Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
来源:互联网 发布:linux dd u盘启动 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/02 01:49
Ogre中的硬件缓存是指在显卡上的存储,这和在内存上的存储一样是可以访问的。有三种硬件缓存:HardwareVertexBuffer(顶点缓存,存储顶点的各种数据)、HardwareIndexBuffer(索引缓存,存储一个mesh的面片的顶点索引),HardwarePixelBuffer(纹理缓存,存储某个纹理贴图的数据)。这些数据在程序运行时都在显卡的存储上,然而你可以去读和写这些数据,来操控程序中物体的形状、纹理等。这个用处是非常大的。在Ogre中与访问这些硬件缓存有关的类及他们相互间的关系如下图: 根据这个图进行解释 1、最上面的hardwarevertexbuffer 创建:使用hardwarebuffermanager的create来创建,创建后利用hardwarevertexbuffer的write写入数据 2.中间的hardwareindexbuffer 3最下面的hardwarepixelbuffer 读写:从texture中可以直接得到这个hardwarepixelbuffer,然后对它lock后就可以得到一个pixelbox的数据,pixebox封装了所有纹理数据及其各种属性信息 创建:texture是由texturemanager创建的 下面是一些具体的使用硬件缓存的例子 读取顶点和索引缓存 Ogre::MeshPtr meshPtr=mainEntity->getMesh(); //得到位置数据的信息 //得到纹理坐标数据的信息 //将第一个点的位置读出 //这个函数的作用是将当前vertexPos指向的数据用其他型(这里是float*)的指针指向,这样读出来的数据就是float型的了,或者用float型的数据进行写入 //得到这个submesh的indexdata //得到indexbuffer //得到具体的索引缓存数据 … … 访问纹理缓存 Ogre::HardwarePixelBufferSharedPtr crossPixbufferPtr=texture.getPointer()->getBuffer(0,0); ……操纵data…… 创建顶点缓存和索引缓存,进而根据其创建一个自定义的mesh void createColourCube() 然后可以从mesh直接创建entity放在场景中 Entity*thisEntity = sceneManager->createEntity("cc", "ColourCube"); 本文来自CSDN博客,转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/leonwei/archive/2010/08/10/5799770.aspx
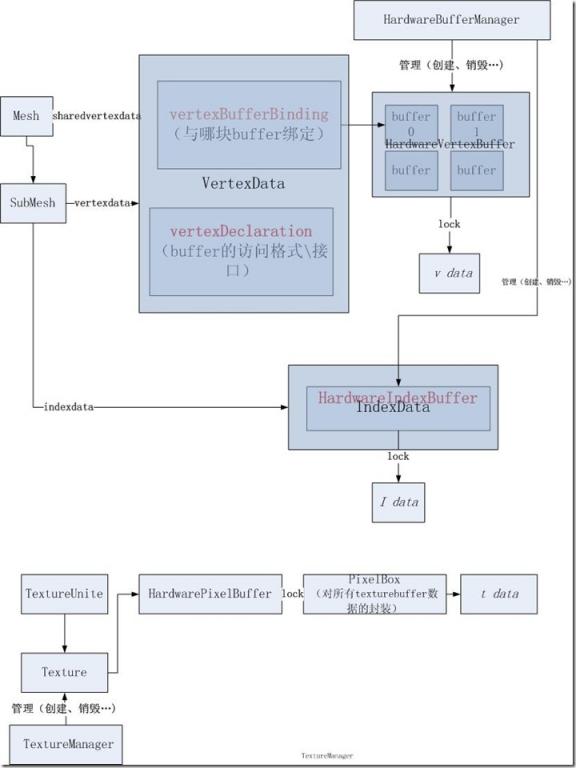
读写:如果mesh使用的所有子mesh共享buffer的形式,则用mesh的sharedvertexdata,否则用submesh的vertexdata来得到vertexdata结构,vertexdata封装了对该mesh的顶点缓存数据的访问方式,但是却不直接包含这些顶点缓存数据。vertexdata中的vettexbufferbinding可以知道当前的vertexdata对应了确切的硬件上的哪块buffer,可以通过vettexbufferbinding的getBuffer确切的得到该顶点缓存,而vertexdata中的vertexdeclaration则是一个对他对应的buffer进行各种访问的接口,里面有访问的格式等。如果要开始操纵这个buffer,需要将getbuffer得到的hardwarevertexbuffer调用lock,然后将这片缓存上锁,这个lock返回了一个void指针,指向的就是缓存数据。拿着这个指针就可以读取改写等
读写:直接使用submesh的indexdata来得到一个indexdata结构,再调用它的hardwareindexbuffer的来得到这个顶点缓存,童年顶点缓存一样再调用lock来进行读写操作
创建:同顶点缓存
//假设这里使用的是share的形式
Ogre::VertexData* vertex_data=meshPtr->sharedVertexData;
const Ogre::VertexElement* posElem =vertex_data->vertexDeclaration->findElementBySemantic(Ogre::VES_POSITION);
const Ogre::VertexElement* texcoElem=vertex_data->vertexDeclaration->findElementBySemantic(Ogre::VES_TEXTURE_COORDINATES );
//得到位置和纹理的缓存
Ogre::HardwareVertexBufferSharedPtr posBuf =vertex_data->vertexBufferBinding->getBuffer(posElem->getSource());
Ogre::HardwareVertexBufferSharedPtr texcoBuf =vertex_data->vertexBufferBinding->getBuffer(texcoElem->getSource());
//顶点位置缓存的lock,读取
unsigned char* vertexPos =static_cast<unsigned char*>(posBuf->lock(Ogre::HardwareBuffer::HBL_READ_ONLY));
float* pReal;
posElem->baseVertexPointerToElement(vertexPos, &pReal);
Ogre::Vector3 pt(pReal[0], pReal[1], pReal[2]);
//访问之后要上锁
posBuf->unlock();
//读取索引信息
Ogre::SubMesh* submesh = meshPtr->getSubMesh( i );
Ogre::IndexData* index_data = submesh->indexData;
int numTris = index_data->indexCount / 3;
Ogre::HardwareIndexBufferSharedPtr ibuf = index_data->indexBuffer;
bool use32bitindexes = (ibuf->getType() == Ogre::HardwareIndexBuffer::IT_32BIT);
unsigned long* pLong = static_cast<unsigned long*>(ibuf->lock(Ogre::HardwareBuffer::HBL_READ_ONLY));
unsigned short* pShort = reinterpret_cast<unsigned short*>(pLong);
ibuf->unlock();
crossPixbufferPtr->lock(Ogre::HardwareBuffer::HBL_NORMAL);
Ogre::PixelBox pb=crossPixbufferPtr->getCurrentLock();
int height = pb.getHeight();
int width = pb.getWidth();
int pitch = pb.rowPitch; // Skip between rows of image
uint32* data=static_cast<uint32*>(pb.data);
crossPixbufferPtr->unlock();
{
/// Create the mesh via the MeshManager
Ogre::MeshPtr msh = MeshManager::getSingleton().createManual("ColourCube", "General");
/// Create one submesh
SubMesh* sub = msh->createSubMesh();
const float sqrt13 = 0.577350269f; /* sqrt(1/3) */
/// Define the vertices (8 vertices, each consisting of 2 groups of 3 floats
const size_t nVertices = 8;
const size_t vbufCount = 3*2*nVertices;
float vertices[vbufCount] = {
-100.0,100.0,-100.0, //0 position
-sqrt13,sqrt13,-sqrt13, //0 normal
100.0,100.0,-100.0, //1 position
sqrt13,sqrt13,-sqrt13, //1 normal
100.0,-100.0,-100.0, //2 position
sqrt13,-sqrt13,-sqrt13, //2 normal
-100.0,-100.0,-100.0, //3 position
-sqrt13,-sqrt13,-sqrt13, //3 normal
-100.0,100.0,100.0, //4 position
-sqrt13,sqrt13,sqrt13, //4 normal
100.0,100.0,100.0, //5 position
sqrt13,sqrt13,sqrt13, //5 normal
100.0,-100.0,100.0, //6 position
sqrt13,-sqrt13,sqrt13, //6 normal
-100.0,-100.0,100.0, //7 position
-sqrt13,-sqrt13,sqrt13, //7 normal
};
RenderSystem* rs = Root::getSingleton().getRenderSystem();
RGBA colours[nVertices];
RGBA *pColour = colours;
// Use render system to convert colour value since colour packing varies
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(1.0,0.0,0.0), pColour++); //0 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(1.0,1.0,0.0), pColour++); //1 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(0.0,1.0,0.0), pColour++); //2 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(0.0,0.0,0.0), pColour++); //3 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(1.0,0.0,1.0), pColour++); //4 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(1.0,1.0,1.0), pColour++); //5 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(0.0,1.0,1.0), pColour++); //6 colour
rs->convertColourValue(ColourValue(0.0,0.0,1.0), pColour++); //7 colour
/// Define 12 triangles (two triangles per cube face)
/// The values in this table refer to vertices in the above table
const size_t ibufCount = 36;
unsigned short faces[ibufCount] = {
0,2,3,
0,1,2,
1,6,2,
1,5,6,
4,6,5,
4,7,6,
0,7,4,
0,3,7,
0,5,1,
0,4,5,
2,7,3,
2,6,7
};
/// Create vertex data structure for 8 vertices shared between submeshes
msh->sharedVertexData = new VertexData();
msh->sharedVertexData->vertexCount = nVertices;
/// Create declaration (memory format) of vertex data
VertexDeclaration* decl = msh->sharedVertexData->vertexDeclaration;
size_t offset = 0;
// 1st buffer
decl->addElement(0, offset, VET_FLOAT3, VES_POSITION);
offset += VertexElement::getTypeSize(VET_FLOAT3);
decl->addElement(0, offset, VET_FLOAT3, VES_NORMAL);
offset += VertexElement::getTypeSize(VET_FLOAT3);
/// Allocate vertex buffer of the requested number of vertices (vertexCount)
/// and bytes per vertex (offset)
HardwareVertexBufferSharedPtr vbuf =
HardwareBufferManager::getSingleton().createVertexBuffer(
offset, msh->sharedVertexData->vertexCount, HardwareBuffer::HBU_STATIC_WRITE_ONLY);
/// Upload the vertex data to the card
vbuf->writeData(0, vbuf->getSizeInBytes(), vertices, true);
/// Set vertex buffer binding so buffer 0 is bound to our vertex buffer
VertexBufferBinding* bind = msh->sharedVertexData->vertexBufferBinding;
bind->setBinding(0, vbuf);
// 2nd buffer
offset = 0;
decl->addElement(1, offset, VET_COLOUR, VES_DIFFUSE);
offset += VertexElement::getTypeSize(VET_COLOUR);
/// Allocate vertex buffer of the requested number of vertices (vertexCount)
/// and bytes per vertex (offset)
vbuf = HardwareBufferManager::getSingleton().createVertexBuffer(
offset, msh->sharedVertexData->vertexCount, HardwareBuffer::HBU_STATIC_WRITE_ONLY);
/// Upload the vertex data to the card
vbuf->writeData(0, vbuf->getSizeInBytes(), colours, true);
/// Set vertex buffer binding so buffer 1 is bound to our colour buffer
bind->setBinding(1, vbuf);
/// Allocate index buffer of the requested number of vertices (ibufCount)
HardwareIndexBufferSharedPtr ibuf = HardwareBufferManager::getSingleton().
createIndexBuffer(
HardwareIndexBuffer::IT_16BIT,
ibufCount,
HardwareBuffer::HBU_STATIC_WRITE_ONLY);
/// Upload the index data to the card
ibuf->writeData(0, ibuf->getSizeInBytes(), faces, true);
/// Set parameters of the submesh
sub->useSharedVertices = true;
sub->indexData->indexBuffer = ibuf;
sub->indexData->indexCount = ibufCount;
sub->indexData->indexStart = 0;
/// Set bounding information (for culling)
msh->_setBounds(AxisAlignedBox(-100,-100,-100,100,100,100));
msh->_setBoundingSphereRadius(Math::Sqrt(3*100*100));
/// Notify -Mesh object that it has been loaded
msh->load();
}
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre HardwareBuffer
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre HardwareBuffer
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre HardwareBuffer
- OGRE -- HardwareBuffer创建Mesh
- [转]Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- Ogre HardwareBuffer [翻译]
- HardwareBuffer 的 shadow buffer
- Ogre
- ogre
- OGRE
- OGRE
- JAVA里怎样对指定目录的文件按文件名排序
- 更好的理解一门语言是学习其他语言
- LINUX 常见问题1000个详细解答[转载]
- 怎样在Java里取得满足条件的文件列表
- Ogre 1.7 SDKTRAY 初探
- Ogre:Hardwarebuffer
- C学习笔记 11 指针的减法
- Jbpm4.4集成SSH
- 湖师大ACM校赛总结
- 感谢所有必须感谢的...
- chapter 3 学习
- 向着第二层 第一阶段第二天
- SQL附加数据库时出现了错误602,提示“对sysindexes运行DBCC CHECKTABLE” 的解决办法
- C++内嵌代码使用压缩的方法(compress和uncompress函数)需要有zlib,编译时加-lz


