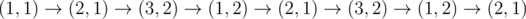Educational Codeforces Round 29
来源:互联网 发布:安信证券客户经理 知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/15 16:23
题意:
两个机器人猜拳,1,2,3分别代表3种可能。他们猜k次拳,第一次的情况已经告诉你了,剩下的局,每局两个人出什么都由上一局确定了,且唯一。让你求k次后,两个人的胜利的局数。
POINT:
总共就9种情况,根据规则找出循环节,再模拟即可。注意LL。
#include <iostream>#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <math.h>#include<algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longstruct node{ LL flag; LL cnt; LL asc; LL bsc;}mp[4][4];LL aa[4][4];LL bb[4][4];void doit(LL n,LL &ansa,LL &ansb,LL a,LL b){ while(n){ if((a==2&&b==1)||(a==3&&b==2)||(a==1&&b==3)){ ansa++; } else if((b==2&&a==1)||(b==3&&a==2)||(b==1&&a==3)){ ansb++; } LL a1=aa[a][b]; b=bb[a][b]; a=a1; n--; }}int main(){ LL n,a,b; memset(mp,0,sizeof mp); scanf("%lld %lld %lld",&n,&a,&b); LL sa=a,sb=b; for(LL i=1;i<=3;i++){ for(LL j=1;j<=3;j++){ scanf("%lld",&aa[i][j]); } } for(LL i=1;i<=3;i++){ for(LL j=1;j<=3;j++){ scanf("%lld",&bb[i][j]); } } LL now=0; LL asc=0; LL bsc=0; while(mp[a][b].flag==0){ mp[a][b].flag=1; mp[a][b].cnt=++now; if((a==2&&b==1)||(a==3&&b==2)||(a==1&&b==3)){ asc++; } else if((b==2&&a==1)||(b==3&&a==2)||(b==1&&a==3)){ bsc++; } mp[a][b].asc=asc; mp[a][b].bsc=bsc; LL a1=aa[a][b]; b=bb[a][b]; a=a1; } if((a==2&&b==1)||(a==3&&b==2)||(a==1&&b==3)){ asc++; } else if((b==2&&a==1)||(b==3&&a==2)||(b==1&&a==3)){ bsc++; } LL xunqian=mp[a][b].cnt-1; LL xun=now-mp[a][b].cnt+1; LL geta=asc-mp[a][b].asc; LL getb=bsc-mp[a][b].bsc; LL ansa=0,ansb=0; if(n<=xunqian){ doit(n,ansa,ansb,sa,sb); } else{ doit(xunqian,ansa,ansb,sa,sb); n=n-xunqian; LL cnt=n/xun; ansa+=cnt*geta; ansb+=cnt*getb; n=n%xun; doit(n,ansa,ansb,a,b); } printf("%lld %lld\n",ansa,ansb);}阅读全文
0 0
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- Educational Codeforces Round 29 题解
- Educational Codeforces Round 1
- Educational Codeforces Round 2
- Educational Codeforces Round 2
- Educational Codeforces Round 2
- Educational Codeforces Round 3
- Codeforces Educational Round 3
- Codeforces Educational Round 5
- Codeforces Educational round 5
- Educational Codeforces Round 5
- Educational Codeforces Round 6
- Method级别的缺陷数据集
- java Rpc之java动态代理
- HTTP的GET和POST的区别
- 使用Myeclipse创建Maven项目
- Github 《Learn Github》
- Educational Codeforces Round 29
- PHP 页面编码声明方法详解(header或meta
- 为什么老外一个人能带宝宝,中国要一家子?
- C语言描述——简单插入排序
- leetcode 55. Jump Game(C语言,跳数,递归思想,两种解法)20
- 无人驾驶系列优秀博客传送门(持续更新)
- python实现汉诺塔(递归实现)
- github创建网页简历
- Linux命令:系统管理命令和系统安全命令