Download it – Struts2-Spring-Integration-Example.zip
In this tutorial, it shows the integration between Struts 2 and Spring.
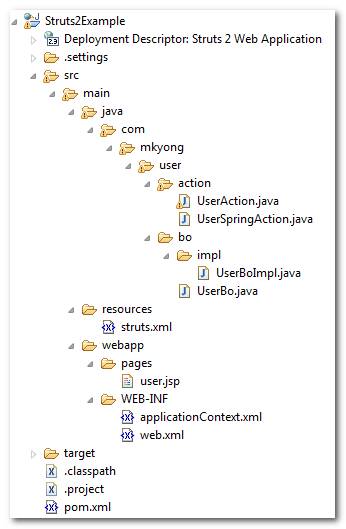
1. Project Structure
Here’s the project folder structure of this tutorials.
2. Struts 2 + Spring Plugin
To integrate Struts 2 and Spring, get and include the “struts2-spring-plugin-xxx.jar” library into your project classpath.
pom.xml
<!-- Struts 2 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId> <artifactId>struts2-core</artifactId> <version>2.1.8</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring framework --> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring</artifactId><version>2.5.6</version></dependency> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-web</artifactId><version>2.5.6</version></dependency> <!-- Struts 2 + Spring plugins --><dependency> <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId> <artifactId>struts2-spring-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.1.8</version> </dependency>
3. Spring Listener
Configure the Spring listener “org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener” in web.xml file.
web.xml
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app> <display-name>Struts 2 Web Application</display-name> <filter><filter-name>struts2</filter-name><filter-class> org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter </filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping><filter-name>struts2</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
3. Register Spring Bean
Register all the Spring’s Beans in the applicationContext.xml file, the Spring listener will locate this xml file automatically.
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="userBo" class="com.mkyong.user.bo.impl.UserBoImpl" /> <bean id="userSpringAction" class="com.mkyong.user.action.UserSpringAction"><property name="userBo" ref="userBo" /></bean> </beans>
UserBo.java
package com.mkyong.user.bo; public interface UserBo{ public void printUser(); }UserBoImpl.java
package com.mkyong.user.bo.impl; import com.mkyong.user.bo.UserBo; public class UserBoImpl implements UserBo{ public void printUser(){System.out.println("printUser() is executed...");} }UserSpringAction.java
package com.mkyong.user.action; import com.mkyong.user.bo.UserBo; public class UserSpringAction{ //DI via SpringUserBo userBo; public UserBo getUserBo() {return userBo;} public void setUserBo(UserBo userBo) {this.userBo = userBo;} public String execute() throws Exception { userBo.printUser();return "success"; }}5. Struts.xml
Declared all the relationship here.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN""http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" /> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="userAction" class="com.mkyong.user.action.UserAction" ><result name="success">pages/user.jsp</result></action> <action name="userSpringAction" class="userSpringAction" ><result name="success">pages/user.jsp</result></action> </package> </struts>
6. Demo
Now, all the Struts 2 and Spring integration work is done, now see the following use case to access the Spring’s “userBo” bean.
- Case 1 : Make Spring act as the Struts 2 Action class, and access the Spring’s bean.
- Case 2 : Access the Spring’s bean in Struts 2 Action class.
Case 1
In this example, the userSpringAction is act as the Struts 2 Action class, and you can DI the Spring’s userBo bean with normal Spring’s way.
//struts.xml<action name="userSpringAction" class="userSpringAction" ><result name="success">pages/user.jsp</result></action> //applicationContext.xml<bean id="userSpringAction" class="com.mkyong.user.action.UserSpringAction"><property name="userBo" ref="userBo" /></bean>
To access this action, use the URL : http://localhost:8080/Struts2Example/userSpringAction
Case 2
By default, Spring listener enables “autowiring by matching the bean name“. So, it will pass the Spring’s “userBo” bean into the UserAction via setUserBo() automatically. See below Struts 2 Action :
The Spring’s autowiring feature can change to name(default), type, auto or constructor, you may need to consult this Struts 2 Spring plugin documentation.
UserAction.java
package com.mkyong.user.action; import com.mkyong.user.bo.UserBo;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class UserAction extends ActionSupport{ //DI via SpringUserBo userBo; public UserBo getUserBo() {return userBo;} public void setUserBo(UserBo userBo) {this.userBo = userBo;} public String execute() throws Exception { userBo.printUser();return SUCCESS; }}To access this action, use the URL : http://localhost:8080/Struts2Example/userAction
WebApplicationContextUtilsAlternatively, you can use the Spring’s generic
WebApplicationContextUtils class to get the Spring’s bean directly.
package com.mkyong.user.action; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils; import com.mkyong.user.bo.UserBo;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class UserAction extends ActionSupport{ public String execute() throws Exception { WebApplicationContext context =WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext( ServletActionContext.getServletContext() ); UserBo userBo1 = (UserBo)context.getBean("userBo");userBo1.printUser(); return SUCCESS; }} A really long and tedious article, make sure you download the full project source code for practice.