自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(四)
来源:互联网 发布:pe系统支持网络功能 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/08 06:58
18.4 完整解决方案
为了能够解释机器人控制指令,Sunny软件公司开发人员使用解释器模式来设计和实现机器人控制程序。针对五条文法规则,分别提供五个类来实现,其中终结符表达式direction、action和distance对应DirectionNode类、ActionNode类和DistanceNode类,非终结符表达式expression和composite对应SentenceNode类和AndNode类。
我们可以通过抽象语法树来表示具体解释过程,例如机器人控制指令“down run 10 and left move 20”对应的抽象语法树如图18-4所示:
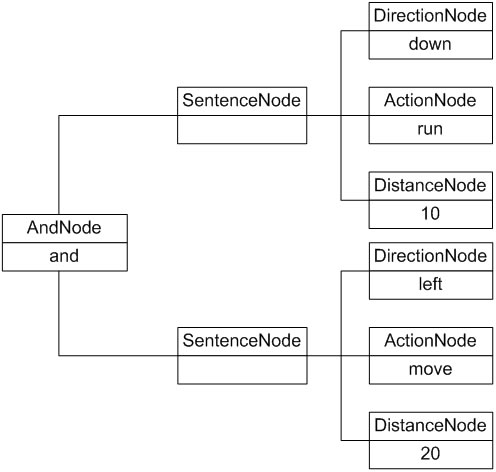
图18-4 机器人控制程序抽象语法树实例
机器人控制程序实例基本结构如图18-5所示:
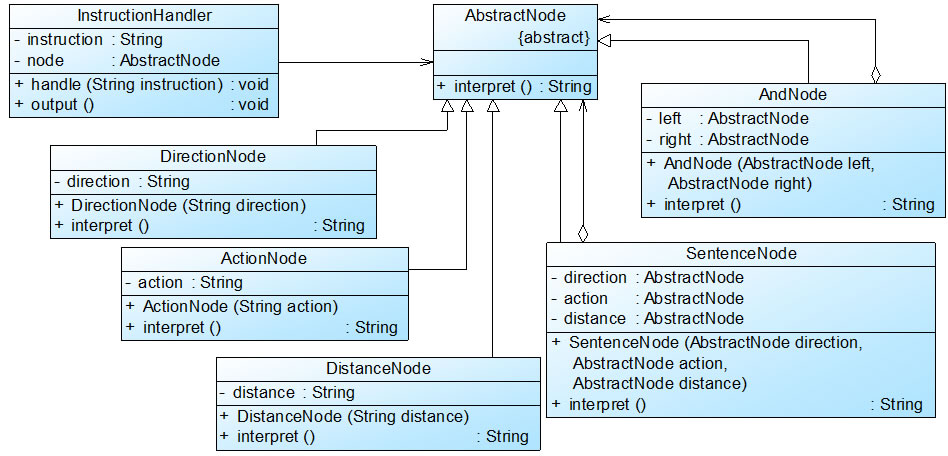
图18-5 机器人控制程序结构图
在图18-5中,AbstractNode充当抽象表达式角色,DirectionNode、ActionNode和DistanceNode充当终结符表达式角色,AndNode和SentenceNode充当非终结符表达式角色。完整代码如下所示:
//注:本实例对机器人控制指令的输出结果进行模拟,将英文指令翻译为中文指令,实际情况是调用不同的控制程序进行机器人的控制,包括对移动方向、方式和距离的控制等 import java.util.*; //抽象表达式 abstract class AbstractNode { public abstract String interpret(); } //And解释:非终结符表达式 class AndNode extends AbstractNode { private AbstractNode left; //And的左表达式 private AbstractNode right; //And的右表达式 public AndNode(AbstractNode left, AbstractNode right) { this.left = left; this.right = right; } //And表达式解释操作 public String interpret() { return left.interpret() + "再" + right.interpret(); } } //简单句子解释:非终结符表达式 class SentenceNode extends AbstractNode { private AbstractNode direction; private AbstractNode action; private AbstractNode distance; public SentenceNode(AbstractNode direction,AbstractNode action,AbstractNode distance) { this.direction = direction; this.action = action; this.distance = distance; } //简单句子的解释操作 public String interpret() { return direction.interpret() + action.interpret() + distance.interpret(); } } //方向解释:终结符表达式 class DirectionNode extends AbstractNode { private String direction; public DirectionNode(String direction) { this.direction = direction; } //方向表达式的解释操作 public String interpret() { if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("up")) { return "向上"; } else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("down")) { return "向下"; } else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("left")) { return "向左"; } else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("right")) { return "向右"; } else { return "无效指令"; } } } //动作解释:终结符表达式 class ActionNode extends AbstractNode { private String action; public ActionNode(String action) { this.action = action; } //动作(移动方式)表达式的解释操作 public String interpret() { if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("move")) { return "移动"; } else if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("run")) { return "快速移动"; } else { return "无效指令"; } } } //距离解释:终结符表达式 class DistanceNode extends AbstractNode { private String distance; public DistanceNode(String distance) { this.distance = distance; } //距离表达式的解释操作 public String interpret() { return this.distance; } } //指令处理类:工具类 class InstructionHandler { private String instruction; private AbstractNode node; public void handle(String instruction) { AbstractNode left = null, right = null; AbstractNode direction = null, action = null, distance = null; Stack stack = new Stack(); //声明一个栈对象用于存储抽象语法树 String[] words = instruction.split(" "); //以空格分隔指令字符串 for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) { //本实例采用栈的方式来处理指令,如果遇到“and”,则将其后的三个单词作为三个终结符表达式连成一个简单句子SentenceNode作为“and”的右表达式,而将从栈顶弹出的表达式作为“and”的左表达式,最后将新的“and”表达式压入栈中。 if (words[i].equalsIgnoreCase("and")) { left = (AbstractNode)stack.pop(); //弹出栈顶表达式作为左表达式 String word1= words[++i]; direction = new DirectionNode(word1); String word2 = words[++i]; action = new ActionNode(word2); String word3 = words[++i]; distance = new DistanceNode(word3); right = new SentenceNode(direction,action,distance); //右表达式 stack.push(new AndNode(left,right)); //将新表达式压入栈中 } //如果是从头开始进行解释,则将前三个单词组成一个简单句子SentenceNode并将该句子压入栈中 else { String word1 = words[i]; direction = new DirectionNode(word1); String word2 = words[++i]; action = new ActionNode(word2); String word3 = words[++i]; distance = new DistanceNode(word3); left = new SentenceNode(direction,action,distance); stack.push(left); //将新表达式压入栈中 } } this.node = (AbstractNode)stack.pop(); //将全部表达式从栈中弹出 } public String output() { String result = node.interpret(); //解释表达式 return result; } } 工具类InstructionHandler用于对输入指令进行处理,将输入指令分割为字符串数组,将第1个、第2个和第3个单词组合成一个句子,并存入栈中;如果发现有单词“and”,则将“and”后的第1个、第2个和第3个单词组合成一个新的句子作为“and”的右表达式,并从栈中取出原先所存句子作为左表达式,然后组合成一个And节点存入栈中。依此类推,直到整个指令解析结束。
编写如下客户端测试代码:
class Client { public static void main(String args[]) { String instruction = "up move 5 and down run 10 and left move 5"; InstructionHandler handler = new InstructionHandler(); handler.handle(instruction); String outString; outString = handler.output(); System.out.println(outString); } } 编译并运行程序,输出结果如下:
向上移动5再向下快速移动10再向左移动5
【作者:刘伟 http://blog.csdn.net/lovelion】
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(四)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(四)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(四)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(一)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(二)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(三)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(五)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(六)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(一)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(二)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(三)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(五)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(六)
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(一)
- POJ 2387 最短路径模板
- js笔记九:当运行脚本
- 解方程
- JDBC示例
- 周六上午
- 自定义语言的实现——解释器模式(四)
- SpringBoot构建微服务实战 之 整合Mybatis(一)
- 使用Git实现小组间合作开发——(1)组员篇
- maven环境隔离详细操作
- NameError: name 'app' is not defined(关键词:flask/bug)
- 奇数位丢弃
- Codevs2492:上帝造题的七分钟 2(并查集)
- 小区广播之对Channels的存储处理
- [BZOJ]2683: 简单题 CDQ分治+树状数组


