散列表的基本概念及其运算
来源:互联网 发布:最强数据恢复软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 18:42
参考文献: 《数据结构(C语言版)》 严蔚敏 吴伟民 编著
开发平台:Ubuntu11.04
编译器:gcc version4.5.2 (Ubuntu/Linaro 4.5.2-8ubuntu4)
散列表(也叫哈希表)是一种查找算法,与链表、树等算法不同的是,散列表算法在查找时不需要进行一系列和关键字(关键字是数据元素中某个数据项的值,用以标识一个数据元素)的比较操作。
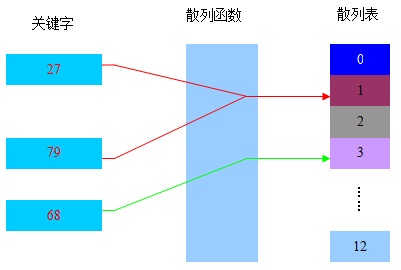
散列表算法希望能尽量做到不经过任何比较,通过一次存取就能得到所查找的数据元素,因而必须要在数据元素的存储位置和它的关键字(可用key表示)之间建立一个确定的对应关系,使每个关键字和散列表中一个唯一的存储位置相对应。因此在查找时,只要根据这个对应关系找到给定关键字在散列表中的位置即可。这种对应关系被称为散列函数(可用h(key)表示)。
根据设定的散列函数h(key)和处理冲突的方法将一组关键字key映像到一个有限的连续的地址区间上,并以关键字在地址区间中的像作为数据元素在表中的存储位置,这种表便被称为散列表,这一映像过程称为散列,所得存储位置称为散列地址。
关键字、散列函数以及散列表的关系如下图所示:
1、散列函数
散列函数是从关键字到地址区间的映像。
好的散列函数能够使得关键字经过散列后得到一个随机的地址,以便使一组关键字的散列地址均匀地分布在整个地址区间中,从而减少冲突。
常用的构造散列函数的方法有:
(1)、直接定址法
取关键字或关键字的某个线性函数值为散列地址,即:
h(key) = key 或 h(key) = a * key + b
其中a和b为常数。
(2)、数字分析法
(3)、平方取值法
取关键字平方后的中间几位为散列地址。
(4)、折叠法
将关键字分割成位数相同的几部分(最后一部分的位数可以不同),然后取这几部分的叠加和(舍去进位)作为散列地址。
(5)、除留余数法
取关键字被某个不大于散列表表长m的数p除后所得的余数为散列地址,即:
h(key) = key MOD p p ≤ m
(6)、随机数法
选择一个随机函数,取关键字的随机函数值为它的散列地址,即:
h(key) = random(key)
其中random为随机函数。
2、处理冲突
对不同的关键字可能得到同一散列地址,即key1 ≠ key2,而h(key1)= h(key2),这种现象称为冲突。具有相同函数值的关键字对该散列函数来说称作同义词。
在一般情况下,散列函数是一个压缩映像,这就不可避免地会产生冲突,因此,在创建散列表时不仅要设定一个好的散列函数,而且还要设定一种处理冲突的方法。
常用的处理冲突的方法有:
(1)、开放定址法
hi =(h(key) + di) MOD m i =1,2,…,k(k ≤ m-1)
其中,h(key)为散列函数,m为散列表表长,di为增量序列,可有下列三种取法:
1)、di = 1,2,3,…,m-1,称线性探测再散列;
2)、di = 12,-12,22,-22,32,…,±k2 (k ≤m/2),称二次探测再散列;
3)、di = 伪随机数序列,称伪随机探测再散列。
(2)、再散列法
hi = rhi(key) i = 1,2,…,k
rhi均是不同的散列函数。
(3)、链地址法
将所有关键字为同义词的数据元素存储在同一线性链表中。假设某散列函数产生的散列地址在区间[0,m-1]上,则设立一个指针型向量void *vec[m],其每个分量的初始状态都是空指针。凡散列地址为i的数据元素都插入到头指针为vec[i]的链表中。在链表中的插入位置可以在表头或表尾,也可以在表的中间,以保持同义词在同一线性链表中按关键字有序排列。
(4)、建立一个公共溢出区
例子以除留余数法和链地址法构造散列表,共用代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define LEN 13struct hash_node { int count; struct hash_node *next;};static int hash(int num){ return num % LEN;}static void collision(struct hash_node *vec[], int elem, struct hash_node *new){ if (vec[elem] == NULL)vec[elem] = new; else {new -> next = vec[elem];vec[elem] = new; }}static void ord_num_print(int i){ if (i == 1)printf("the 1st element: "); else if (i == 2)printf("the 2nd element: "); else if (i == 3)printf("the 3rd element: "); else printf("the %dth element: ", i);}static void print_hash(struct hash_node *vec[]){ int i; struct hash_node *tmp; for (i = 0; i < LEN; i++)if (vec[i] == NULL){ ord_num_print(i+1); printf("NULL\n");}else{ ord_num_print(i+1); tmp = vec[i]; do {printf("%d ", tmp->count); }while ((tmp = tmp->next) && tmp != NULL); printf("\n");}}static void create_hash(struct hash_node *vec[], int num){ FILE *fp; int i, tmp, arr[num]; struct hash_node *p; fp = fopen("./hash", "r"); for (i = 0; i < num; i++)fscanf(fp, "%d", &arr[i]); fclose(fp); for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {p = malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));p -> count = arr[i];p -> next = NULL;tmp = hash(arr[i]);collision(vec, tmp, p); }}其中,hash是散列函数,collision函数用于处理冲突。
create_hash函数通过读取./hash文件中的num个关键字来构建一个散列表。例子中hash文件的内容如下:
19 14 23 01 68 20 84 27 55 11 10 79
3、元素插入
void insert_hash_node(struct hash_node *vec[], int data){ int tmp; struct hash_node *p = malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node)); p -> count = data; p -> next = NULL; tmp = hash(data); collision(vec, tmp, p);}4、元素删除
void delete_hash_node(struct hash_node *vec[], int data){ int elem; struct hash_node *p, *tmp; elem = hash(data); if (vec[elem] == NULL) {fprintf(stderr, "vec[%d] is NULL\n", elem);exit(-2); } else {tmp = vec[elem];while (tmp -> count != data) { if (tmp -> next == NULL) {fprintf(stderr, "not found %d\n", data);exit(-3); } p = tmp; tmp = tmp -> next;}p -> next = tmp -> next;free(tmp); }}在main函数中,通过三步来验证上述所列的各种函数,第一步调用create_hash函数创建一个具有12个关键字的散列表(见下图),第二步插入关键字29,第三步删除关键字1。
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ int i, num; struct hash_node *vec[LEN]; /* num, the number of integers in the ./hash file */ if (argc < 2) {fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s num\n", argv[0]);exit(-1); } for (i = 0; i < LEN; i++)vec[i] = NULL; num = atoi(argv[1]); printf("\tthe first times\n"); create_hash(vec, num); print_hash(vec); printf("\n\tthe second times\n"); insert_hash_node(vec, 29); print_hash(vec); printf("\n\tthe third times\n"); delete_hash_node(vec, 1); print_hash(vec); return 0;}

执行和输出结果:
$ ./hash_list 12
the first timesthe 1st element: NULLthe 2nd element: 79 27 1 14 the 3rd element: NULLthe 4th element: 55 68 the 5th element: NULLthe 6th element: NULLthe 7th element: 84 19 the 8th element: 20 the 9th element: NULLthe 10th element: NULLthe 11th element: 10 23 the 12th element: 11 the 13th element: NULLthe second timesthe 1st element: NULLthe 2nd element: 79 27 1 14 the 3rd element: NULLthe 4th element: 29 55 68 the 5th element: NULLthe 6th element: NULLthe 7th element: 84 19 the 8th element: 20 the 9th element: NULLthe 10th element: NULLthe 11th element: 10 23 the 12th element: 11 the 13th element: NULLthe third timesthe 1st element: NULLthe 2nd element: 79 27 14 the 3rd element: NULLthe 4th element: 29 55 68 the 5th element: NULLthe 6th element: NULLthe 7th element: 84 19 the 8th element: 20 the 9th element: NULLthe 10th element: NULLthe 11th element: 10 23 the 12th element: 11 the 13th element: NULL
- 散列表的基本概念及其运算
- 散列表的基本概念及其运算
- 散列表的基本概念
- 散列表的基本概念
- 散列表 基本概念
- 多线程的基本概念及其简单应用
- Java继承的基本概念及其限制 总结
- 离散数学及其应用--第一章-命题逻辑的基本概念
- Java继承的基本概念及其限制
- Java继承的基本概念及其限制 总结
- Http的定义及其基本概念介绍
- ajax的基本概念及其使用(5步)
- Http的定义及其基本概念介绍
- 泛型的作用及其基本概念
- 图的基本概念及其抽象数据类型
- 矩阵的运算及其运算规则
- 矩阵的运算及其运算规则
- 集合的表示及其运算
- RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 3154)
- HDU 4089 Activation(概率DP)
- [gdc2012]战地3的地形系统
- ASA5510映射FTP端口
- 超链接
- 散列表的基本概念及其运算
- 9 个指导开发者快速编码/学习的网站推荐
- CentOS 5.8 asterisk-1.8.10.1 安装之二:安装freepbx
- 分析u-boot.lds
- Silverlight Tookit控件集
- django + apache + windows server 2003 + sql server 2005 + mod_wsgi 配置
- ABI---应用程序二进制接口
- 数字图像基础,分辨率
- Java连接数据库代码


