定时器
- TensorFlow(四)分类


