Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
来源:互联网 发布:常用的网络语言有哪些 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 14:11
引言
前面我们介绍了Mongoose所有的几个主要的数据结构mg_context、mg_connection、mg_request_info,还有Mongoose的生命主线。有了这些基础就可以来看看Mongoose的核心处理工作是怎样的。如果你还没有阅读前面的文章,你可以通过下面的隧道直通:
- Mongoose源码剖析:外篇之web服务器
- Mongoose源码剖析:Introduction and Installation
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
本文从下面几个方面去介绍Mongoose的核心处理模块,连接建立之后的:
- 请求解析
- 请求验证
- 请求满足
1、连接的建立
Mongoose的主线程master_thread在接受一个新的client连接请求时,会将client的socket地址放入一个queue(调用put_socket()方法);而当worker_thread线程处理client的请求时,是通过get_socket()方法从queue取出client的socket地址,然后与它建立连接。
建立连接就用到了数据结构mg_connection,该结构保存了client的连接信息。该结构体中有两个非常重要的成员:mg_request_info用于保存client的请求信息、mg_context用于保存该client请求的mongoose上下文。建立连接的代码片段如下:
while (get_socket(ctx, &conn.client) == TRUE) {conn.birth_time = time(NULL);conn.ctx = ctx;if (conn.client.is_ssl && (conn.ssl = SSL_new(conn.ctx->ssl_ctx)) == NULL) {cry(&conn, "%s: SSL_new: %d", __func__, ERRNO);} else if (conn.client.is_ssl && SSL_set_fd(conn.ssl, conn.client.sock) != 1) {cry(&conn, "%s: SSL_set_fd: %d", __func__, ERRNO);} else if (conn.client.is_ssl && SSL_accept(conn.ssl) != 1) {cry(&conn, "%s: SSL handshake error", __func__);} else {process_new_connection(&conn);}close_connection(&conn);}
其中以SSL_开头的函数都是加载自SSL的库,加载库调用了如下接口:static bool_t set_ssl_option(struct mg_context *ctx, const char *pem),有兴趣的话你可以追踪下去。
2、请求信息获取
建立连接之后,在process_new_connection中会去读取client的请求信息,然后才去解析请求。读取client端的请求的信息用到了下面的方法:
/* * Keep reading the input (either opened file descriptor fd, or socket sock, * or SSL descriptor ssl) into buffer buf, until \r\n\r\n appears in the * buffer (which marks the end of HTTP request). Buffer buf may already * have some data. The length of the data is stored in nread. * Upon every read operation, increase nread by the number of bytes read. */static intread_request(FILE *fp, SOCKET sock, SSL *ssl, char *buf, int bufsiz, int *nread){intn, request_len;request_len = 0;while (*nread < bufsiz && request_len == 0) {n = pull(fp, sock, ssl, buf + *nread, bufsiz - *nread);if (n <= 0) {break;} else {*nread += n;request_len = get_request_len(buf, (size_t) *nread);}}return (request_len);}
其中pull()方法的代码如下:
/* * Read from IO channel - opened file descriptor, socket, or SSL descriptor. * Return number of bytes read. */static intpull(FILE *fp, SOCKET sock, SSL *ssl, char *buf, int len){intnread;if (ssl != NULL) {nread = SSL_read(ssl, buf, len);} else if (fp != NULL) {nread = fread(buf, 1, (size_t) len, fp);if (ferror(fp))nread = -1;} else {nread = recv(sock, buf, (size_t) len, 0);}return (nread);}
这样client发送的HTTP请求消息就被worker_thread读取到了,并存储在buf中, 接下来的工作就是解析读取到的请求信息,明白client到底想干嘛,说白了就从buf中提取信息并存储到结构体mg_request_info中去。
3、请求解析
请求解析的工作都封装在parse_http_request()函数汇中,它的代码如下:
/* * Parse HTTP request, fill in mg_request_info structure. */static bool_tparse_http_request(char *buf, struct mg_request_info *ri, const struct usa *usa){char*http_version;intn, success_code = FALSE;ri->request_method = skip(&buf, " ");ri->uri = skip(&buf, " ");http_version = skip(&buf, "\r\n");if (is_known_http_method(ri->request_method) && ri->uri[0] == '/' && sscanf(http_version, "HTTP/%d.%d%n", &ri->http_version_major, &ri->http_version_minor, &n) == 2 && http_version[n] == '\0') {parse_http_headers(&buf, ri);ri->remote_port = ntohs(usa->u.sin.sin_port);(void) memcpy(&ri->remote_ip, &usa->u.sin.sin_addr.s_addr, 4);ri->remote_ip = ntohl(ri->remote_ip);success_code = TRUE;}return (success_code);}
这里主要用到了skip()、parse_http_headers()方法,其中skip()很关键,代码如下:
/* * Skip the characters until one of the delimiters characters found. * 0-terminate resulting word. Skip the rest of the delimiters if any. * Advance pointer to buffer to the next word. Return found 0-terminated word. */static char *skip(char **buf, const char *delimiters){char*p, *begin_word, *end_word, *end_delimiters;begin_word = *buf;end_word = begin_word + strcspn(begin_word, delimiters);end_delimiters = end_word + strspn(end_word, delimiters);for (p = end_word; p < end_delimiters; p++)*p = '\0';*buf = end_delimiters;return (begin_word);}
我们来分析一下skip的作用及实现。如要从buf中解析出client请求的methods是哪个(PUT、GET、POST等等)?只需要这样做就可以了:
ri->request_method = skip(&buf, " ");
为了分析,到底是如何实现这个的,我在porcess_new_connection()中加入下面一行输出buf信息的代码:

看当我们想mongoose发送的请求信息,这时我们在浏览其中输入http://ip:8080,终端会输出buf的信息,如下: 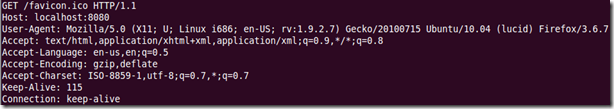
看到第一行就是GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1。知道了buf中的字符信息,但在我们分析skip(&buf, " ")是如何提取出GET的之前,还要知道strcspn、strspn的作用,下面是它们的原型:
#include <string.h> size_t strspn(const char *s, const char *accept); size_t strcspn(const char *s, const char *reject);
下面解释它们的作用:
DESCRIPTION
The strspn() function calculates the length of the initial segment of s
which consists entirely of characters in accept.The strcspn() function calculates the length of the initial segment of s which consists entirely of characters not in reject.
RETURN VALUE
The strspn() function returns the number of characters in the initial segment of s which consist only of characters from accept.The strcspn() function returns the number of characters in the initial segment of s which are not in the string reject.
现在已经万事俱备了,skip(&buf, " ")的执行情况如下:

其余的解析工作也是类似地进行的,我就不一一阐述了。
4、请求验证
请求验证分布在从连接请求开始到请求得到回应的整个过程中。在请求解析之前,比如验证socket的合法性等。在请求解析之后,从buf中解析出HTTP请求消息的各个字段之后,就做一些简单的验证工作,比如说HTTP版本的验证。如果在解析buf时出错,说明请求的格式不对。
而且在满足client请求的时候也要进行一些验证,诸如是否有浏览目录的权限、请求的文件是否存在等等,我就不在详述了。
5、请求满足
在parse_http_request()之后,调用analyze_request()去满足client的请求。这是Mongoose的核心内容,也是不同web服务器软件相区别的地方。analyze_request()封装了一些操作,即调用了一些接口去满足client的请求,代码如下:
/* * This is the heart of the Mongoose's logic. * This function is called when the request is read, parsed and validated, * and Mongoose must decide what action to take: serve a file, or * a directory, or call embedded function, etcetera. */static voidanalyze_request(struct mg_connection *conn){struct mg_request_info *ri = &conn->request_info;charpath[FILENAME_MAX], *uri = ri->uri;struct mgstatst;const struct callback*cb;if ((conn->request_info.query_string = strchr(uri, '?')) != NULL)* conn->request_info.query_string++ = '\0';(void) url_decode(uri, (int) strlen(uri), uri, strlen(uri) + 1, FALSE);remove_double_dots_and_double_slashes(uri);convert_uri_to_file_name(conn, uri, path, sizeof(path));if (!check_authorization(conn, path)) {send_authorization_request(conn);} else if (check_embedded_authorization(conn) == FALSE) {/* * Embedded code failed authorization. Do nothing here, since * an embedded code must handle this itself by either * showing proper error message, or redirecting to some * sort of login page, or something else. */} else if ((cb = find_callback(conn->ctx, FALSE, uri, -1)) != NULL) {if ((strcmp(ri->request_method, "POST") != 0 && strcmp(ri->request_method, "PUT") != 0) || handle_request_body(conn, NULL))cb->func(conn, &conn->request_info, cb->user_data);} else if (strstr(path, PASSWORDS_FILE_NAME)) {/* Do not allow to view passwords files */send_error(conn, 403, "Forbidden", "Access Forbidden");} else if ((!strcmp(ri->request_method, "PUT") || !strcmp(ri->request_method, "DELETE")) && (conn->ctx->options[OPT_AUTH_PUT] == NULL || !is_authorized_for_put(conn))) {send_authorization_request(conn);} else if (!strcmp(ri->request_method, "PUT")) {put_file(conn, path);} else if (!strcmp(ri->request_method, "DELETE")) {if (mg_remove(path) == 0)send_error(conn, 200, "OK", "");elsesend_error(conn, 500, http_500_error, "remove(%s): %s", path, strerror(ERRNO));} else if (mg_stat(path, &st) != 0) {send_error(conn, 404, "Not Found", "%s", "File not found");} else if (st.is_directory && uri[strlen(uri) - 1] != '/') {(void) mg_printf(conn, "HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently\r\n" "Location: %s/\r\n\r\n", uri);} else if (st.is_directory && substitute_index_file(conn, path, sizeof(path), &st) == FALSE) {if (is_true(conn->ctx->options[OPT_DIR_LIST])) {send_directory(conn, path);} else {send_error(conn, 403, "Directory Listing Denied", "Directory listing denied");}#if !defined(NO_CGI)} else if (match_extension(path, conn->ctx->options[OPT_CGI_EXTENSIONS])) {if (strcmp(ri->request_method, "POST") && strcmp(ri->request_method, "GET")) {send_error(conn, 501, "Not Implemented", "Method %s is not implemented", ri->request_method);} else {send_cgi(conn, path);}#endif /* NO_CGI */#if !defined(NO_SSI)} else if (match_extension(path, conn->ctx->options[OPT_SSI_EXTENSIONS])) {send_ssi(conn, path);#endif /* NO_SSI */} else if (is_not_modified(conn, &st)) {send_error(conn, 304, "Not Modified", "");} else {send_file(conn, path, &st);}}
上面的代码比较好理解我就不把它嚼烂之后,再展现给你!那样也没有意思~\(≧▽≦)/~啦啦啦。感兴趣的自己去逐一分析。
作者:吴秦
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skynet/
本文基于署名 2.5 中国大陆许可协议发布,欢迎转载,演绎或用于商业目的,但是必须保留本文的署名吴秦(包含链接).
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- web服务器之mongoose:核心处理模块
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- Nginx源码分析:核心模块剖析及常见问题
- Mongoose源码剖析:数据结构篇
- 2011.04.28_luyiqiang_继续和谐VMP 学习笔记
- Mongoose源码剖析:mongoose的工作模型
- 获得系统语言。
- 计算php页面执行时间类
- Mongoose源码剖析:核心处理模块
- 真想写一篇各个平台开发的文章,可是怕引起争议,暂时淡定
- 2896
- sprintf函数的用法
- 序列化
- 理解基类中成员的访问限定符和派生类的继承方式
- C语言中的文件格式化读写函数:fprintf和fscanf
- sql2008读书笔记_索引
- 用oledb处理excel


