Java源码之ConcurrentHashMap
来源:互联网 发布:gson解析复杂的json 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/28 16:45
⑴背景
ConcurrentHashMap是线程安全高效的HashMap。而HashMap在多线程情况下强行使用HashMap的put方法可能会导致程序死循环,使CPU使用率达到100%。(http://firezhfox.iteye.com/blog/2241043),而使用HashTable效率不高,于是就出现了ConcurrentHashMap。
⑵HashTable与ConcurrentHashMap的区别
①HashTable容器使用synchronized来保证线程安全,但HashTable在线程竞争激烈情况下HashTable的效率非常低。因为当一个线程访问HashTable的同步方法,其他线程也访问HashTable的同步方法时,会进入轮询或者阻塞状态。
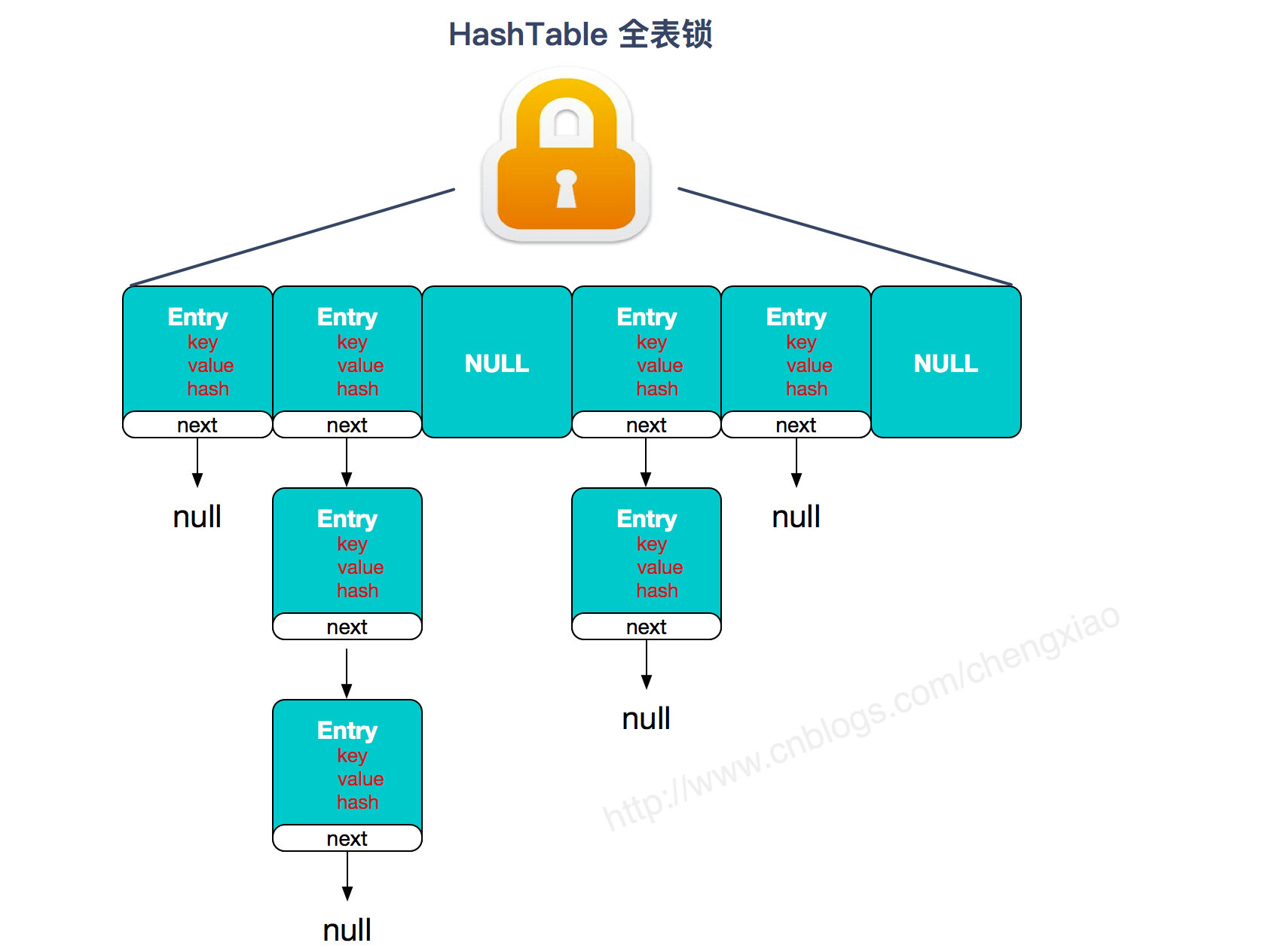
②ConcurrentHashMap并发访问效率高得益于锁分段技术,HashTable容器在竞争激烈的并发环境下表现出效率低下的原因是所有访问HashTable的线程都必须竞争同一把锁。而如果容器中有多把锁,每把锁都分别用于某一部分数据,那么当多线程访问容器中不同数据段数据时,线程间就不会存在锁定竞争,从而可以提高并发访问效率,ConcurrentHashMap的锁分段技术就是这个原理。 将数据分成一段一段地储存,然后每段数据配一把锁,当某一线访问其中一个数据段时,其他段的数据也能够被其他线程访问。

ConcurrentHashMap类图

ConcurrentHashMap结构图(锁分段)
ConcurrentHashMap是由Segment数组结构和HashEnrty数组结构组成。Segment是可重入锁,HashEntry用于存储键值对,HashEntry结构与HashMap中,类似就不重复说明了。
⑶源码解析
1 /** 2 * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, 3 * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. 4 * 5 * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key 6 * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)}, 7 * then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns 8 * {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) 9 *10 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null11 */12 public V get(Object key) {13 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;14 int h = spread(key.hashCode());15 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&16 (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {17 if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {18 if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))19 return e.val;20 }21 else if (eh < 0)22 return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;23 while ((e = e.next) != null) {24 if (e.hash == h &&25 ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))26 return e.val;27 }28 }29 return null;30 }
1 /** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */ 2 final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { 3 if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 4 int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); 5 int binCount = 0; 6 for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { 7 Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; 8 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 9 tab = initTable();10 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {11 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,12 new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))13 break; // no lock when adding to empty bin14 }15 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)16 tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);17 else {18 V oldVal = null;19 synchronized (f) {20 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {21 if (fh >= 0) {22 binCount = 1;23 for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {24 K ek;25 if (e.hash == hash &&26 ((ek = e.key) == key ||27 (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {28 oldVal = e.val;29 if (!onlyIfAbsent)30 e.val = value;31 break;32 }33 Node<K,V> pred = e;34 if ((e = e.next) == null) {35 pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,36 value, null);37 break;38 }39 }40 }41 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {42 Node<K,V> p;43 binCount = 2;44 if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,45 value)) != null) {46 oldVal = p.val;47 if (!onlyIfAbsent)48 p.val = value;49 }50 }51 }52 }53 if (binCount != 0) {54 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)55 treeifyBin(tab, i);56 if (oldVal != null)57 return oldVal;58 break;59 }60 }61 }62 addCount(1L, binCount);63 return null;64 }
这篇博主写得不错
- Java源码之ConcurrentHashMap
- Java源码之ConcurrentHashMap
- java.util.concurrent 之ConcurrentHashMap 源码分析
- JAVA之ConcurrentHashMap源码深度分析
- JDK1.8源码学习之ConcurrentHashMap.java
- Java集合之ConcurrentHashMap源码浅析
- Java集合之ConcurrentHashMap源码分析
- ConcurrentHashMap之源码分析
- Java源码分析:ConcurrentHashMap
- Java-ConcurrentHashMap源码分析
- Java 源码阅读-concurrentHashMap
- java concurrentHashMap 源码解析
- 我之见--java多线程 ConcurrentHashMap 源码分析
- 第六章 JAVA集合之ConcurrentHashMap源码浅析
- Java1.8之ConcurrentHashMap源码
- jdk源码分析之ConcurrentHashMap
- jdk源码分析之ConcurrentHashMap
- jdk8之ConcurrentHashMap源码解析
- BFS-迷宫问题
- ElementUI案例演示:导航、布局、加载动画
- 三:Python 2 or 3?
- hdoj-1035Robot Motion
- 字典
- Java源码之ConcurrentHashMap
- 【面试】--java相关
- String类中的常用方法
- Windows下配置Caffe+Tensorflow几个非常重要的注意点和所需安装包!!
- linux虚拟机克隆遇到的问题
- Eclipse连接MySQL数据库
- 2017-2018 ACM-ICPC, NEERC, Northern Subregional Contest
- 数列求和
- 四:Python安装


