scipy-图像操作
来源:互联网 发布:win10网络共享密码设置 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/03 18:59
参考:
1、https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/ndimage.html#module-scipy.ndimage
2、http://scipy-lectures.github.com/advanced/image_processing/index.html
3、http://blog.csdn.net/zt_706/article/details/11476433
- 1打开和读写图像文件
- 将一个数组写入文件
- 从一个图像文件创建数组
- 打开一个raw文件相机 3-D图像
- 对于大数据使用npmemmap进行内存映射
- 批量处理图像文件
- 2呈现图像
- 使用matplotlib和imshow将图像呈现在matplotlib图像figure中
- 其它包有时使用图形工具箱来可视化GTKQt
- 3-D可视化Mayavi
- 3基本操作
- 图像是数组numpy array
- 统计信息
- 几何转换
- 4图像滤镜
- 模糊平滑
- 均匀滤镜
- 锐化
- 消噪
- 非局部滤波器
- 模糊平滑
- 5数学形态学
- 6特征提取
- 边缘检测
- canny滤镜
- 分割
这个教程中使用的工具:
- numpy:基本数组操作
- scipy:scipy.ndimage子模块致力于图像处理(n维图像)。参见http://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/tutorial/ndimage.html
from scipy import ndimage- 一些例子用到了使用np.array的特殊的工具箱:
- Scikit Image
- scikit-learn
图像中的常见问题有:
- 输入/输出:呈现图像
- 基本操作:裁剪、翻转、旋转、比例缩放……
- 图像滤镜:消噪,锐化
- 图像分割:不同对应对象的像素标记
更有力和完整的模块:
- OpenCV (Python绑定)
- CellProfiler
- ITK,Python绑定
- 更多……
1、打开和读写图像文件
将一个数组写入文件:
In [1]: from scipy import miscIn [2]: l = misc.lena()In [3]: misc.imsave('lena.png', l) # uses the Image module (PIL)In [4]: import pylab as plIn [5]: pl.imshow(l)Out[5]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x4118110>从一个图像文件创建数组:
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom scipy import miscimport pylab as plimg1=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L')img2=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='RGB')img3=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='RGBA')pl.imshow(img2,cmap='gray')pl.show()misc.imsave('lena.png',img2) # 保存# pl可以使用plt替换或
from scipy import ndimagendimage.imread('lena.png',mode='L') # 加载灰度图ndimage.imread('lena.png', mode='RGB') # 加载RGB图ndimage.imread('lena.png', mode='RGBA') # 加载RGBA图打开一个raw文件(相机, 3-D图像)
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport numpy as npimport pylab as plimg=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L')# print(img.dtype) # uint8img.tofile('lena.raw') # 创建一个raw文件lena_from_raw = np.fromfile('lena.raw',np.uint8) # 加载 lena.raw 文件print(lena_from_raw.shape)# lena_from_raw=np.reshape(lena_from_raw,[512,512])lena_from_raw.shape = (512, 512)pl.imshow(lena_from_raw,cmap='gray')pl.show()import osos.remove('lena.raw') # 删除文件对于大数据,使用np.memmap进行内存映射:
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport numpy as npimport pylab as plimg=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='RGB')# print(img.dtype) # uint8img.tofile('lena.raw') # 创建一个raw文件 保存成raw文件lena_memmap = np.memmap('lena.raw', dtype=np.uint8, shape=(512,512,3)) # 加载raw文件pl.imshow(lena_memmap,cmap='gray')pl.show()import osos.remove('lena.raw') # 删除文件批量处理图像文件:
In [22]: for i in range(10): ....: im = np.random.random_integers(0, 255, 10000).reshape((100, 100)) ....: misc.imsave('random_%02d.png' % i, im) ....: In [23]: from glob import globIn [24]: filelist = glob('random*.png')In [25]: filelist.sort()2、呈现图像
使用matplotlib和imshow将图像呈现在matplotlib图像(figure)中:
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport numpy as npimport pylab as plimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimg=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L')plt.imshow(img,cmap=plt.cm.gray)plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray', vmin=30, vmax=200) # 设置最大最小之增加对比# 更好地观察强度变化,使用interpolate=‘nearest’plt.imshow(img[200:220, 200:220], cmap=plt.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')plt.axis('off') # 移除axes和ticksplt.contour(img, [60, 211]) # 绘制等高线plt.show()# ---将plt换成pl-----------------------------------------------------------------pl.imshow(img,cmap=plt.cm.gray)pl.imshow(img, cmap='gray', vmin=30, vmax=200) # 设置最大最小之增加对比# 更好地观察强度变化,使用interpolate=‘nearest’pl.imshow(img[200:220, 200:220], cmap=pl.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')pl.axis('off') # 移除axes和tickspl.contour(img, [60, 211]) # 绘制等高线pl.show()其它包有时使用图形工具箱来可视化(GTK,Qt)
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport numpy as npimport skimage.io as im_ioimg=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L')im_io.use_plugin('gtk', 'imshow')im_io.imshow(img)im_io.show()3-D可视化:Mayavi
参见可用Mayavi进行3-D绘图和体积数据
- 图形平面工具
- 等值面
- ……
3、基本操作
图像是数组(numpy array)。
>>> lena = misc.lena()>>> lena[0, 40]166>>> # Slicing>>> lena[10:13, 20:23]array([[158, 156, 157],[157, 155, 155],[157, 157, 158]])>>> lena[100:120] = 255>>>>>> lx, ly = lena.shape>>> X, Y = np.ogrid[0:lx, 0:ly]>>> mask = (X - lx/2)**2 + (Y - ly/2)**2 > lx*ly/4>>> # Masks>>> lena[mask] = 0>>> # Fancy indexing>>> lena[range(400), range(400)] = 255统计信息
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport numpy as npimport pylab as plimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport cv2lena=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L') # 数据类型 numpy arraylena.mean() # 平均值lena.max() # 最大值lena.min() # 最小值# 图像直方图# 1、使用np.histogramhist, bins = np.histogram(lena.ravel(), bins=256, range=[0,256],normed=True)plt.plot(hist)plt.legend(loc='best')plt.show()# 2、使用plt.histplt.hist(lena.ravel(),256,[0,256]); plt.show()# 3、使用opencvhist_full = cv2.calcHist([lena],[0],None,[256],[0,256])plt.plot(hist_full)plt.xlim([0,256])plt.show()几何转换
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport numpy as npimport scipyimport pylab as plimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport cv2lena=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L') # 数据类型 numpy arraylx, ly = lena.shape# 裁剪crop_lena = lena[lx/4:-lx/4, ly/4:-ly/4]# 上下翻转flip_ud_lena = np.flipud(lena)# 左右翻转flip_lr_lena = np.fliplr(lena)# 任意角度旋转rotate_lena = ndimage.rotate(lena, 45)rotate_lena_noreshape = ndimage.rotate(lena, 45, reshape=False) # 不改变原图大小# 任意缩放zoomed_lena = ndimage.zoom(lena, 2) # 放大2倍zoomed_lena2 = ndimage.zoom(lena, 0.5) # 缩小1/2倍4、图像滤镜
局部滤镜
:用相邻像素值的函数替代当前像素的值。
相邻:方形(指定大小),圆形, 或者更多复杂的结构元素。
模糊/平滑
scipy.ndimage中的高斯滤镜:
>>> from scipy import misc>>> from scipy import ndimage>>> lena = misc.lena()>>> blurred_lena = ndimage.gaussian_filter(lena, sigma=3)>>> very_blurred = ndimage.gaussian_filter(lena, sigma=5)均匀滤镜
>>> local_mean = ndimage.uniform_filter(lena, size=11)锐化
锐化模糊图像:
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport pylab as plfrom scipy import ndimagelena=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L') # 数据类型 numpy array# 锐化模糊图像blurred_l = ndimage.gaussian_filter(lena, 3)# 通过增加拉普拉斯近似增加边缘权重filter_blurred_l = ndimage.gaussian_filter(blurred_l, 1)alpha = 30sharpened = blurred_l + alpha * (blurred_l - filter_blurred_l)pl.subplot(131),pl.imshow(blurred_l,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('blurred_l')pl.subplot(132),pl.imshow(filter_blurred_l,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('filter_blurred_l')pl.subplot(133),pl.imshow(sharpened,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('sharpened')pl.show()消噪
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport pylab as plfrom scipy import ndimageimport numpy as nplena=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L') # 数据类型 numpy array# 向lena增加噪声l = lena[230:310, 210:350]noisy = l + 0.4*l.std()*np.random.random(l.shape)# 高斯滤镜平滑掉噪声……还有边缘gauss_denoised = ndimage.gaussian_filter(noisy, 2)# 大多局部线性各向同性滤镜都模糊图像(ndimage.uniform_filter)unif_denoised=ndimage.uniform_filter(noisy,2)# 中值滤镜更好地保留边缘med_denoised = ndimage.median_filter(noisy, 3)pl.subplot(141),pl.imshow(noisy,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('noisy')pl.subplot(142),pl.imshow(gauss_denoised,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('gauss_denoised')pl.subplot(143),pl.imshow(unif_denoised,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('unif_denoised')pl.subplot(144),pl.imshow(med_denoised,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('med_denoised')pl.show()其它排序滤波器:
ndimage.maximum_filter,ndimage.percentile_filter
其它局部非线性滤波器:
维纳滤波器(scipy.signal.wiener)等
非局部滤波器
总变差(TV)消噪。找到新的图像让图像的总变差(正态L1梯度的积分)变得最小,当接近测量图像时
#!/usr/bin/env python3# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-from scipy import miscimport pylab as plfrom scipy import ndimageimport numpy as np# from skimage.filter import denoise_tv_bregman,denoise_tv_chambollefrom skimage.restoration import denoise_tv_bregman,denoise_tv_chambollelena=misc.imread('Lenna.png',mode='L') # 数据类型 numpy array# 向lena增加噪声l = lena[230:310, 210:350]noisy = l + 0.4*l.std()*np.random.random(l.shape)tv_denoised_b = denoise_tv_bregman(noisy, weight=10)tv_denoised_c = denoise_tv_chambolle(noisy, weight=10)ax=pl.figure()ax.add_subplot(131),pl.imshow(noisy,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('noisy')pl.show()# pl.subplot(131),pl.imshow(noisy,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('noisy')# pl.subplot(132),pl.imshow(tv_denoised_b,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('tv_denoised_b')# pl.subplot(133),pl.imshow(tv_denoised_c,cmap='gray'),pl.axis('off'),pl.title('tv_denoised_c')## pl.show()5、数学形态学
结构元素
>>> el = ndimage.generate_binary_structure(2, 1)>>> elarray([[False, True, False], [ True, True, True], [False, True, False]], dtype=bool)>>> el.astype(np.int)array([[0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0]])腐蚀 = 最小化滤镜。用结构元素覆盖的像素的最小值替代一个像素值:
>>> a = np.zeros((7,7), dtype=np.int)>>> a[1:6, 2:5] = 1>>> aarray([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])>>> ndimage.binary_erosion(a).astype(a.dtype)array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])>>> #Erosion removes objects smaller than the structure>>> ndimage.binary_erosion(a, structure=np.ones((5,5))).astype(a.dtype)array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])膨胀:最大化滤镜:
>>> a = np.zeros((5, 5))>>> a[2, 2] = 1>>> aarray([[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])>>> ndimage.binary_dilation(a).astype(a.dtype)array([[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 1., 1., 1., 0.], [ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])对灰度值图像也有效
>>> np.random.seed(2)>>> x, y = (63*np.random.random((2, 8))).astype(np.int)>>> im[x, y] = np.arange(8)>>> bigger_points = ndimage.grey_dilation(im, size=(5, 5), structure=np.ones((5, 5)))>>> square = np.zeros((16, 16))>>> square[4:-4, 4:-4] = 1>>> dist = ndimage.distance_transform_bf(square)>>> dilate_dist = ndimage.grey_dilation(dist, size=(3, 3), \... structure=np.ones((3, 3)))开操作:腐蚀+膨胀
应用:移除噪声
>>> square = np.zeros((32, 32))>>> square[10:-10, 10:-10] = 1>>> np.random.seed(2)>>> x, y = (32*np.random.random((2, 20))).astype(np.int)>>> square[x, y] = 1>>> open_square = ndimage.binary_opening(square)>>> eroded_square = ndimage.binary_erosion(square)>>> reconstruction = ndimage.binary_propagation(eroded_square, mask=square)
示例代码
闭操作:膨胀+腐蚀
许多其它数学分形:击中(hit)和击不中(miss)变换,tophat等等。
6、特征提取
边缘检测
使用梯度操作(Sobel)来找到搞强度的变化 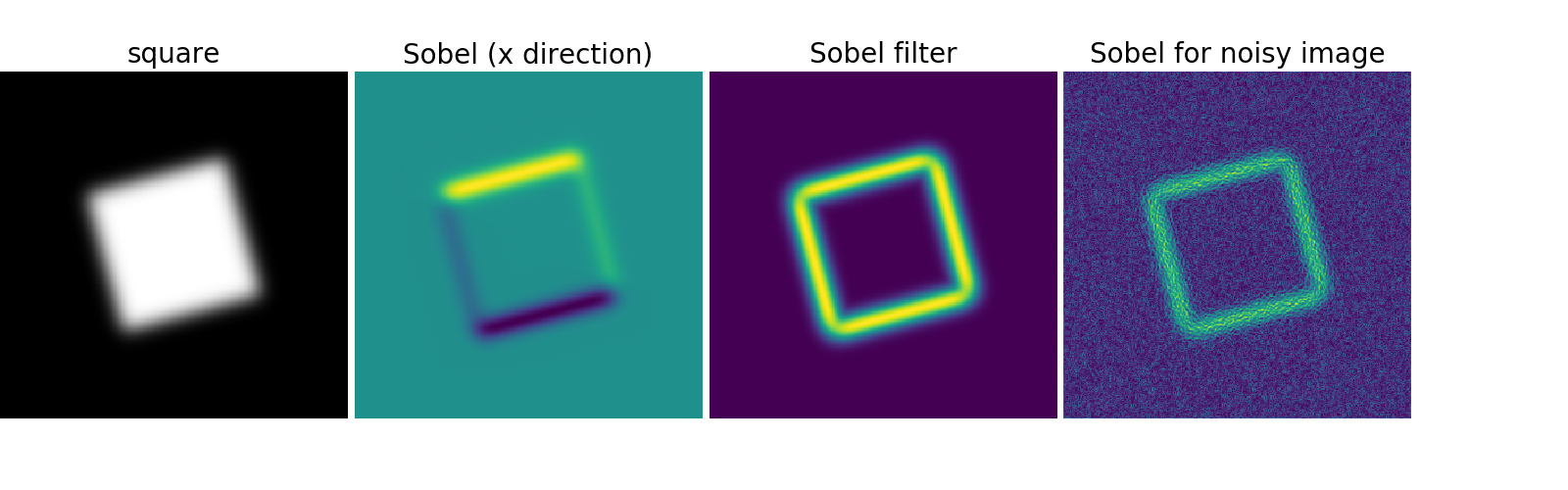
示例源码
canny滤镜
Canny滤镜可以从skimage中获取(文档)
>>> #from skimage.filter import canny>>> #or use module shipped with tutorial>>> im += 0.1*np.random.random(im.shape)>>> edges = canny(im, 1, 0.4, 0.2) # not enough smoothing>>> edges = canny(im, 3, 0.3, 0.2) # better parameters
示例代码
分割
基于直方图的分割(没有空间信息)
>>> n = 10 >>> l = 256 >>> im = np.zeros((l, l)) >>> np.random.seed(1) >>> points = l*np.random.random((2, n**2)) >>> im[(points[0]).astype(np.int), (points[1]).astype(np.int)] = 1 >>> im = ndimage.gaussian_filter(im, sigma=l/(4.*n)) >>> mask = (im > im.mean()).astype(np.float) >>> mask += 0.1 * im >>> img = mask + 0.2*np.random.randn(*mask.shape) >>> hist, bin_edges = np.histogram(img, bins=60) >>> bin_centers = 0.5*(bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) >>> binary_img = img > 0.5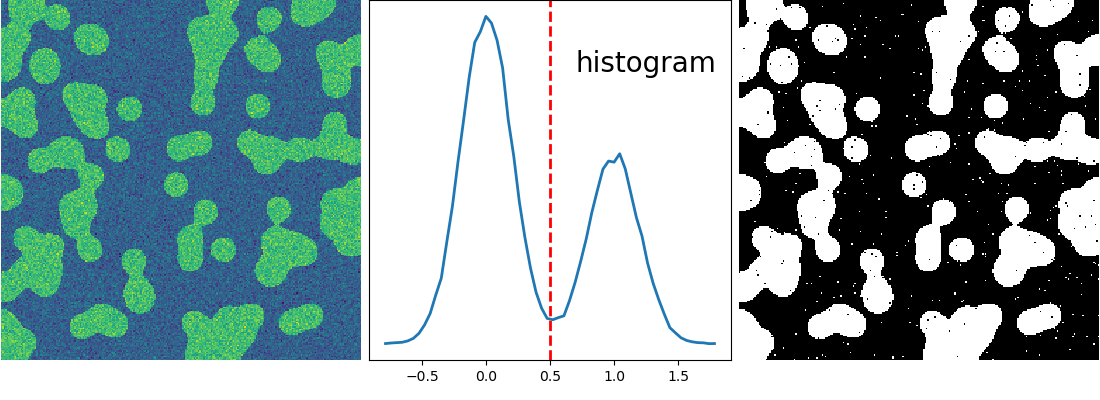
示例代码
自动阈值:使用高斯混合模型
>>> mask = (im > im.mean()).astype(np.float)>>> mask += 0.1 * im>>> img = mask + 0.3*np.random.randn(*mask.shape)>>> from sklearn.mixture import GMM>>> classif = GMM(n_components=2)>>> classif.fit(img.reshape((img.size, 1))) GMM(...)>>> classif.means_array([[ 0.9353155 ], [-0.02966039]])>>> np.sqrt(classif.covars_).ravel()array([ 0.35074631, 0.28225327])>>> classif.weights_array([ 0.40989799, 0.59010201])>>> threshold = np.mean(classif.means_)>>> binary_img = img > threshold
使用数学形态学来清理结果:
>>> # Remove small white regions>>> open_img = ndimage.binary_opening(binary_img)>>> # Remove small black hole>>> close_img = ndimage.binary_closing(open_img)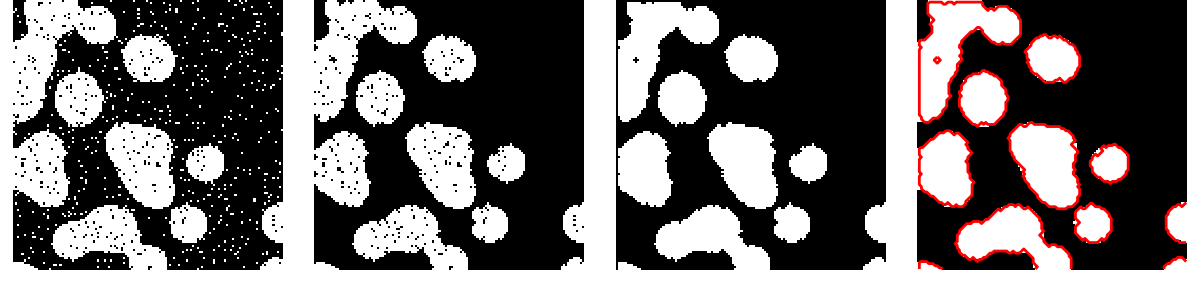
示例源码
其他略参考:http://scipy-lectures.github.com/advanced/image_processing/index.html
- scipy-图像操作
- Scipy的几个简单图像操作
- 使用SciPy进行常用的图像操作
- Python使用scipy和numpy操作处理图像
- python-scipy 图像处理
- scipy的图像测试
- scipy的基本操作
- python scipy卷积 图像卷积
- scipy 图像处理(scipy.misc、scipy.ndimage)、matplotlib 图像处理
- [笔记]SciPy、Matplotlib基础操作
- 使用Numpy和Scipy处理图像
- 使用Numpy和Scipy处理图像
- 使用Numpy和Scipy处理图像
- 使用Numpy和Scipy处理图像
- 4-python图像处理之Scipy
- 使用Numpy和Scipy处理图像
- scipy的二维图像卷积运算
- scipy对图像进行模糊处理
- TemplateView , ListView ,DetailView三种常用类视图用法
- 单元测试 testng.xml load class not found
- 模型检验概述
- (DT系列三)系统启动时, dts 是怎么被加载的
- C++中 explicit的用法
- scipy-图像操作
- CentOS修改yum源为Aliyun
- 如何生成高程剖面图
- 【HDU 5023】A Corrupt Mayor's Performance Art 【线段树+状态压缩】
- 修改centos7的系统编码为"en_US.UTF-8"
- JAVA_编程小案例_打印菱形
- easyui datagrid前台传值后台乱码
- [java]Java使用占位符拼接字符串
- js获取服务器时间



