1330 Nearest Common Ancestors //LCA
来源:互联网 发布:英语短语词组软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/17 08:27
Description
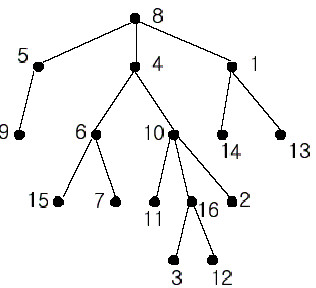
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2161 148 510 165 94 68 44 101 136 1510 116 710 216 38 116 1216 752 33 43 11 53 5
Sample Output
43
Source
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int MAX=10001;
int f[MAX];
int r[MAX];
int indegree[MAX];//保存每个节点的入度
int visit[MAX];
vector<int> tree[MAX],Qes[MAX];
int ancestor[MAX];
void init(int n)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
r[i]=1;//类似于rank数组
f[i]=i;//用于并查集记录父亲节点
indegree[i]=0;//节点的层号
visit[i]=0;//是否被访问
ancestor[i]=0;//祖先
tree[i].clear();//清空
Qes[i].clear();
}
}
int find(int n)
{ //查找函数,并压缩路径
if(f[n]==n) return n;
else f[n]=find(f[n]);
return f[n];
}
int Union(int x,int y)
{ //合并函数,如果属于同一分支则返回0,成功合并返回1
int a=find(x);
int b=find(y);
if(a==b) return 0;
//相等的话,x向y合并
else if(r[a]<=r[b])
{
f[a]=b;
r[b]+=r[a];
}
else
{
f[b]=a;
r[a]+=r[b];
}
return 1;
}
void LCA(int u)
{
ancestor[u]=u;
int size=tree[u].size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
LCA(tree[u][i]);
Union(u,tree[u][i]);
ancestor[find(u)]=u;
}
visit[u]=1;
size=Qes[u].size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{ //如果已经访问了问题节点,就可以返回结果了.
if(visit[Qes[u][i]]==1)
{
printf("%d/n",ancestor[find(Qes[u][i])]);
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
int n;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
init(n);
int s,t;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&s,&t);
tree[s].push_back(t);
indegree[t]++;
}
scanf("%d%d",&s,&t);//这里可以输入多组询问
Qes[s].push_back(t);//相当于询问两次
Qes[t].push_back(s);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{ //寻找根节点
if(indegree[i]==0)
{
LCA(i);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
- 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors //LCA
- Nearest Common Ancestors--LCA
- [PKU 1330]Nearest Common Ancestors(LCA)
- POJ-1330 Nearest Common Ancestors【LCA】
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors [LCA+RMQ]
- POJ 1330Nearest Common Ancestors LCA模板
- poj 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(LCA)
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors (LCA)
- poj 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors (LCA)
- poj 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(LCA模板)
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA
- poj 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA targin
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA题解
- poj 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors (LCA)
- Nearest Common Ancestors - POJ 1330 LCA
- 【LCA】 POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA
- linux嵌入式资源
- 修正网页中div或ul或其他块元素在IE6,IE7,FF,Opera中显示不同的杀手锏
- 父子对话框 变量及函数的调用
- 《FRINGE》の近期看书计划
- SQL2008的数据更新跟踪测试
- 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors //LCA
- charindex代替like并非"更快更全面"
- 写一个对象集合排序的类
- ASCII压缩算法实现
- C++结构体 应用
- jsp页面的数据导入Excel中并下载Excel
- Java从入门到精通 - Java数字处理类
- socket的一个实例
- sybio


