Linux进程学习心得
来源:互联网 发布:ubuntu 安装mysql 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/03 17:14
EG1 : system函数:
NAME system - execute a shell commandSYNOPSIS #include <stdlib.h> int system(const char *command);DESCRIPTION system() executes a command specified in command by calling /bin/sh -c command, and returns after the command has been completed. During exe‐ cution of the command, SIGCHLD will be blocked, and SIGINT and SIGQUIT will be ignored.将一个系统命令(比如是"gvim new_file")以字符串的形式传给system()中的command,system函数执行该命令,就像我们在命令行行中执行:gvim new_file的效果是一样的。以下是一个简单的程序样例:
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<sys/types.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<sys/wait.h>int main(int argc , char **agrv){pid_t pid ;int state ;pid = fork() ;if(pid < 0){printf("Erorr!\n");return -1 ;}if(pid == 0){//子进程system("gvim new_file");exit(0) ;}else{//父进程if( waitpid(pid, &state , 0) !=pid )state = -1 ;//父进程等待子进程执行完之后再继续执行,waitpid函数成功是返回state值改变的在子进程的ID ,错误返回-1printf("The state is : %d\n",state);}return 0;}以下写的这个my_system函数的功能和上面的system是类似的,不过就是自己写的而已:
#include<stdio.h>#include<sys/types.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<sys/wait.h>#define SHELL "/bin/sh"int my_system(const char *command){int state ;pid_t pid ;pid = fork() ;if(pid == 0){//子进程execl(SHELL,SHELL,"-c",command ,NULL);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}else if(pid > 0){//父进程if( waitpid(pid , &state , 0) != pid) state = -1 ;}elsestate = -1 ; return state ;}int main(){printf("This is the return value : %d\n",my_system("gvim creat_new_file"));return 0;}EG2 :多进程和sleep函数
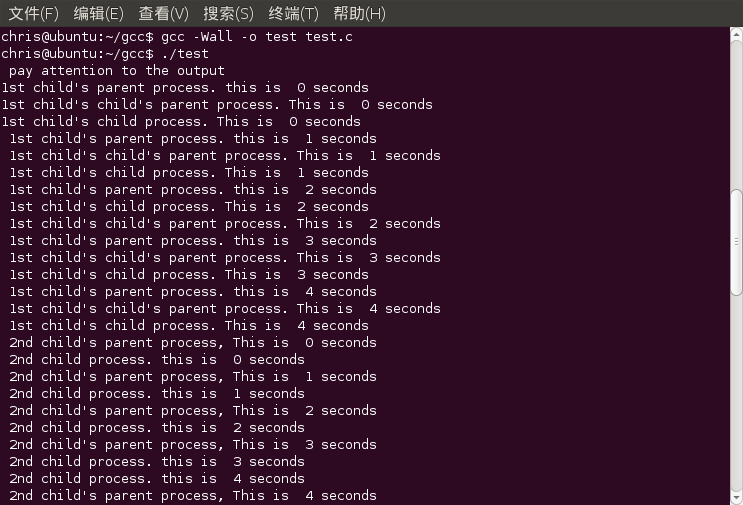
/*Linux进程学习,多进程和sleep函数。2011-12-24Ivan_zjj*/#include<stdio.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<sys/types.h>int main(){int status = 0;pid_t child_1_pid,child_2_pid;child_1_pid = fork(); /* 这是第一个子进程 */if (child_1_pid == 0){ /* 这是第一个子进程的代码 */ pid_t child_child_pid; child_child_pid = fork(); /* 这是第一个子进程的子进程 */ if( child_child_pid == 0){ /* 这是第一个子进程的子进程的代码 */ int child_child_i; for ( child_child_i = 0; child_child_i < 5; child_child_i++){ printf("1st child's child process. This is %2d seconds\n ", child_child_i); sleep(1); /* 注意:修改等待时间,会得到什么结果呢? */ } _exit(0); } else if( child_child_pid > 0 ){ /* 这是第一个子进程的子进程的第一个子进程的代码 */ int child_1_i; for( child_1_i = 0; child_1_i < 5; child_1_i++){ printf("1st child's child's parent process. This is %2d seconds\n ", child_1_i); sleep(1); } _exit(0); } else{ /* 创建第一个子进程的子进程失败了 */ status = -1; _exit(0); }}else if( child_1_pid > 0 ){ /* 这是第一个子进程的父进程(即最高的那个父进程) */int child_1_parent_i;for( child_1_parent_i = 0; child_1_parent_i < 5; child_1_parent_i++){ printf("1st child's parent process. this is %2d seconds\n ", child_1_parent_i); sleep(1); } //_exit(0); /* 要是不将这行注释掉, 下面的第二个进程就不能创建了。因为父进程运行到这里就返回了。*/}else{ /* 创建第一个子进程失败 */ printf(" fork 1st child process failed\n "); status = -1; _exit(1);}/* 创建第一级的第二个子进程 */child_2_pid = fork();if( child_2_pid == 0){ /* 这是第一级的第二个的子进程的代码 */ int child_2_i; for( child_2_i = 0; child_2_i < 5; child_2_i++) { printf("2nd child process. this is %2d seconds\n ",child_2_i); sleep(1); } _exit(0);}else if( child_2_pid > 0){ /* 这是第一级的第二个子进程的父进程(最高级进程)的代码 */ int child_2_parent_i; for( child_2_parent_i = 0; child_2_parent_i < 5; child_2_parent_i++) { printf("2nd child's parent process, This is %2d seconds\n ",child_2_parent_i); sleep(1); } _exit(0);}else{ /* 创建第一级第二个子进程失败 */ printf(" fork 2nd child process failed\n"); status = -1; _exit(1);}return status;}void sleep( int seconds ) : Sleep for the specified number of seconds运行结果:
- Linux进程学习心得
- Linux学习心得
- linux学习心得
- linux学习心得
- linux学习心得
- linux学习心得
- Linux学习心得
- Linux学习心得
- linux学习心得
- linux学习心得
- Linux 学习心得
- linux学习心得
- Linux学习心得
- 网易公开课《Linux内核分析》学习心得-理解进程调度时机跟踪分析进程调度与进程切换的过程
- 网易公开课《Linux内核分析》学习心得-分析Linux内核创建一个新进程的过程
- 嵌入式每日学习心得 守护进程
- linux多线程编程学习心得
- linux /dev/loop学习心得
- 比较好的学习资料
- 我的程序猿之路
- 开始使用CSDN的Blog,第一篇文章
- 谢天谢地 重回CSDN!
- 终于拿到自己的用户名和口令了
- Linux进程学习心得
- android Import 第三方库 JAR
- JAVA 中文与ASICLL码的相互转换
- c语言运算符优先级
- Http get Android
- javascript面向对象编程资料
- [Android SQLite]数据存储与访问 - 内部存储
- [Android SQLite]数据存储与访问 - 外部存储
- javascript来判断某个时间是不是处于夏令时


