Collections.synchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap、Hashtable之间的区别 为什么要比较Hashtable、SynchronizedMap()、Co
来源:互联网 发布:java类变量初始化 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/01 07:16
Collections.synchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap、Hashtable之间的区别
为什么要比较Hashtable、SynchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap之间的关系?因为常用的HashMap是非线程安全的,不能满足在多线程高并发场景下的需求。
那么为什么说HashTable是线程不安全的?具体参阅关于java集合类HashMap的理解
如何线程安全的使用HashMap
了解了 HashMap 为什么线程不安全,那现在看看如何线程安全的使用 HashMap。这个无非就是以下三种方式:
- Hashtable
- ConcurrentHashMap
- Synchronized Map
Hashtable
那先说说Hashtable,Hashtable源码中是使用 synchronized 来保证线程安全的,比如下面的 get 方法和 put 方法:
public synchronized V get(Object key) { // 省略实现}public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { // 省略实现}
所以当一个线程访问 HashTable 的同步方法时,其他线程如果也要访问同步方法,会被阻塞住。举个例子,当一个线程使用 put 方法时,另一个线程不但不可以使用 put 方法,连 get 方法都不可以,好霸道啊!!!so~~,效率很低,现在基本不会选择它了。
Collections.synchronizedMap()
看了一下源码,synchronizedMap()的实现还是很简单的。
1 // synchronizedMap方法 2 public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) { 3 return new SynchronizedMap<>(m); 4 } 5 // SynchronizedMap类 6 private static class SynchronizedMap<K,V> 7 implements Map<K,V>, Serializable { 8 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1978198479659022715L; 9 10 private final Map<K,V> m; // Backing Map11 final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize12 13 SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {14 this.m = Objects.requireNonNull(m);15 mutex = this;16 }17 18 SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m, Object mutex) {19 this.m = m;20 this.mutex = mutex;21 }22 23 public int size() {24 synchronized (mutex) {return m.size();}25 }26 public boolean isEmpty() {27 synchronized (mutex) {return m.isEmpty();}28 }29 public boolean containsKey(Object key) {30 synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsKey(key);}31 }32 public boolean containsValue(Object value) {33 synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsValue(value);}34 }35 public V get(Object key) {36 synchronized (mutex) {return m.get(key);}37 }38 39 public V put(K key, V value) {40 synchronized (mutex) {return m.put(key, value);}41 }42 public V remove(Object key) {43 synchronized (mutex) {return m.remove(key);}44 }45 // 省略其他方法46 }
从源码中可以看出调用 synchronizedMap() 方法后会返回一个 SynchronizedMap 类的对象,而在 SynchronizedMap 类中使用了 synchronized 同步关键字来保证对 Map 的操作是线程安全的。
ConcurrentHashMap
Spring的源码中有很多使用ConcurrentHashMap的地方。具体参阅》》》》》》》》。需要注意的是,上面博客是基于 Java 7 的,和8有区别,在8中 CHM 摒弃了 Segment(锁段)的概念,而是启用了一种全新的方式实现,利用CAS算法。
下面通过一个具体例子看看Collections.synchronizedMap()和ConcurrentHashMap哪个性能更高。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public final static int THREAD_POOL_SIZE = 5; 4 5 public static Map<String, Integer> crunchifyHashTableObject = null; 6 public static Map<String, Integer> crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = null; 7 public static Map<String, Integer> crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = null; 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {10 11 // Test with Hashtable Object12 crunchifyHashTableObject = new Hashtable<>();13 crunchifyPerformTest(crunchifyHashTableObject);14 15 // Test with synchronizedMap Object16 crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, Integer>());17 crunchifyPerformTest(crunchifySynchronizedMapObject);18 19 // Test with ConcurrentHashMap Object20 crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();21 crunchifyPerformTest(crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject);22 23 }24 25 public static void crunchifyPerformTest(final Map<String, Integer> crunchifyThreads) throws InterruptedException {26 27 System.out.println("Test started for: " + crunchifyThreads.getClass());28 long averageTime = 0;29 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {30 31 long startTime = System.nanoTime();32 ExecutorService crunchifyExServer = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_POOL_SIZE);33 34 for (int j = 0; j < THREAD_POOL_SIZE; j++) {35 crunchifyExServer.execute(new Runnable() {36 @SuppressWarnings("unused")37 @Override38 public void run() {39 40 for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {41 Integer crunchifyRandomNumber = (int) Math.ceil(Math.random() * 550000);42 43 // Retrieve value. We are not using it anywhere44 Integer crunchifyValue = crunchifyThreads.get(String.valueOf(crunchifyRandomNumber));45 46 // Put value47 crunchifyThreads.put(String.valueOf(crunchifyRandomNumber), crunchifyRandomNumber);48 }49 }50 });51 }52 53 // Make sure executor stops54 crunchifyExServer.shutdown();55 56 // Blocks until all tasks have completed execution after a shutdown request57 crunchifyExServer.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.DAYS);58 59 long entTime = System.nanoTime();60 long totalTime = (entTime - startTime) / 1000000L;61 averageTime += totalTime;62 System.out.println("2500K entried added/retrieved in " + totalTime + " ms");63 }64 System.out.println("For " + crunchifyThreads.getClass() + " the average time is " + averageTime / 5 + " ms\n");65 }66 }
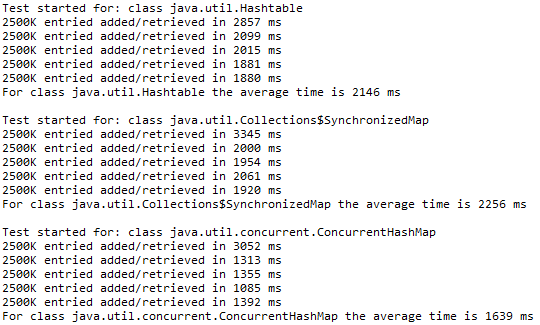
结果显示,ConcurrentHashMap性能是明显优于Hashtable和SynchronizedMap的,ConcurrentHashMap花费的时间比前两个的一半还少。
为什么要比较Hashtable、SynchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap之间的关系?因为常用的HashMap是非线程安全的,不能满足在多线程高并发场景下的需求。
那么为什么说HashTable是线程不安全的?具体参阅关于java集合类HashMap的理解
如何线程安全的使用HashMap
了解了 HashMap 为什么线程不安全,那现在看看如何线程安全的使用 HashMap。这个无非就是以下三种方式:
- Hashtable
- ConcurrentHashMap
- Synchronized Map
Hashtable
那先说说Hashtable,Hashtable源码中是使用 synchronized 来保证线程安全的,比如下面的 get 方法和 put 方法:
public synchronized V get(Object key) { // 省略实现}public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { // 省略实现}
所以当一个线程访问 HashTable 的同步方法时,其他线程如果也要访问同步方法,会被阻塞住。举个例子,当一个线程使用 put 方法时,另一个线程不但不可以使用 put 方法,连 get 方法都不可以,好霸道啊!!!so~~,效率很低,现在基本不会选择它了。
Collections.synchronizedMap()
看了一下源码,synchronizedMap()的实现还是很简单的。
1 // synchronizedMap方法 2 public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) { 3 return new SynchronizedMap<>(m); 4 } 5 // SynchronizedMap类 6 private static class SynchronizedMap<K,V> 7 implements Map<K,V>, Serializable { 8 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1978198479659022715L; 9 10 private final Map<K,V> m; // Backing Map11 final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize12 13 SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) {14 this.m = Objects.requireNonNull(m);15 mutex = this;16 }17 18 SynchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m, Object mutex) {19 this.m = m;20 this.mutex = mutex;21 }22 23 public int size() {24 synchronized (mutex) {return m.size();}25 }26 public boolean isEmpty() {27 synchronized (mutex) {return m.isEmpty();}28 }29 public boolean containsKey(Object key) {30 synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsKey(key);}31 }32 public boolean containsValue(Object value) {33 synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsValue(value);}34 }35 public V get(Object key) {36 synchronized (mutex) {return m.get(key);}37 }38 39 public V put(K key, V value) {40 synchronized (mutex) {return m.put(key, value);}41 }42 public V remove(Object key) {43 synchronized (mutex) {return m.remove(key);}44 }45 // 省略其他方法46 }
从源码中可以看出调用 synchronizedMap() 方法后会返回一个 SynchronizedMap 类的对象,而在 SynchronizedMap 类中使用了 synchronized 同步关键字来保证对 Map 的操作是线程安全的。
ConcurrentHashMap
Spring的源码中有很多使用ConcurrentHashMap的地方。具体参阅》》》》》》》》。需要注意的是,上面博客是基于 Java 7 的,和8有区别,在8中 CHM 摒弃了 Segment(锁段)的概念,而是启用了一种全新的方式实现,利用CAS算法。
下面通过一个具体例子看看Collections.synchronizedMap()和ConcurrentHashMap哪个性能更高。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public final static int THREAD_POOL_SIZE = 5; 4 5 public static Map<String, Integer> crunchifyHashTableObject = null; 6 public static Map<String, Integer> crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = null; 7 public static Map<String, Integer> crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = null; 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {10 11 // Test with Hashtable Object12 crunchifyHashTableObject = new Hashtable<>();13 crunchifyPerformTest(crunchifyHashTableObject);14 15 // Test with synchronizedMap Object16 crunchifySynchronizedMapObject = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, Integer>());17 crunchifyPerformTest(crunchifySynchronizedMapObject);18 19 // Test with ConcurrentHashMap Object20 crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();21 crunchifyPerformTest(crunchifyConcurrentHashMapObject);22 23 }24 25 public static void crunchifyPerformTest(final Map<String, Integer> crunchifyThreads) throws InterruptedException {26 27 System.out.println("Test started for: " + crunchifyThreads.getClass());28 long averageTime = 0;29 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {30 31 long startTime = System.nanoTime();32 ExecutorService crunchifyExServer = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_POOL_SIZE);33 34 for (int j = 0; j < THREAD_POOL_SIZE; j++) {35 crunchifyExServer.execute(new Runnable() {36 @SuppressWarnings("unused")37 @Override38 public void run() {39 40 for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {41 Integer crunchifyRandomNumber = (int) Math.ceil(Math.random() * 550000);42 43 // Retrieve value. We are not using it anywhere44 Integer crunchifyValue = crunchifyThreads.get(String.valueOf(crunchifyRandomNumber));45 46 // Put value47 crunchifyThreads.put(String.valueOf(crunchifyRandomNumber), crunchifyRandomNumber);48 }49 }50 });51 }52 53 // Make sure executor stops54 crunchifyExServer.shutdown();55 56 // Blocks until all tasks have completed execution after a shutdown request57 crunchifyExServer.awaitTermination(Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.DAYS);58 59 long entTime = System.nanoTime();60 long totalTime = (entTime - startTime) / 1000000L;61 averageTime += totalTime;62 System.out.println("2500K entried added/retrieved in " + totalTime + " ms");63 }64 System.out.println("For " + crunchifyThreads.getClass() + " the average time is " + averageTime / 5 + " ms\n");65 }66 }

结果显示,ConcurrentHashMap性能是明显优于Hashtable和SynchronizedMap的,ConcurrentHashMap花费的时间比前两个的一半还少。
- Collections.synchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap、Hashtable之间的区别 为什么要比较Hashtable、SynchronizedMap()、Co
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap比较
- Hashtable、synchronizedMap、ConcurrentHashMap 比较
- ConcurrentHashMap、Collections.synchronizedMap、Hashtable讨论
- HashMap、 HashTable 、Collections.synchronizedMap、 ConcurrentHashMap
- ConcurrentHashMap、Collections.synchronizedMap、Hashtable的区别与讨论
- ConcurrentHashMap Collections.synchronizedMap和Hashtable讨论
- ConcurrentHashMap Collections.synchronizedMap和Hashtable讨论
- ConcurrentHashMap Collections.synchronizedMap和Hashtable讨论
- Java 对象和类
- Java 基础语法
- Java 开发环境配置
- SVN和Git的区别
- Java 基本数据类型
- Collections.synchronizedMap()、ConcurrentHashMap、Hashtable之间的区别 为什么要比较Hashtable、SynchronizedMap()、Co
- 做小程序费用太高?帮你选一个最省钱的方案
- 二分查找法
- 论文笔记:Personalized Tag Recommendation for Images Using Deep Transfer Learning
- 微服务MySQL分库分表数据到MongoDB同步方案
- windows+R 运行 快捷命令
- php获取leancloud的多重数组
- 【体感手势】口袋模式或者防误触
- IDEA入门级使用教程



