NTP 协议
来源:互联网 发布:windows hello 不可用 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 23:34
NTP: Network Time Protocal
一、定义:
为实现高精确度的时间同步,而设计的网络时钟同步协议。在Linux系统中,它的最新实现是NTP 4.0(一个分布式的网络时钟同步程序)。相关定义和实现参看RFC1305和www.ntp.org。NTP协议属于应用层协议,是用于在分布式时间服务器和客户端之间进行时间同步的,它定义了协议实现过程中所使用的结构、算法、实体和协议。NTP协议是基于IP和UDP的,也可以被其它协议组使用。NTP是从时间协议(TIME PROTOCOL)和ICMP 时间戳报文(ICMPTIMESTAMP MESSAGE)演变而来,主要是从准确性和强壮性方面进行了特殊的设计。
NTP的优点:
采用分层的方法来定义时钟的准确性,可以迅速同步网络中各 台设备的时间。
支持访问控制和MD5验证。
可以选择采用单播、广播或组播发送协议报文。

图1 NTP 工作原理
上图1所示的是NTP基本工作原理,路由器A和路由器B通过网络相连,它们都有自己独立的系统时钟,要实现各自系统时钟的自动同步,作如下假设:
路由器A和B的系统时钟同步之前,路由器A的时钟设定为10:00:00am,路由器B的时钟设定为11:00:00am。
以路由器B为NTP时间服务器,即路由器A将使自己的时钟与路由器B的时钟同步。
数据包在路由器A和B之间单向传输所需要的时间为1秒。
系统时钟同步的工作过程如下:
路由器A发送一个NTP消息包给路由器B,该消息包带有它离开路由器A时的时间戳,该时间戳为10:00:00am(T1)。
当此NTP消息包到达路由器B时,路由器B加上自己的时间戳,该时间戳为11:00:01am(T2)。
当此NTP消息包离开路由器B时,路由器B再加上自己的时间戳,该时间戳为11:00:02am(T3)。
当路由器A接收到该响应消息包时,加上一个新的时间戳,该时间戳为10:00:03am(T4)。
至此,RouterA 拥有足够信息来计算以下两个重要参数:
NTP 消息来回一个周期的时延:Delay=(T4-T1)-(T3-T2)。
RouterA 相对RouterB 的时间差:Offset=((T2-T1)+(T3-T4))/2。
RouterA 根据这些信息来设定自己的时钟,实现与RouterB 的时钟同步。
NTP的四种工作模式:
服务器 / 客户模式(server / client)
这种模式只需要在客户端配置,服务器端除了配置NTP 主时钟外,不需要进行其他专门配置。并且,只能是客户端同步到服务器,服务器不会同步到客户端。
配置完成后:
客户端向服务器发送同步请求报文,报文中的 Mode 字段设置为3(客户模式)。
服务器端收到请求报文后,自动工作在服务器模式,并发送应答报文,报文中的
Mode 字段设置为4(服务器模式)。
客户端收到应答报文后,进行时钟过滤和选择,并同步到优选的服务器端。
对等体模式(symmetric active / symmetric passive)
在对等体模式中,只需要在主动对等体(Symmetric active)端进行配置,被动对等体
(Symmetric passive)端无需配置NTP 命令。对等体模式下,主动对等体和被动对等体可以互相同步,等级低(层数大)的对等体向等级高(层数小)的对等体同步。
配置完成后:
主动对等体向被动对等体发送同步请求报文,报文中的 Mode 字段设置为1(主动对等体)。
被动对等体收到请求报文后,自动工作在被动对等体模式,并发送应答报文,报文中的Mode 字段设置为2(被动对等体)。
广播模式(broadcast server / broadcast client)
在广播模式下,服务器端和客户端都需要配置相关命令。配置完成后:
服务器端周期性向广播地址 255.255.255.255 发送时钟同步报文。
客户端侦听来自服务器的广播消息包。
客户端接收到第一个广播消息包后,为估计网络延迟,客户端先启用一个短暂的服务器/客户端模式与远程服务器交换消息。
然后,客户端进入广播客户端模式,继续侦听广播消息包的到来,根据到来的广播消息包对本地时钟进行同步。
组播模式(multicast server / multicast client)
在组播模式下,服务器端和客户端都需要配置相关命令。配置完成后:
服务器端周期性向组播目的地址 224.0.1.1 发送时钟同步报文。
客户端侦听来自服务器的组播消息包。
当客户端接收到第一个组播消息包后,为估计网络延迟,客户端先启用一个短暂的服务器/客户端模式与远程服务器交换消息。
然后,客户端进入组播客户端模式,继续侦听组播消息包的到来,根据到来的组播消息包对本地时钟进行同步。
NTP的工作模式MODE。不同值表示的含义如下:
0:reserved,保留
1:symmetric active,主动对等体模式
2:symmetric passive,被动对等体模式
3:client,客户模式
4:server,服务器模式
5:broadcast,广播模式
6:reserved for NTP control messages,NTP 控制报文
7:reserved for private use,内部使用预留
我们采用第一和第二种模式。
NTP网络结构
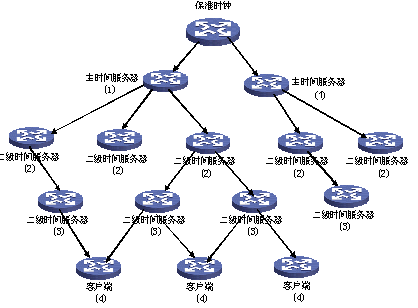
图2 NTP树形网络结构(同层之间还可以互联同步,这样更稳定)
NTP模型中,多个通过有线或无线系统与国家标准时钟同步的主 参考源被连接到网络内被广泛访问的资源,如:骨干网关,这些主参考源作为主时间服务器运行在网络中。NTP的目的就是通过INTERNET将这些主时间服务器的计时信息传送到其它时间服务器,并且反复核对时钟以减少由于仪器或传播失误而产生的误差。另外一些局网内部的运行NTP的主机或网关,作为二级时间服务器运行在网络中。二级时间服务器通过NTP将时间信息传送到局网内部的其它主机。为了提高可靠性,可以在被选择的主机上配备准确性较低但比较便宜的RADIO CLOCK作为备份,以备主参考服务器和/或次级时间服务器出错或者是主机与时间服务器之间的通信发生故障时使用。
二 、NTP实现介绍(Linux下)
ntpd :NTP Demaon程序:
ntpd是开机自启动的服务,会自动和远端的同步服务器进行时间的同步,注意:和ntpdate不同的是,它是慢同步,而ntpdate是立即同步。使用ntpd同步的好处对于那些对时间稳定性要求高的服务,可以提供缓慢稳定的时间
变化,而不是一步改变。
ntp.conf配置文件说明:ntp.conf文件里面配置的是一些访问安全策略和ntp命令。具体如下:
主要的命令和选项说明
1 Access Control Options
1.1 discard设置速率控制,保护NTP服务器受客户端过多的干扰。
discard [average vag] [minimum min] [monitor prob]
vag: 规定最小的平均包间隙时间,以log2的形式,单位为妙,默认值是3
min: 规定最小的包间隙时间,形式如上
prob:规定最近收到包超过最大接受单元MRU的概率。用于优化性能。
1.2 restrict设置访问控制的策略
restrict default [flag][...] 必须是第一个,对所有的(address 0.0.0.0, mask 0.0.0.0 for IPv4 and address :: mask :: for IPv6)默认的规定
restrict source [flag][...] 对source的规定
restrict address [mask mask] [flag][...] 对网络address的规定
address:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx形式的主机或网络地址,也可以是dns名字。
mask :掩码,全1 指明address是一个主机地址
常见的flag:
flake: 以0.1的概率丢弃NTP包,测试用。
ignore :拒绝所有的包,包括ntpq和ntpdc的查询包。
kod : 如果设置了limited标识和使用discard命令控制速率,则返回一个Kod(kiss-O'-death)包。
limited : 拒绝服务,如果数据包超过了diacard设置的速率。对ntpq和ntpdc不起作用。
lowpriotrap:对匹配的主机的trap设置低优先级。
mssntp :启动Microsoft的简单ntp协议
nomodify:拒绝ntpq和ntpdc的修改消息。时间同步服务不受影响
noquery : 拒绝ntpq和ntpdc的查询,时间同步服务不受影响
nopeer :拒绝没有认证的消息包,主要针对association相关的包。
noserve :拒绝除ntpq和ntpdc的消息报文。
notrap :拒绝对匹配主机提供Mode 6的控制消息服务。
notrust :拒绝对不经过加密验证的包服务
ntpport :拒绝对源端口是NTP指定端口123的数据包服务
version :拒绝对非当前版本的数据包服务
1.3 例子
An example may clarify how it works. Our campus has twoclass-B networks, 128.4 for the ECE and CIS departments and 128.175 forthe rest of campus. Let's assume (not true!) that subnet 128.4.1 homescritical services like class rosters and spread sheets. A suitable ACLmight be
restrict default nopeer # deny new associations
restrict 128.175.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 # allow campus access
restrict 128.4.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 none # allow ECE and CIS access
restrict 128.4.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 notrust # require authentication on subnet 1
restrict time.nist.gov
2 Reference Clock Commands 参考时钟(主时钟)命令
2.1 配置参考时钟
server 127.127.t.u [prefer] [mode int] [minpoll int] [maxpoll int]
prefer :将参考时钟设为首选
mode :规定模式的值
minpoll和maxpoll :规定查询的间隔,以2的幕的形式。取值范围在4-17。minpoll和maxpoll默认值都是6,即2的6次方=64秒。对应Modem的参考时钟,minpoll去10,即17.1分钟,maxpoll默认值是14,即4.5小时。
2.2 配置参考时钟的其他信息,必须紧跟着server后面
fudge 127.127.t.u [time1 sec] [time2 sec] [stratum int] [refid string] [flag1 0|1] [flag2 0|1] [flag3 0|1] [flag4 0|1]
time1 : 常数,用来调成偏移offset值
time2 : 设置一个固点的小数,这个与驱动无关。
stratum : 设置一个0-15的一个层数。值越小,表明离时间源更近,更准确。
refid : 设置ASCII形式的字符串ID。
3 Server Command
3.1 配置命令: 规定时间服务器的地址即操作模式。
server address [options ...]
peer address [options ...]
broadcast address [options ...]
manycastclient address [options ...]
pool address [options ...]
unpeer [address | associd]
server : 以c/s模式,与远程的服务器或本地参考时钟持续的调整时间
peer : 以symmetric-active模式,与远端的节点同步时间。即同层的节点间同步,可以增加稳定性。
broadcast:对广播和多播地址,调整
manycastclient: 根据多播组的地址进行调整。
pool : 调整与以DNS名字规定的池的关联。
unpeer : 根据地址或ID,移除以前注册的关联,可以用ntpq在运行时配置。
注:server 与 peer的区别:server是上一级的时间服务器。peer是同级的同步节点。
options说明:
autokey :发送和接受经过Autokey机制验证的数据包
burst :当server可达时,以默认发包速率的8倍向服务器发包。
iburst : 当server不可达时,以默认发包速率的8倍向服务器发包。
key :发送和接受经过symmetric key机制验证的数据包.
prefer : 设置首选
ttl :为多播和广播数据包设置ttl
version :设置version number。1-4,默认值是4
preempt :设置关联为可抢占式的。
noselect :标识server 或peer 不执行selection算法,即不会被选择作为源来同步时间
其他命令
broadcastclient :enable broadcast client
manycastserver address [...] : enable manycast server
multicastclient address [...] : enable multicast client
4 Miscellaneous Commands
broadcastdelay - specify broadcast delay
driftfile - specify frequency file
enable - enable options
disable - disable options
includefile - specify include file
interface - specify which local network addresses to use
leapfile - specify leapseconds file
logconfig - configure log file
nic - alias for interface
mru - control monitor MRU list limits
phone - specify modem phone numbers
saveconfigdir - specify saveconfig directory
setvar - set system variables
tinker - modify sacred system parameters (dangerous)
tos - modify service parameters
trap - set trap address
ttl - set time to live
5 同步服务器的挑选标准
3 Association Management:ntpv4中有不同的模式,
ntp相关程序的参考帮助网站:http://www.eecis.udel.edu/~mills/ntp/html/ntpdc.html
ntpq 命令查看:
Runntpq -p HOSTNAME, or one of the web-based utilities at 9.5. On-lineTroubleshooting Utilities, to see the status of ntpd on HOSTNAME(without HOSTNAME the local host is queried). Check the officialdocumentation for a detailed description of the ntpq utility (http://www.eecis.udel.edu/~mills/ntp/html/ntpq.html). It will report something like this:
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
ff05::101 .MCST. 16 u - 64 0 0.000 0.000 4000.00
*example.site.co .PPS. 1 u 320 1024 377 1.955 -1.234 1.368
第一个特殊字母的意思:
contains the "tally code" character. Short overview:
* the source you are synchronized to (syspeer)
o the PPS source if your ntpd (ppspeer, only if you have a PPS capable system and refclock)
+ candidate, i.e. it is considered a good source
- outlyer, i.e. quality is not good enough
x falseticker, i.e. this one is considered to distriute bad time
Seethe Select field of the Peer status word on the NTP Event Messages andStatus Words page for more information on the tally codes.
remote :the hostname or IP of the remote machine.
refid: the identification of the time source to which the remotemachines is synced. May be (for example) a radio clock or another ntpserver)
st: the stratum of the remote machine. 16 is "unsynchronized". 0 isthe best value, that could be (for example) a radio clock or the ntpservers private caesium clock (see http://www.eecis.udel.edu/~mills/ntp/html/index.html#intro for more information about ntp in general).
when: how many seconds since the last poll of the remote machine.
poll :the polling interval in seconds.
reach :an 8-bit left-rotating register. Any 1 bit means that a "time packet" was received.
delay :the time delay (in milliseconds) to communicate with the remote.
offset :the offset (in milliseconds) between our time and that of the remote.
jitter :the observed jitter (in milliseconds) of time with the remote.
ntpdc
格式:ntpdc [ -ilnps ] [ -c command ] [ host ] [ ... ]
查询ntpd 关于当前状态,并要求修改状态。可以运行在交互模式和命令行模式。ntpd的几乎所有配置,都可以通过ntpdc在运行时来配置。
ntptrace
注意事项:
1 不推荐使用 utpdate 来同步时间
2 ntpd要尽早启动起来,在net和dns服务之后,在时间要求高的服务之前。
3 避免DNS启动慢,应尽量使用同步源的IP Address,而不是域名。
4 NTP中address分为4类:
type 定义
s ABC类单播地址
b broadcast
m multicast
r 127.124.x.x
疑问:
1 通过ntpq命令,我们可以查看当前各个时间源服务器的状态已经当前主机在和谁进行同步。问题是,ntpd能否做到这点,会不会对一个时间有问题的源进行同步?
2 目前我们NTP同步服务器网络部署情况?采取的拓扑结构?建议采用树形,并且同层同步的模式,这样更加稳定,即使上层服务器出问题,也可以减小影响。
- NTP 协议
- NTP 协议
- NTP协议
- NTP协议
- NTP协议
- NTP协议
- NTP协议
- Linux NTP协议
- NTP协议原理简介
- NTP协议实现
- NTP协议原理简介
- NTP协议实现
- 网络协议之NTP
- NTP网络时间协议
- NTP协议解析
- NTP协议与计算
- ntp协议及客户端开发
- NTP网络校时协议
- foreach
- MSF for CMMI Process Improvement 5.0学习之CMMI背景信息
- 查看服务器性能
- c++引用
- ASP.NET页面事件:顺序与回传详解
- NTP 协议
- 在VC6中使用CDialogBar类
- C++ using namespace std 详解
- testtt
- Web Spam相关实验室与学者
- 对于HBase的理解
- sln------------------unrecognized version
- Response.Write后页面刷新字体变大
- javascript高级程序设计 -- 读书笔记(三)


