hdu 4069 squiggly sudoku
来源:互联网 发布:网络歌曲 什么什水自流 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/19 17:07
Squiggly Sudoku
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 691 Accepted Submission(s): 291
Problem Description
Today we play a squiggly sudoku, The objective is to fill a 9*9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each of the nine Connecting-sub-grids that compose the grid contains all of the digits from 1 to 9.
Left figure is the puzzle and right figure is one solution.
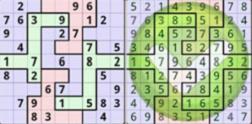
Now, give you the information of the puzzle, please tell me is there no solution or multiple solution or one solution.
Left figure is the puzzle and right figure is one solution.

Now, give you the information of the puzzle, please tell me is there no solution or multiple solution or one solution.
Input
The first line is a number T(1<=T<=2500), represents the number of case. The next T blocks follow each indicates a case.
Each case contains nine lines, Each line contains nine integers.
Each module number tells the information of the gird and is the sum of up to five integers:
0~9: '0' means this gird is empty, '1' - '9' means the gird is already filled in.
16: wall to the up
32: wall to the right
64: wall to the down
128: wall to the left
I promise there must be nine Connecting-sub-grids, and each contains nine girds.
Each case contains nine lines, Each line contains nine integers.
Each module number tells the information of the gird and is the sum of up to five integers:
0~9: '0' means this gird is empty, '1' - '9' means the gird is already filled in.
16: wall to the up
32: wall to the right
64: wall to the down
128: wall to the left
I promise there must be nine Connecting-sub-grids, and each contains nine girds.
Output
For each case, if there are Multiple Solutions or no solution just output "Multiple Solutions" or "No solution". Else output the exclusive solution.(as shown in the sample output)
Sample Input
3144 18 112 208 80 25 54 144 48135 38 147 80 121 128 97 130 32137 32 160 144 114 167 208 0 32192 100 160 160 208 96 183 192 101209 80 39 192 86 48 136 80 114152 48 226 144 112 160 160 149 48128 0 112 166 215 96 160 128 41128 39 153 32 209 80 101 136 35192 96 200 67 80 112 208 68 96 144 48 144 81 81 16 53 144 48128 96 224 144 48 128 103 128 38163 208 80 0 37 224 209 0 32135 48 176 192 64 112 176 192 104192 101 128 89 80 82 32 150 48149 48 224 208 16 48 224 192 33128 0 114 176 135 0 80 112 169137 32 148 32 192 96 176 144 32192 96 193 64 80 80 96 192 96144 88 48 217 16 16 80 112 176224 176 129 48 128 40 208 16 37145 32 128 96 196 96 176 136 32192 32 227 176 144 80 96 192 32176 192 80 98 160 145 80 48 224128 48 144 80 96 224 183 128 48128 36 224 144 51 144 32 128 105131 64 112 136 32 192 36 224 176224 208 80 64 64 116 192 83 96
Sample Output
Case 1:521439678763895124984527361346182795157964832812743956235678419479216583698351247Case 2:No solutionCase 3:Multiple Solutions
Source
The 36th ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Fuzhou Site —— Online Contest
Recommend
lcy
数独,与普通数独不同的是把传统的数独的 3*3 的九宫换成了 9 格相连的奇怪图形;同样要求在这 9 个格子里数字不重复,行不重复,列不重复。
给不同的九个奇怪图形标号 0 到 8 就行了。然后用搜索,一直 TLE,用了各种加速手段。。。
后来用了DLX,一开始还是 TLE,最后牺牲了一下代码的优雅度,把一个 return 提到循环内,终于 AC 了,我了个去,数据真 BT。
好吧,做过这一题之后也算有所收获吧。
有了 DLX 模板了,虽然是连偷带抄,但也是自己一行一行打,调试出来的;
也看了 Knuth 的 Algoritm X,明白了有一些问题可以转化成 Extra Cover Problem 用 Algorithm X 来解决,这时就可以让 DLX 发挥威力啦。
#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <cassert>using namespace std;#define ROWS_MAX (9*9*9 + 1)#define COLS_MAX (9*9*4 + 1)#define NODES_MAX (ROWS_MAX * COLS_MAX + COLS_MAX + 1)#define ON_BACKTRACKED() \ do {if (slns >= 2) return;} while (0)struct DLX { /* * 'U', 'D', 'L', 'R', 'S' are notations from Knuth's paper. * 'col' access a node's column number; * 'row' access a node's row number. */ int U [NODES_MAX]; int D [NODES_MAX]; int L [NODES_MAX]; int R [NODES_MAX]; int S [NODES_MAX]; int col [NODES_MAX]; int row [NODES_MAX]; int nodes; int rows, cols; int sln [ROWS_MAX]; // solution for 'Extra Cover Problem' int tryingSln [ROWS_MAX]; // the trying solution int slns; // number of solutions int slnElems; // number of elements in the saved solution 'sln'#ifdef _DEBUG int treeSize;#endif int AddNode (int up, int down, int left, int right) { U [nodes] = up; D [nodes] = down; L [nodes] = left; R [nodes] = right; D [up] = U [down] = L [right] = R [left] = nodes; return nodes++; } void Init (int (*mat)[COLS_MAX], int rs, int cs) { rows = rs; cols = cs; nodes = 0; AddNode (0, 0, 0, 0); for (int i=1; i<=cols; ++i) { row[i] = 0; col[i] = i; AddNode (i, i, L[0], 0); } memset (S, 0, sizeof (S)); for (int i=1; i<=rows; ++i) { int added = -1; for (int k=1; k<=cols; ++k) { if (! mat [i][k]) { continue; } if (added == -1) { added = AddNode (U[k], k, nodes, nodes); } else { added = AddNode (U[k], k, added, R[added]); } ++S[k]; row[added] = i; col[added] = k; } } } void Cover (int c) { L[R[c]] = L[c]; R[L[c]] = R[c]; for (int r=D[c]; r!=c; r=D[r]) { for (int x=R[r]; x!=r; x=R[x]) { --S[col[x]]; U[D[x]] = U[x]; D[U[x]] = D[x]; } } } void Uncover (int c) { for (int r=U[c]; r!=c; r=U[r]) { for (int x=L[r]; x!=r; x=L[x]) { ++S[col[x]]; D[U[x]] = x; U[D[x]] = x; } } R[L[c]] = c; L[R[c]] = c; }#ifdef _DEBUG void PrintCol (int c) { printf ("col %d:\n", c); for (int i=D[c]; i!=c; i=D[i]) { printf ("=>(%d [%d] %d)<=", L[i], i, R[i]); } printf ("\n"); } void Print () { for (int i=1; i<=cols; ++i) { PrintCol (i); } }#endif void AlgorithmX (int depth) {#ifdef _DEBUG //Print(); ++treeSize;#endif if (R[0] == 0) { // return succefully ++slns; slnElems = depth; memcpy (sln, tryingSln, sizeof (sln)); return; } int minSCol = R[0]; for (int c=R[0]; c!=0; c=R[c]) { if (S[c] < S[minSCol]) { minSCol = c; } } if (S[minSCol] == 0) { // return failed return; } Cover (minSCol); for (int r=D[minSCol]; r!=minSCol; r=D[r]) { for (int c=R[r]; c!=r; c=R[c]) { Cover (col[c]); } tryingSln[depth] = row[r]; AlgorithmX (depth + 1); ON_BACKTRACKED(); for (int c=L[r]; c!=r; c=L[c]) { Uncover (col[c]); } } Uncover (minSCol); }};#define UWALL(x) ((x) & 16)#define RWALL(x) ((x) & 32)#define DWALL(x) ((x) & 64)#define LWALL(x) ((x) & 128)#define NO(x) ((x) & ~16 & ~32 & ~64 & ~128)int sudoku[9][9];int block[9][9];DLX dlx;void FloodFill (int row, int col, int no) { assert (0 <= row && row < 9); assert (0 <= col && col < 9); if (block[row][col] != -1) { return; } block[row][col] = no; if (! UWALL(sudoku[row][col])) { FloodFill (row - 1, col, no); } if (! RWALL(sudoku[row][col])) { FloodFill (row, col + 1, no); } if (! DWALL(sudoku[row][col])) { FloodFill (row + 1, col, no); } if (! LWALL(sudoku[row][col])) { FloodFill (row, col - 1, no); }}#ifdef _DEBUGvoid PrintSudoku () { printf ("\n"); for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { printf ("%s", UWALL(sudoku[i][k]) ? "+---" : " "); } printf ("\n"); for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { printf ("%s %d ", LWALL(sudoku[i][k]) ? "|" : " ", NO(sudoku[i][k])); } printf ("\n"); } printf ("\n");}void PrintBlock () { printf ("\n"); for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { printf ("%2d%s", block[i][k], k==8 ? "\n" : ""); } } printf ("\n");}#endifvoid Solve () { for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { if (scanf ("%d", &sudoku[i][k]) == EOF) { return; } } } // devide the chess board into 9 blocks, numbered 0, 1, ..., 8. memset (block, -1, sizeof (block)); int b = 0; for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { if (block[i][k] == -1) { FloodFill (i, k, b++); } } } assert (b == 9);#ifdef _DEBUG //PrintSudoku(); //PrintBlock();#endif // the following procedure checks whether the sudoku is solvable. bool isCovered[4 * 9 * 9 + 1]; memset (isCovered, 0, sizeof (isCovered)); bool isSolvable = true; for (int i=0; i<9 && isSolvable; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9 && isSolvable; ++k) { int no = NO(sudoku[i][k]); if (! no) { continue; } isCovered[i * 9 + k + 1] = true; if (isCovered[81 + block[i][k] * 9 + no]) { isSolvable = false; } else { isCovered[81 + block[i][k] * 9 + no] = true; } if (isCovered[81 * 2 + i * 9 + no]) { isSolvable = false; } else { isCovered[81 * 2 + i * 9 + no] = true; } if (isCovered[81 * 3 + k * 9 + no]) { isSolvable = false; } else { isCovered[81 * 3 + k * 9 + no] = true; } } } static int cs = 0; if (! isSolvable) { printf ("Case %d:\nNo solution\n", ++cs); return; } /* * the following procedure transform the sudoku into a 'Extra Cover Problem' * so that we can run the 'Algorithm X' and take advantage of 'DLX'. */ int mat[9 * 9 * 9 + 1][4 * 9 * 9 + 1]; memset (mat, 0, sizeof (mat)); for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { for (int n=0; n<9; ++n) { mat[i*81 + k*9 + n + 1][i*9 + k + 1] = 1; mat[i*81 + k*9 + n + 1][81 + block[i][k]*9 + n + 1] = 1; mat[i*81 + k*9 + n + 1][81*2 + i*9 + n + 1] = 1; mat[i*81 + k*9 + n + 1][81*3 + k*9 + n + 1] = 1; } } } dlx.Init (mat, 9 * 9 * 9, 4 * 9 * 9); for (int i=1; i<=4*9*9; ++i) { if (isCovered[i]) { dlx.Cover (i); } }#ifdef _DEBUG dlx.treeSize = 0;#endif dlx.slns = 0; dlx.AlgorithmX (0);#ifdef _DEBUG printf ("tree size = %d\n", dlx.treeSize);#endif if (dlx.slns <= 0) { printf ("Case %d:\nNo solution\n", ++cs); return; } if (dlx.slns >= 2) { printf ("Case %d:\nMultiple Solutions\n", ++cs); return; } printf ("Case %d:\n", ++cs); for (int i=0; i<dlx.slnElems; ++i) { int n = dlx.sln[i] - 1; int r = n / 81; int c = n / 9 % 9; n = n % 9 + 1; assert (! NO(sudoku[r][c])); sudoku[r][c] |= n; } for (int i=0; i<9; ++i) { for (int k=0; k<9; ++k) { assert (NO(sudoku[i][k])); printf ("%d%s", NO(sudoku[i][k]), k==8 ? "\n" : ""); } }}int main () { int cs; scanf ("%d", &cs); while (cs--) { Solve(); } return 0;}- hdu 4069 squiggly sudoku
- HDU 4069 Squiggly Sudoku
- HDU 4069 Squiggly Sudoku DLX
- HDU 4069 Squiggly Sudoku DLX 精确覆盖
- [DLX+bfs] hdu 4069 Squiggly Sudoku
- 【dfs预处理+DLX】hdu 4069 Squiggly Sudoku
- HDU 4069 Squiggly Sudoku 数独DLX 福州网络赛
- HDU 4069 Squiggly Sudoku【Dancing Links精确覆盖】
- HDU 4069 Squiggly Sudoku Dancing-Links(DLX)+Floodfill
- HDOJ 4069 Squiggly Sudoku 精确覆盖+搜索
- hdu 4069 Squiggly Sudoku——11年福州网络赛DLX
- hdu4069 Squiggly Sudoku
- HDU4069-Squiggly Sudoku
- DLX精确覆盖 hdu4069 Squiggly Sudoku
- Sudoku HDU
- HDU 1426 Sudoku Killer
- HDU 1426 Sudoku Killer
- hdu 1426 Sudoku Killer
- 实习中的问题(一)
- Ubuntu下GCC之libpcap库数据库通信协议解析基础框架代码
- 降落伞原则
- 数据在内存的存放
- 如何让TortoiseSVN仅导出新增或修改过(变更过)的文件
- hdu 4069 squiggly sudoku
- oracle点滴
- shell中的系统变量
- winForm listview 添加进程项目
- Fedora中配置SSH
- UILocalNotification实现本地的闹钟提醒的方法
- Netlink系列2Netlink socket地址结构
- SharedPreferences的用法
- Sql 每月,每日,每年统计


