const
来源:互联网 发布:sqlserver 并发数 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 06:29
C++ const 允许指定一个语义约束,编译器会强制实施这个约束,允许程序员告诉编译器某值是保持不变的。如果在编程中确实有某个值保持不变,就应该明确使用const,这样可以获得编译器的帮助。
1.const 修饰成员变量
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int main(){ 4 int a1=3; ///non-const data 5 const int a2=a1; ///const data 6 7 int * a3 = &a1; ///non-const data,non-const pointer 8 const int * a4 = &a1; ///const data,non-const pointer 9 int * const a5 = &a1; ///non-const data,const pointer10 int const * const a6 = &a1; ///const data,const pointer11 const int * const a7 = &a1; ///const data,const pointer12 13 return 0;14 }
const修饰指针变量时:
(1)只有一个const,如果const位于*左侧,表示指针所指数据是常量,不能通过解引用修改该数据;指针本身是变量,可以指向其他的内存单元。
(2)只有一个const,如果const位于*右侧,表示指针本身是常量,不能指向其他内存地址;指针所指的数据可以通过解引用修改。
(3)两个const,*左右各一个,表示指针和指针所指数据都不能修改。
2.const修饰函数参数
传递过来的参数在函数内不可以改变,与上面修饰变量时的性质一样。
void testModifyConst(const int _x) { _x=5; ///编译出错}
3.const修饰成员函数
(1)const修饰的成员函数不能修改任何的成员变量(mutable修饰的变量除外)
(2)const成员函数不能调用非onst成员函数,因为非const成员函数可以会修改成员变量
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Point{ 4 public : 5 Point(int _x):x(_x){} 6 7 void testConstFunction(int _x) const{ 8 9 ///错误,在const成员函数中,不能修改任何类成员变量10 x=_x;11 12 ///错误,const成员函数不能调用非onst成员函数,因为非const成员函数可以会修改成员变量13 modify_x(_x);14 }15 16 void modify_x(int _x){17 x=_x;18 }19 20 int x;21 };
4.const修饰函数返回值
(1)指针传递
如果返回const data,non-const pointer,返回值也必须赋给const data,non-const pointer。因为指针指向的数据是常量不能修改。
1 const int * mallocA(){ ///const data,non-const pointer 2 int *a=new int(2); 3 return a; 4 } 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 const int *a = mallocA(); 9 ///int *b = mallocA(); ///编译错误10 return 0;11 }
(2)值传递
如果函数返回值采用“值传递方式”,由于函数会把返回值复制到外部临时的存储单元中,加const 修饰没有任何价值。所以,对于值传递来说,加const没有太多意义。
所以:
不要把函数int GetInt(void) 写成const int GetInt(void)。
不要把函数A GetA(void) 写成const A GetA(void),其中A 为用户自定义的数据类型。
======================================================
==============================================================
=====================================================
值传递与引用传递
一、值类型与引用类型
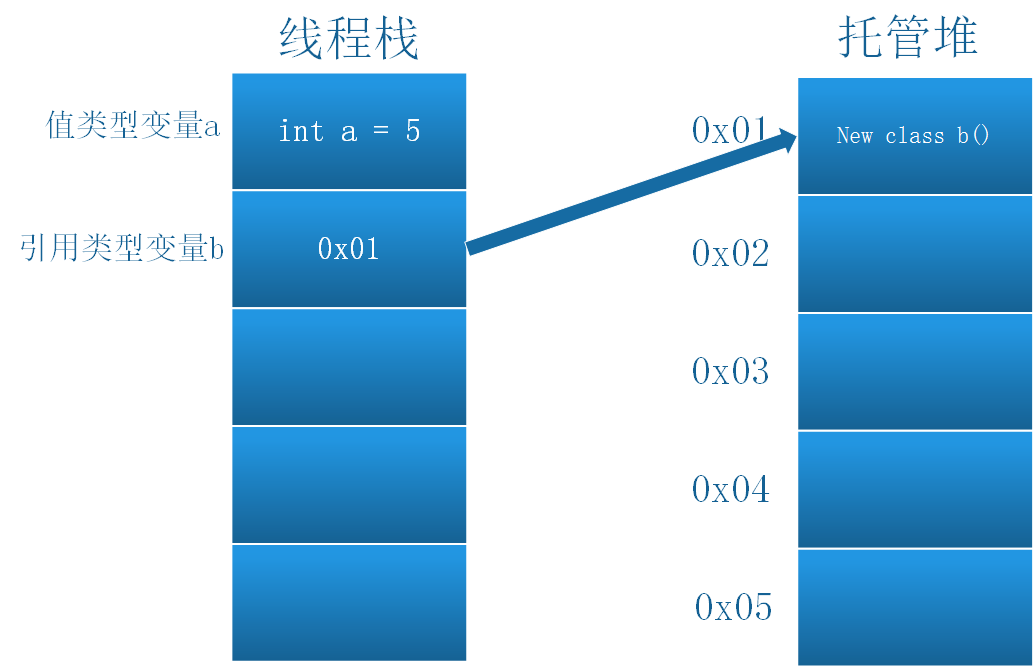
1.堆栈中的存放:
值类型默认存放在栈中,但当值类型是在引用类型中声明的时候,则存放在其所在的引用类型的堆中。
引用类型存放在堆中。其在堆中的内存地址存放在栈中。
2.参数传递方式
值类型参数可以值传递,也可通过ref、out关键字修饰,进行引用传递。
引用类型参数只能以引用传递方式传递。
二、值传递与引用传递
1.值传递
值传递是将变量的一个副本传递到方法中,方法中如何操作该变量副本,都不会改变原变量的值。
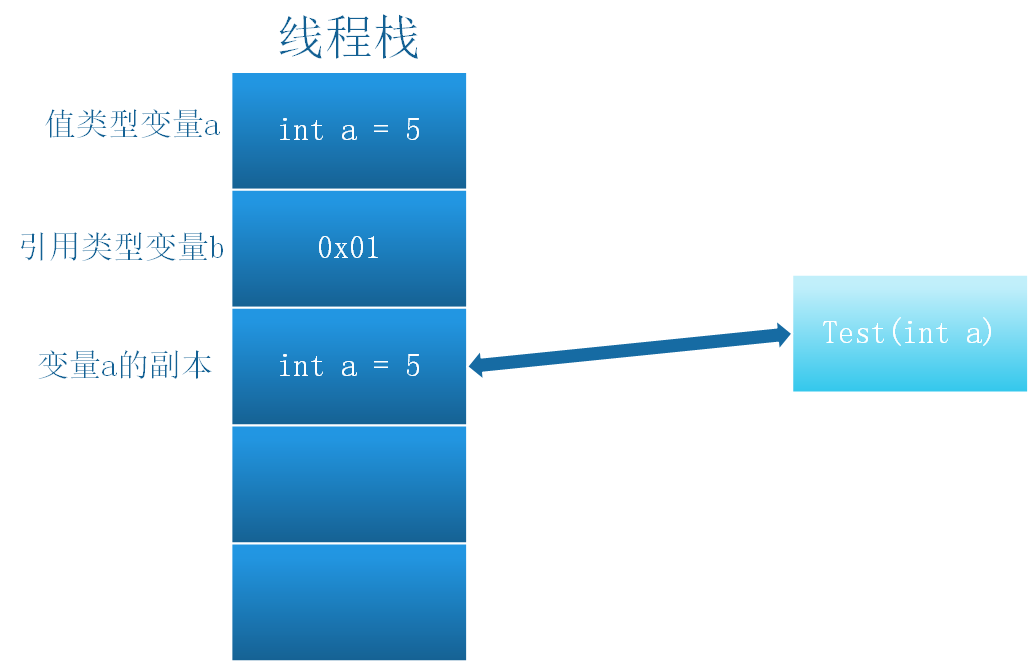
在下面的例子中。将变量 a 以值传递方式传给方法 Test(),在Test执行a++操作时,实际是对a的副本进行操作,Main方法中打印a的值,结果仍为 a=1 。
1 class Program 2 { 3 public static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 int a = 1; 6 Test(a); 7 Console.WriteLine(a); 8 9 Console.Write("Press any key to continue . . . ");10 Console.ReadKey(true);11 }12 13 //值传递14 static void Test(int a)15 {16 a++;17 }18 }
结果:1
2.引用传递
引用传递是将变量的内存地址传递给方法,方法操作变量时会找到保存在该地址的变量,对其进行操作。会对原变量造成影响。
这里用“原变量”一词只是为了与值传递进行对比说明,实际上所有方法都是操作同一对象,不应有“原变量”一说。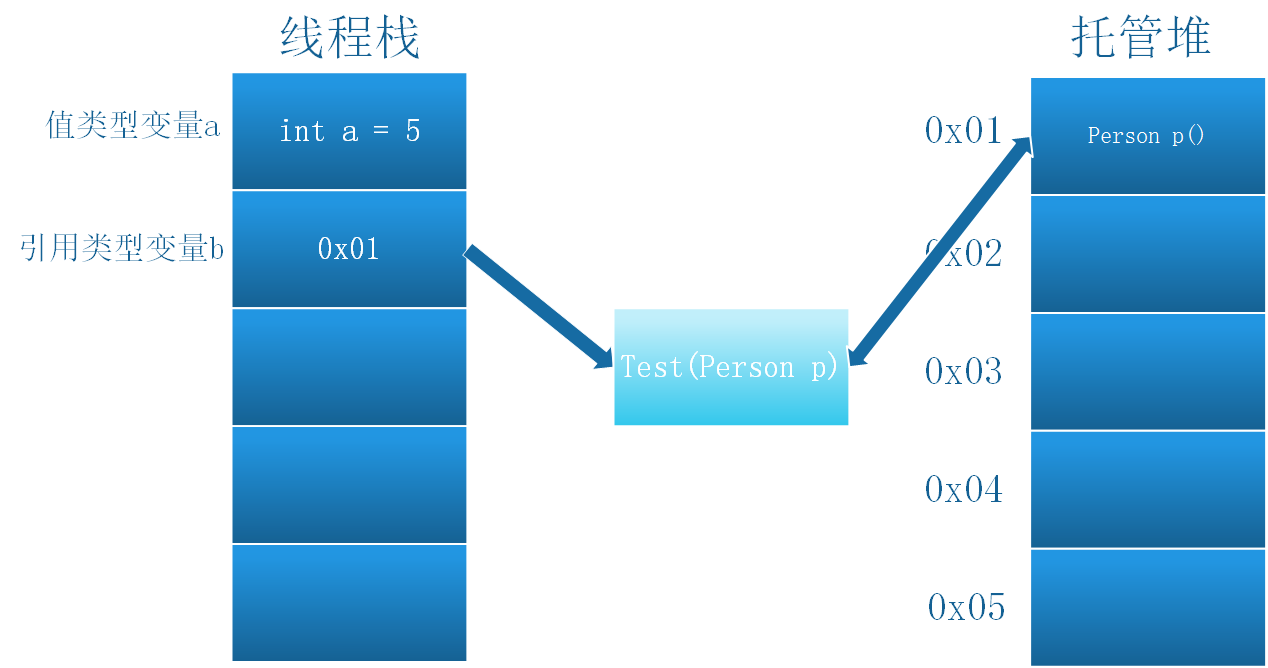
例子中,将Person对象p和变量 a (通过ref关键字修饰)以引用传递方式传给方法 Test()。在Test对变量进行操作时,是通过传递过来的地址010x,在堆中找到p,并对其进行操作。所以Main函数中再打印结果,已经发生变化。
1 class Program 2 { 3 public static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 int a = 1; 6 Person p=new Person{Age=20}; 7 //通过ref关键字,对值类型变量a进行引用传递 8 Test(ref a,p); 9 Console.WriteLine(a);10 Console.WriteLine(p.Age);11 12 Console.Write("Press any key to continue . . . ");13 Console.ReadKey(true);14 }15 16 //引用传递17 static void Test(ref int a,Person p)18 {19 a++;20 p.Age++;21 }22 23 }24 25 class Person26 {27 public int Age{get;set;}28 }
结果:2
21
- const
- const
- const
- CONST
- const
- const
- const
- const
- const
- const
- Const
- const
- const
- const
- CONST
- const
- const
- const
- 13. Roman to Integer
- Python StringIO模块(或Six.BytesIO()模块)实现在内存缓冲区中读写数据
- 使用 VMware player 安装 Unbuntu 16.04 桌面版
- SQL---常用sql整理
- linux tomcat 注册服务
- const
- BZOJ 2144 跳跳棋(LCA+欧几里德+二分答案)
- 554. Brick Wall (map)
- IDF 2016 | PC“遭弃”,虚拟现实、无人驾驶成为英特尔主角
- “下一代搜索引擎”Vurb,为何贱卖给Snapchat
- 文章标题
- 总结
- 网络端口号大全
- Java中去除字符串中所有空格的几种方法



