C++ Map常见用法说明
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝指数官网手机版 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/18 02:03
http://blog.csdn.net/shuzfan/article/details/53115922#三-取值
- 一 声明
- 二 插入操作
- 1 使用 进行单个插入
- 1 使用insert进行单个和多个插入
- 三 取值
- 四 容量查询
- 五 迭代器
- 六 删除交换
- 1 删除
- 2 交换
- 七 顺序比较
- 八 查找
- 九 操作符
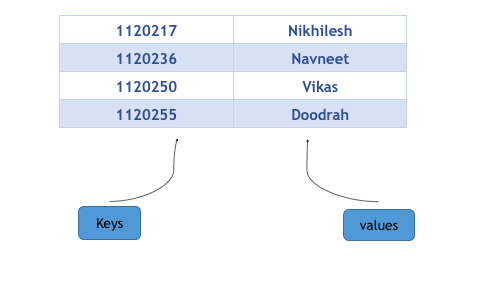
C++中map提供的是一种键值对容器,里面的数据都是成对出现的,如下图:每一对中的第一个值称之为关键字(key),每个关键字只能在map中出现一次;第二个称之为该关键字的对应值。
——————————————————————————————————————————————
一. 声明
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
——————————————————————————————————————————————
二. 插入操作
2.1 使用[ ]进行单个插入
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.1 使用insert进行单个和多个插入
insert共有4个重载函数:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
下面是具体使用示例:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
——————————————————————————————————————————————
三. 取值
Map中元素取值主要有at和[ ]两种操作,at会作下标检查,而[]不会。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
——————————————————————————————————————————————
四. 容量查询
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
——————————————————————————————————————————————
五. 迭代器
共有八个获取迭代器的函数:* begin, end, rbegin,rend* 以及对应的 * cbegin, cend, crbegin,crend*。
二者的区别在于,后者一定返回 const_iterator,而前者则根据map的类型返回iterator 或者 const_iterator。const情况下,不允许对值进行修改。如下面代码所示:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
返回的迭代器可以进行加减操作,此外,如果map为空,则 begin = end。
——————————————————————————————————————————————
六. 删除交换
6.1 删除
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
6.2 交换
- 1
- 2
——————————————————————————————————————————————
七. 顺序比较
- 1
- 2
示例:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
——————————————————————————————————————————————
八. 查找
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
举例:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
——————————————————————————————————————————————
九. 操作符
operator: == != < <= > >=
注意 对于==运算符, 只有键值对以及顺序完全相等才算成立。
- C++ Map常见用法说明
- C++ Map常见用法说明
- C++ Map常见用法说明
- C++ Map常见用法说明
- C++ Map常见用法说明
- python map 常见用法
- map常见用法
- Hystrix常见用法说明
- C/C++常见关键字含义和用法说明
- Map的常见用法总结
- STL中的map常见用法
- C++中的map常见用法
- java中Map常见用法
- BigDecimal常见用法详细说明
- c++map的用法
- c++map的用法
- C++map用法
- c++map的用法
- 异常链
- 应付帐
- webapp mui & HTML5+ (四) 之 窗口(页面初始化、跳转、传参)
- BMA250传感器驱动
- jquery Ajax提交表单(使用jquery Ajax上传附件)
- C++ Map常见用法说明
- 分类
- 3.3
- javaScript 基本语法
- c++builder 读取文件,提取绝对路径,提取文件名 函数应用实例
- 关于AndroidStudio3.0.1打包apk能在7.0安装,而在7.0以下不能安装的问题
- java语言实现操作系统中的文件管理系统
- Linux命令日志
- https站点调用wcf的问题解决



