objective-c shallow- and deep-copy
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝怎么买呼死你 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/20 12:50
转自:https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/#documentation/General/Conceptual/DevPedia-CocoaCore/ObjectCopying.html
Object Copying
Copying an object creates a new object with the same class and properties as the original object. You copy an object when you want your own version of the data that the object contains. If you receive an object from elsewhere in an application but do not copy it, you share the object with its owner (and perhaps others), who might change the encapsulated contents. If you are creating a subclass, you might consider making it possible for others to copy instances of your class. Generally, an object should be “copyable” when it is a value object—an object whose main purpose is to encapsulate some data.
Requirements for Object Copying
An object can be copied if its class adopts the NSCopying protocol and implements its single method, copyWithZone:. If a class has mutable and immutable variants, the mutable class should adopt the NSMutableCopying protocol (instead of NSCopying) and implement themutableCopyWithZone: method to ensure that copied objects remain mutable. You make a duplicate of an object by sending it a copy ormutableCopy message. These messages result in the invocation of the appropriate NSCopying or NSMutableCopying method.
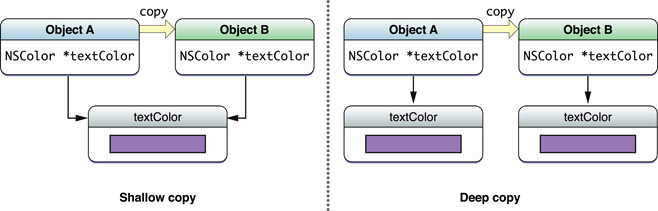
Copies of objects can be shallow or deep. Both shallow- and deep-copy approaches directly duplicate scalar properties but differ on how they handle pointer references, particularly references to objects (for example, NSString *str). A deep copy duplicates the objects referenced while a shallow copy duplicates only the references to those objects. So if object A is shallow-copied to object B, object B refers to the same instance variable (or property) that object A refers to. Deep-copying objects is preferred to shallow-copying, especially with value objects.
Memory-Management Implications
Like object creation, object copying returns an object with a retain count of 1. In memory-managed code, the client copying the object is responsible for releasing the copied object. Copying an object is similar in purpose to retaining an object in that both express an ownership in the object. However, a copied object belongs exclusively to the new owner, who can mutate it freely, while a retained object is shared between the owners of the original object and clients who have retained the object.- objective-c shallow- and deep-copy
- Deep Copy and Shallow Copy
- Shallow Copy and Deep Copy
- shallow copy and deep copy
- Deep copy and shallow copy
- deep copy and shallow copy
- Java Clone, Shallow Copy and Deep Copy
- Python: Shallow and deep copy operations
- [Python]Shallow and Deep copy operation
- Deep copy & Shallow copy
- Shallow copy & Deep copy
- 深拷贝与浅拷贝(Deep Copy and Shallow Copy)
- 深拷贝与浅拷贝(Deep Copy and Shallow Copy)
- difference between Python shallow copy and deep copy
- shallow copy and deep copy in Prototype Pattern
- shallow & deep copy
- Shallow vs. deep copy
- deep copy vs shallow copy
- ubuntu 添加自启动脚本
- 要开始当一名码农~
- DD_belatedPNG 背景图片消失bug
- Log4j 配置错误信息发送Mail
- 在C中如何使函数返回数组
- objective-c shallow- and deep-copy
- VS2010中的调试技巧
- JBox2d入门学习二 -----我的小鸟
- 抢30游戏
- wm_concat函数
- 一个C程序员的个人开发经验,抛个砖头,各位砸玉 (二)函数怎么写
- About Honeywell Aerospace (1)
- libxml2在iOS4上由于xmlFreeDoc导致程序Crash的解决方法
- 不完全归纳设置isolation level为transaction level的两点影响


