牛顿迭代例子Newton-Raphson Method
来源:互联网 发布:梭哈网络用语啥意思 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/12 20:17
Aim: Find oˆ such that
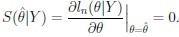
Problem: Analytic solution of likelihood equations not always available.
Example: Censored exponentially distributed observations
Suppose that 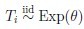 and that the censored times
and that the censored times
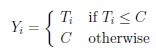
are observed. Let m be the number of uncensored observations. Then
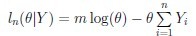
with first and second derivative

Thus we obtain for the observed and expected information
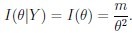
Thus the MLE can be obtained be the Newton-Raphson iteration
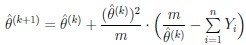
Numerical example: Choose starting value in (0, 1)
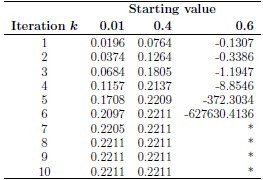
Implementation in R:
#Statistics 24600 - Spring 2004#Instructor: Michael Eichler##Method : Newton-Raphson method#Example: Exponential distribution#----------------------------------#Log-likelihood with first and second derivativeln<-function(p,Y,R) { m<-sum(R==1) ln<-m*log(p)-p*sum(Y) attr(ln,"gradient")<-m/p-sum(Y) attr(ln,"hessian")<--m/p^2 ln}#Newton-Raphson methodnewmle<-function(p,ln) { l<-ln(p) pnew<-p-attr(l,"gradient")/attr(l,"hessian") pnew}#Simulate censored exponentially distributed dataY<-rexp(10,1/5)R<-ifelse(Y>10,0,1)Y[R==0]=10#Plot first derivative of the log-likelihoodx<-seq(0.05,0.6,0.01)plot(x,attr(ln(x,Y,R),"gradient"),type="l", xlab=expression(theta),ylab="Score function")abline(0,0)#Apply Newton-Raphson iteration 3 timesp<-newmle(p,ln,Y=Y,R=R)pp<-newmle(p,ln,Y=Y,R=R)pp<-newmle(p,ln,Y=Y,R=R)p
- 牛顿迭代例子Newton-Raphson Method
- 牛顿-拉夫逊方法(Newton-Raphson method)
- 牛顿迭代法(牛顿-拉弗森方法(Newton-Raphson method))
- Newton-Raphson method
- 使用牛顿迭代方法(Newton’s method)来估计方程的解
- 牛顿法 Newton Method
- Newton法(牛顿法 Newton Method)
- Newton法(牛顿法 Newton Method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- 牛顿法(Newton's Method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- MATLAB Code For Inverse and Forward Kinematics (Newton-Raphson Method)
- 牛顿法(Newton’s method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- 牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)
- sizeof
- ASP.NET中使用jQGrid
- minigui2.04 海思平台 minigui 多国语言
- ARDrone 1.0 win32程序源码和ARDrone 2.0 C#控制程序源码-----PC控制飞机
- 使用 GDB 调试多进程程序
- 牛顿迭代例子Newton-Raphson Method
- java中使用正则表达式
- C# Form 点击关闭按钮 如何隐藏
- href="#"与href="javascript:void(0)"的区别
- Android_动态壁纸介绍
- 读《经济大棋局,我们怎么办》有感
- Win32ASM-进程学习【2】
- ORA-01704: 文字字符串过长
- jolt大奖图书


