Locating the postion of exception 定位异常的位置
来源:互联网 发布:甘肃启航网络 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 07:55
Introduction
No matter you area computer programmer or a user, I think you have seen the dialog to remindyour application is crashed, and remind to you to contact application vendor orreport to Microsoft.
User only need reboot the device and report this issue to the service. Forprogrammer, it is the horrific beginning, but don’t worry, this article willhelp you locate the position that causes the crash.
There are many articles to explain this, but I find they are out of date, forexample Visual studio can’t support line numbers in the MAP file, so the oldway that depends on the line number to locate the position isn’t feasible.
I will takeVS2005 for example to introduce 2 new ways to locate the position of the exception:
1. Use MAP and cod file according to the exception address.
2. Use symbol and dump file (PDB, dump)
1. Using MAP and COD file
First of all,you'll need a MAP file. If you don't have one, it will be nearly impossible tofind where your application crashed using the crash address. So first, I'llshow you how to create a MAP file.

You only needset “Generate Map file” to “Yes”.
Now I write a simple code to cause the exception below:
int *ip = NULL;
*ip =1234;
Obviously, itwill cause an access violation exception.
It is the samewith the other article’s description; An error box occurs and tell you theexception address.
In my program,it is “0x00011064”.
My map file is below(I only cite the necessary part):
exception
Timestamp is 4ad6ba58 (Thu Oct 15 13:59:522009)
Preferred load address is 00010000
Start Length Name Class
0001:00000000 00000d54H .text CODE
…
Address Publicsby Value Rva+Base Lib:Object
0000:00000000 ___safe_se_handler_count 00000000 <absolute>
0000:00000000 ___safe_se_handler_table 00000000 <absolute>
0001:00000000 WinMain 00011000 f exception.obj
0001:000000d4 ?MyRegisterClass@@YAGPAUHINSTANCE__@@PA_W@Z 000110d4 f exception.obj
0001:00000184 ?InitInstance@@YAHPAUHINSTANCE__@@H@Z 00011184 f exception.obj
0001:000002f0 ?WndProc@@YAJPAUHWND__@@IIJ@Z000112f0 f exception.obj
0001:00000564 ?About@@YAHPAUHWND__@@IIJ@Z 00011564 f exception.obj
…
Here, we stilluse the old way to locate the exception function first, the exception addressis 0x00011064, it is in the between “0x00011000—WinMain” and “0x000110d4—MyRegisterClass”,so the express is in the “WinMain”
Because fromthe visual studio 2003, linker doesn’t support “Line Number” in the map file,the old way that depends on the “Line Number” and “code segment” start addresscan’t work, we don’t use “Preferred load address” any more, here it is0x00010000.
But we stillneed a offset, the entry address of WinMain is 0x00011000 and exception addressis 0x00011064, so the offset is:
OFFSET =EXPRESS ADDRESS – FUNCTION ENTRY ADDRESS = 0x00011064–0x00011000= 0x64
Now even weknow the offset, but we still can’t use it to locate in the source codes,because this offset is calculate in the binary file.
We have todepend on some other information, in my way, it is COD file.
In order tooutput the COD file, you also need do some set below:
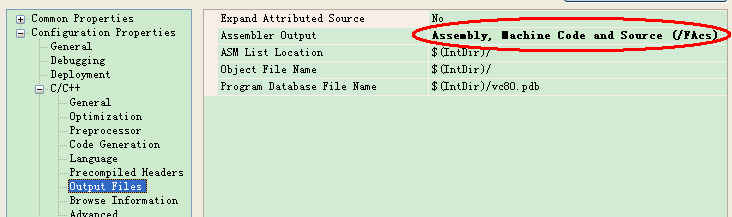
Then you willfind some COD files, like stdafx.cod.
Here I also takea part of this file for example and add some comments in black to explain.
; 44 : //”; 44”indicates the line number in the soure code, your *.cpp file
; 45 : int *ip = NULL; //here you also can see the your C codes, it is in the line 45.
00050 e3a03000 mov r3, #0
00054 e58d3020 str r3, [sp, #0x20]
;46 : *ip= 1234; //line number in the C codes, the following partbetween “;46” and “;47” they
//are the asmcodes to implent the “*ip = 1234;”
00058 e59d2020 ldr r2, [sp, #0x20]
0005c e3a03b01 mov r3, #1, 22
00060 e38330d2 orr r3, r3, #0xD2
00064 e5823000 str r3, [r2]
00068 |$LN3@WinMain| //here you can see the 0x68, it isthe offset
; 47 : // Main message loop:
; 48 : while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
00068 e3a03000 mov r3, #0
Now from thisCOD file, according to my comments, I think you can locate the line number ofthe source code. I repeat again:
The offset we calculatedis 0x68, so we need check this line, it is “00068 |$LN3@WinMain|”, then we trace it is source numberabove, it is “;46”.
Until now, wehave already located the express position in the source codes.
Below is mysource code, it is correct.
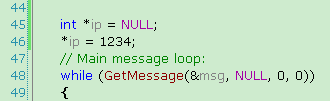
It is really agreat and wonderful way.
But pleaseremember to backup these files: MAP and all the COD files.
2. Using symbol and dump file
There isanother easier way, but 2 files are necessary, one is PDB file of yourexecutable program and the other is dump file.
PDB file iscreated after build and it should pair with executable file.
Dump file iscreated by OS, take WinCE for example, if you enable WER(Windows ErrorReporting), there will be kdmp files created if unhandled exception occurs.
To analyzethis, you can use Visual Studio or WinDbg tools, they can help us to locate theexception easily.
A. UsingWinDbg
1. Open WinDbg, before open crash dump file, youneed set the “Symbol file path…”, “Source file path…” and “Image file path…”

2. Open the dump file by “Open Crash Dump…”, then youwill see the result immediately, like below, it will highlight the exceptionposition of the source code.
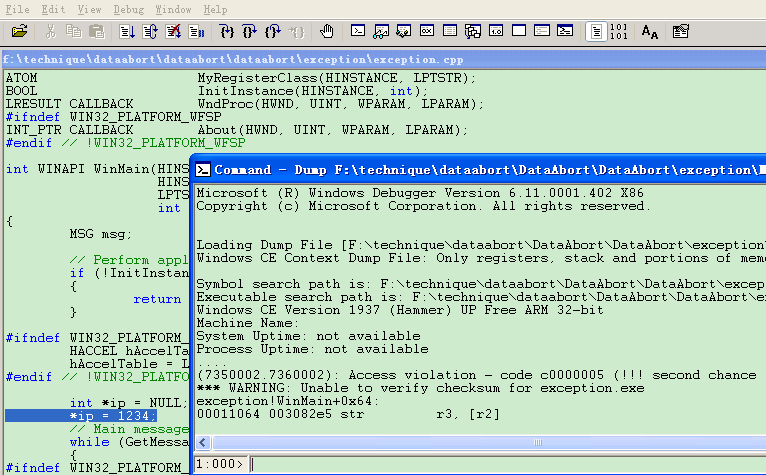
See, it is the same result with the one we analyzewith MAP and COD file.
This way is more convenient than last one, we needn’tcalculate at all, it can help us to locate automatically.
NOTE:
1. Youmust use the paired PDB and EXE files, or you may get the wrong result.
2. Ifyou can’t get the code located, I think you set the wrong path I said in theStep1.
B. UsingVisual Studio
With Visual Studio, we also can get the resultquickly, it is the similar way to set.
1. Openthe dump file, here my dump file is ce010309.kdmp.
2. Setthe “Source path mapping…” in the “Debug”, in my opinion, you’d better put thedump file, PDB file and source file in the same path, at least in the same diskpartition, then you needn’t set this path, VS will set it itself. This willhelp you to avoid lots of troubles.
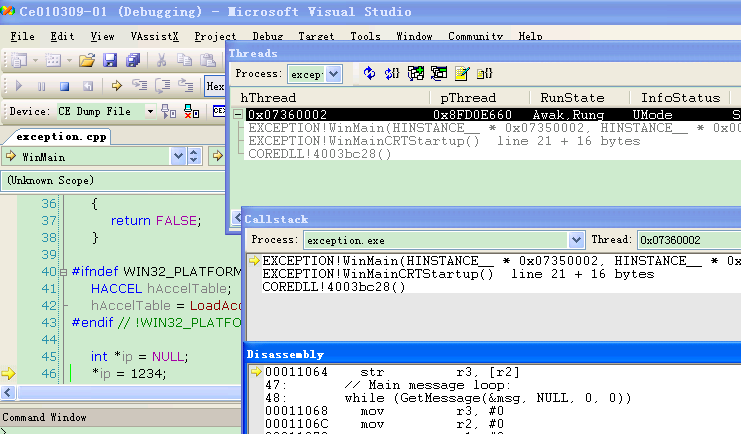
3. Choose“Target”à”Attach device”, then VS will run, youcan see the “Callstack”, “Disassembly”, “Thread”, you can see others in the “Debug->window->…”.
Here I explain “Disassembly”, you can see “0x00011064 str r3, [r2]”, I think you can remember 0x00011064is the exception address, VS locates it immediately, press right click of mouseon this line and choose “go to source”, then you will see the source code andit also indicates with a yellow arrow. It is the same result with WinDbg.
Summary
I hope you have realized that crash isn’t toohorrific, isn’t it?
Keeping necessary PDB, MAP and COD filesafter every release can make the exception easier.
But I also hope your program won’t crash. Designbetter, less trouble.
<!-- /* Font Definitions */ @font-face{font-family:宋体;panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1;mso-font-alt:SimSun;mso-font-charset:134;mso-generic-font-family:auto;mso-font-pitch:variable;mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;}@font-face{font-family:Verdana;panose-1:2 11 6 4 3 5 4 4 2 4;mso-font-charset:0;mso-generic-font-family:swiss;mso-font-pitch:variable;mso-font-signature:536871559 0 0 0 415 0;}@font-face{font-family:"/@宋体";panose-1:2 1 6 0 3 1 1 1 1 1;mso-font-charset:134;mso-generic-font-family:auto;mso-font-pitch:variable;mso-font-signature:3 135135232 16 0 262145 0;} /* Style Definitions */ p.MsoNormal, li.MsoNormal, div.MsoNormal{mso-style-parent:"";margin:0cm;margin-bottom:.0001pt;text-align:justify;text-justify:inter-ideograph;mso-pagination:none;font-size:10.5pt;mso-bidi-font-size:12.0pt;font-family:"Times New Roman";mso-fareast-font-family:宋体;mso-font-kerning:1.0pt;}h2{mso-margin-top-alt:auto;margin-right:0cm;mso-margin-bottom-alt:auto;margin-left:0cm;mso-pagination:widow-orphan;mso-outline-level:2;font-size:18.0pt;font-family:宋体;mso-bidi-font-family:宋体;mso-bidi-language:#D348;}a:link, span.MsoHyperlink{color:blue;text-decoration:underline;text-underline:single;}a:visited, span.MsoHyperlinkFollowed{color:purple;text-decoration:underline;text-underline:single;} /* Page Definitions */ @page{mso-page-border-surround-header:no;mso-page-border-surround-footer:no;}@page Section1{size:612.0pt 792.0pt;margin:72.0pt 90.0pt 72.0pt 90.0pt;mso-header-margin:36.0pt;mso-footer-margin:36.0pt;mso-paper-source:0;}div.Section1{page:Section1;}-->
License
This article, along with any associated source codeand files, is licensed under The Code Project OpenLicense (CPOL)
转载请注明出处
- Locating the postion of exception 定位异常的位置
- C++出现exception异常的位置如何定位?
- Postion定位的疑惑
- SAP找表的18中技巧(方法) 18 Techniques for Locating the Underlying Data of a Screen Field
- iOS开发------使用Xcode编译器定位抛出异常的位置
- 理解postion()和value-of
- 使用反射时发生“exception has been thrown to the target of an invocation”异常
- CSS的POSTION属性
- python的异常Exception
- java的异常Exception
- java的异常Exception
- Xcode准确定位异常代码位置
- Microsoft C++ 异常: 内存位置 0x002af444 处的 cv::Exception。
- Microsoft C++ 异常: 内存位置 0x001df54c 处的 cv::Exception。
- Opencv:Microsoft C++ 异常: 内存位置 0x002af444 处的 cv::Exception
- 中的 0x74b4c54f 处有未经处理的异常: Microsoft C++ 异常: 内存位置 0x0019dbc0 处的 cv::Exception。
- 0x757da832 处有未经处理的异常: Microsoft C++ 异常: 内存位置 0x0052f888 处的 cv::Exception。
- Io exception: The Network Adapter could not establish the connection异常的解决办法
- vs 2008 类的结构
- 经典文章>
- 到处都是Unix的胎记
- [FAQ]MySQL新建用户无法登录?
- 文件中将TAB误认为是空格导致explode无效无语中..
- Locating the postion of exception 定位异常的位置
- 关于本博客数据仓库方面的原创文章汇总
- extern &&extern c
- Android入门前言(一)之------Android应用开发入门五问
- 依然很菜鸟。
- VC使用MSXML解析XML文档
- SQL2005跨库复制表和 自增列清零
- 第五章介质访问控制子层
- 在Java内部类中使用外部类的成员方法以及成员变量


