From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation,search
Programming language comparisons | - General comparison
- Basic syntax
- Basic instructions
- Arrays
- Associative arrays
- String operations
- String functions
- List comprehension
- Object-oriented programming
- Object-oriented constructors
- Database access
- Database RDBMS
- Evaluation strategy
- List of "hello world" programs
- ALGOL 58's influence on ALGOL 60
- ALGOL 60: Comparisons with other languages
- Comparison of ALGOL 68 and C++
- ALGOL 68: Comparisons with other languages
- Compatibility of C and C++
- Comparison of Pascal and Borland Delphi
- Comparison of Object Pascal and C
- Comparison of Pascal and C
- Comparison of Java and C++
- Comparison of C# and Java
- Comparison of C# and Visual Basic .NET
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number ofrelational database management systems. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. This article is not all-inclusive or necessarily up to date. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are based on the stable versions without any add-ons, extensions or external programs.
Contents
- 1General information
- 2Timeline
- 3Operating system support
- 4Fundamental features
- 5Limits
- 6Tables and views
- 7Indexes
- 8Database capabilities
- 9Data types
- 10Other objects
- 11Partitioning
- 12Access control
- 13Databases vs schemas (terminology)
- 14See also
- 15References
- 16External links
General information
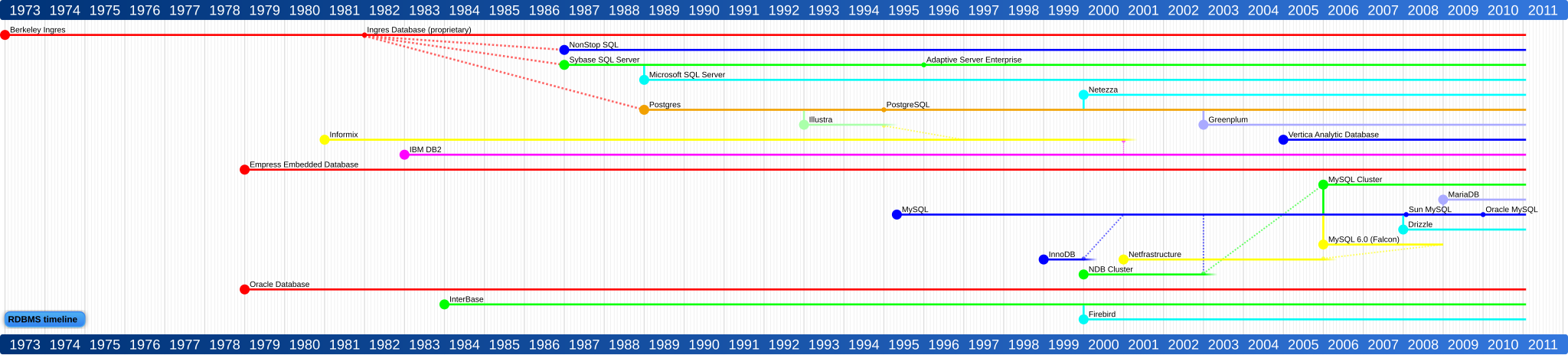
4D (4th Dimension) | 4D s.a.s1984v12.2 SQL ProprietaryADABAS | Software AG19708.1 ProprietaryAdaptive Server Enterprise | Sybase198715.7 ProprietaryAdvantage Database Server (ADS) | Sybase199210.12010-12ProprietaryAltibase | Altibase Corp.[1]2000-075.1.1 ProprietaryApache Derby | Apache200410.8.2.22011-10-24Apache LicenseCUBRID | NHN Corporation[2]2008-118.4.12012-02-24GPL v2Datacom | CA, Inc.?11.2 ProprietaryDB2 | IBM198310.12012-04-30ProprietaryDrizzle | Brian Aker2008Build 1126 BSD,GPL v2Empress Embedded Database | Empress Software Inc[3]197910.202010-03ProprietaryFileMaker | FileMaker[4]198412.02012-04-12ProprietaryFirebird | Firebird project[5]2000-07-252.5.12011-10-04IPL[6] and IDPL[7]HSQLDB | HSQL Development Group20012.2.6[8]2011-11-20BSDH2 | H2 Software20051.3.1602011-09-11EPL and modifiedMPLInformix Dynamic Server | IBM198011.70.xC42011-03-28ProprietaryIngres | Ingres Corp.1974Ingres Database 102010-10-12GPL andProprietaryInterBase | Embarcadero1984InterBase XE2010-09-21ProprietaryLinter SQL RDBMS | RELEX Group19906.x ProprietaryLucidDB | The Eigenbase Project[9]2007-010.9.3 GPL v2MariaDB | MariaDB Community2010-02-015.5.23[10]2012-04-11GPL v2MaxDB | SAP AG2003-057.62008-01ProprietaryMicrosoft Access (JET) | Microsoft199214 (2010) ProprietaryMicrosoft Visual Foxpro | Microsoft1984[11]9 (2005)2007-10-11[11]ProprietaryMicrosoft SQL Server | Microsoft19892012 (v11) ProprietaryMicrosoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | Microsoft20002010 (v3.5 SP2) ProprietaryMonetDB/SQL | The MonetDB Developer Team200411.9.12012-04MonetDB Public License v1.1[12]mSQL | Hughes Technologies19943.9[13]2011-02ProprietaryMySQL | Sun Microsystems (nowOracle Corporation)1995-115.5.172011-10-21GPL orProprietaryNexusdb | Nexus Database Systems Pty Ltd[14]2003-093.042010-05-08ProprietaryHP NonStop SQL | Hewlett-Packard1987SQL/MX 2.3 ProprietaryOmnis Studio | TigerLogic Inc[15]1982-074.3.1 Release 1no2008-05ProprietaryOpenBase SQL | OpenBase International[16]199111.0.0 ProprietaryOpenEdge | Progress Software Corporation198411.0 ProprietaryOpenLink Virtuoso | OpenLink Software[17]19986.x2011-11GPL orProprietaryOracle | Oracle Corporation1979-1111g Release 22009-09ProprietaryOracle Rdb | Oracle Corporation19847.2.5.02011-06-20[18]ProprietaryParadox | Corel Corporation[19]1985112003ProprietaryPervasive PSQL | Pervasive Software1982112011-07ProprietaryPolyhedra DBMS | ENEA AB19938.52011-06ProprietaryPostgreSQL | PostgreSQL Global Development Group[20]1989-069.1.3[21]2012-02-27PostgreSQL Licence (a liberal Open Source license)[22]R:Base | R:BASE Technologies[23]19827.6 ProprietaryRDM Embedded | Raima Inc.[24]198410.12011-08-31ProprietaryRDM Server | Raima Inc.[25]19938.3 ProprietaryScimoreDB | Scimore[26]20053.02008-03-03ProprietarySmallSQL | SmallSQL2005-04-160.202008-12LGPLSQL Anywhere | Sybase199212.02010-07-09ProprietarySQLBase | Unify Corp.[27]198211.52008-11ProprietarySQLite | D. Richard Hipp2000-08-173.7.6.32011-05-19[28]Public domainSuperbase | Superbase1984Scientific (2004) ProprietaryTeradata | Teradata198413.10 ProprietaryUniData | Rocket Software19887.2.122011-10ProprietaryXeround Cloud Database | Xeround Systems20103.12011-10-11SaaSTimeline
Timeline of the development of major RDBMS software:
Operating system support
The operating systems that the RDBMSes can run on.
4th Dimension | YesYesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoADABAS | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoYesNoNoAdaptive Server Enterprise | YesNoYesYesYesNoNoNoYesYesAdvantage Database Server | YesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoAltibase | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoApache Derby2 | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYes?NoCUBRID | YesPartial10YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoDrizzle | NoYesYesYesYesNoNoNoNoNoDB25 | YesYes (Express C)YesNoYesNoNoYesNoNoEmpress Embedded Database | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoNoNoYesFirebird | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoMaybeNoNoHSQLDB2 | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYes??H22 | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYes??FileMaker | YesYesNoNoNoNoNoNoYesNoInformix Dynamic Server | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYesNoNoIngres | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoPartialNoNoInterBase | YesYesYesNoYes (Solaris)NoNoNoNoNoLinter SQL RDBMS6 | YesYesYesYesYes6NoNoNo?YesLucidDB | YesYesYesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoMariaDB | YesYes[29]YesMaybeYesNoNoNo??MaxDB | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoMaybeNoNoMicrosoft Access (JET) | YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoMicrosoft Visual Foxpro | YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoMicrosoft SQL Server | YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoMicrosoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoMonetDB/SQL | YesYesYesNoYesNoNoNo??MySQL8 | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYes?NoOmnis Studio | YesYesYesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoOpenBase SQL | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoNoNoNoOpenEdge | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoOpenLink Virtuoso | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYesNoNoOracle4 | YesYesYesNoYesNoNoYesNoNoOracle Rdb3 | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoPervasive PSQL | YesYes (OEM only)YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoPolyhedra7 | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoPostgreSQL | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoNoNoYesR:Base | YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoRDM Embedded | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoNoNoNoRDM Server | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoNoNoNoScimoreDB | YesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoSmallSQL2 | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYesNoNoSQL Anywhere | YesYesYesNoYesNoNoNoNoYesSQLBase | YesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoSQLite | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesMaybeYesYesSuperbase | YesNoNoNoNoYesNoNoNoNoTeradata | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoUniData | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoUniVerse | YesNoYesNoYesNoNoNoNoNoXeround Cloud Database | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYes | Fundamental features
Information about what fundamental RDBMS features are implemented natively.
4th Dimension | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLADABAS | YesNoYesYesproprietary direct call & SQL (via 3rd party)Adaptive Server Enterprise | YesYesYesYesSQLAdvantage Database Server | YesYesYesYes4API &SQLAltibase | YesYesYes?SQLApache Derby | YesYesYesYesSQLCUBRID | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLDrizzle | YesYesYesYesSQLDB2 | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLEmpress Embedded Database | YesYesYesYesAPI &SQLFirebird | YesYesYesYesSQLHSQLDB | YesYesYesYesSQLH2 | YesYesYesYesSQLInformix Dynamic Server | YesYesYesYesSQLIngres | YesYesYesYesSQL & QUELInterBase | YesYesYesYesSQLLinter SQL RDBMS | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLLucidDB | YesNoNoYesSQLMaxDB | YesYesYesYesSQLMicrosoft Access (JET) | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLMicrosoft Visual FoxPro | NoYesYesNoGUI &SQLMicrosoft SQL Server | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLMicrosoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLMonetDB/SQL | YesYesYesYes?MySQL | Yes2Partial3Yes2 except forDDL [30]YesSQLOpenBase SQL | YesYesYesYesGUI &SQLOracle | YesYesYes except for DDL [30]YesAPI &GUI & SQLOracle Rdb | YesYesYesYesSQLOpenLink Virtuoso | YesYesYesYesAPI &GUI & SQLPolyhedra DBMS | YesYesYesYesSQLPostgreSQL | YesYesYesYesAPI &GUI & SQLRDM Embedded | YesYesYesYesSQL & APIRDM Server | YesYesYesYesSQL & APIScimoreDB | YesYesYesPartialSQLSQL Anywhere | YesYesYesYesSQLSQLBase | YesYesYesYesAPI &GUI & SQLSQLite | YesYesYesOptional[31]SQLTeradata | YesYesYesYesSQLUniData | YesNoYesYesMultipleUniVerse | YesNoYesYesMultipleXeround Cloud Database | YesNoYesYesSQL | ACID | Referential integrity | Transactions | Unicode | Interface | Note (1): Currently only supports read uncommited transaction isolation. Version 1.9 adds serializable isolation and version 2.0 will be fully ACID compliant.
Note (2):MySQL provides ACID compliance through the default InnoDB storage engine.[32][33]
Note (3):"For other [than InnoDB] storage engines, MySQL Server parses and ignores the FOREIGN KEY and REFERENCES syntax in CREATE TABLE statements. The CHECK clause is parsed but ignored by all storage engines."[34]
Note (4): Support for Unicode is new in version 10.0.
Limits
Information about data size limits.
4th Dimension | limited ? ?65135200 GB (2 GiBUnicode)200 GB (2 GiBUnicode)64 bits ? ? ?Advantage Database Server | Unlimited16 EiB65530 B65135 / (10+ AvgFieldNameLength)4 GiB ?64 bits ? ?128Apache Derby | UnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimited1012 (5000 in views)2 147 483 647 chars254 (VARCHAR: 32672)64 bits0001-01-019999-12-31128CUBRID | 2 EB2 EBUnlimited6400Unlimited1 GB64 bits0001-01-019999-12-31254Drizzle | Unlimited64 TB8 kB10004 GB (longtext, longblob)64 kB (text)64 bits0001999964DB2 | 512 TiB512 TB32 677 B10122 GB32 KiB)64 bits00019999128Empress Embedded Database | Unlimited263-1 bytes2 GB327672 GB2 GB64 bits0000-01-019999-12-3132FileMaker | 8TB8TB8TB256,000,0004GB10^9 characters10^9 numbers w/ range 10^-400 to 10^4000001-01-014000-12-31100Firebird | Unlimited1~32 TB65 536 BDepends on data types used.2 GB32 767 B64 bits1003276831HSQLDB | 64 TBUnlimited8Unlimited8Unlimited864 TB7Unlimited8Unlimited80001-01-019999-12-31128H2 | 64 TBUnlimited8Unlimited8Unlimited864 TB7Unlimited864 bits-9999999999999999Unlimited8 | Max DB size | Max table size | Max row size | Max columns per row | Max Blob/Clob size | Max CHAR size | Max NUMBER size | Min DATE value | Max DATE value | Max column name size | Informix Dynamic Server | ~128 PB~128 PB32 765 bytes (exclusive of large objects)327654 TB32765103201/01/00011012/31/9999128 bytesIngres | UnlimitedUnlimited256 kB10242 GB32 000 B64 bits0001999932InterBase | Unlimited1~32 TB65 536 BDepends on data types used.2 GB32 767 B64 bits1003276831Linter SQL RDBMS | Unlimited230 rows64 kB (w/o BLOBs), 4 GB (BLOB)2504 GB4 kB64 bits0001-01-012099-12-31128Microsoft Access (JET) | 2 GB2 GB16 MB25564 kB (memo field), 1 GB ("OLE Object" field)255 B (text field)32 bits0100999964Microsoft Visual Foxpro | Unlimited2 GB65 500 B2552 GB16 MB32 bits00019999 ?Microsoft SQL Server | 524 258 TB (32 767 files * 16 TB max file size)524 258 TB8060 bytes (Unlimited)6300002 GB2 GB6126 bits200019999128Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | 4 GB4 GB8060 bytes1024500 MB4000126 bits 200019999128MySQL 5 | UnlimitedMyISAM storage limits: 256 TB; Innodb storage limits: 64 TB64 kB3409644 GB (longtext, longblob)64 kB (text)64 bits1000999964OpenLink Virtuoso | 32 TBDB size (or 32 TB)4K2002 GB2 GB2**3109999100Oracle | Unlimited (4 GB * block size per tablespace)4 GB * block size (with BIGFILE tablespace)8 kB1000Unlimited4000 B126 bits-4712999930 | Max DB size | Max table size | Max row size | Max columns per row | Max Blob/Clob size | Max CHAR size | Max NUMBER size | Min DATE value | Max DATE value | Max column name size | Polyhedra | Limited by available RAM, address space232 rowsUnlimited655364 GB (subject to RAM)4 GB (subject to RAM)32 bits0001-01-018000-12-31255PostgreSQL | Unlimited32 TB1.6 TB250-1600 depending on type1 GB (text, bytea) - stored inline or 2 GB (stored in pg_largeobject)1 GBUnlimited-4713587489763RDM Embedded | Unlimited248-1 rows32 KB10004 GBchar: 256, varchar: 4 KB64 bits0001-01-0111758978-12-3131RDM Server | Unlimited264-1 rows32 KB32768Unlimited32 KB64 bits0001-01-0111758978-12-3132ScimoreDB | Unlimited16 EB8050 B25516 TB8000 B64 bits ? ? ?SQL Anywhere | 104 TB (13 files, each file up to 8 TB (32k pages))Limited by file sizeLimited by file size450002 GB2 GB64 bits0001-01-019999-12-31 ?SQLite | 128 TB (231 pages * 64 kB max page size)Limited by file sizeLimited by file size327672 GB2 GB64 bitsNo DATE type9No DATE type9UnlimitedTeradata | UnlimitedUnlimited64 kB wo/lobs (64 GB w/lobs)20482 GB10 00064 bits ?9999-12-31 Select 80991231 (date);30UniVerse | UnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedUnlimitedXeround Cloud Database | UnlimitedUnlimited32GB, depending on available memory10004GB64K64 bits1000999964 | Max DB size | Max table size | Max row size | Max columns per row | Max Blob/Clob size | Max CHAR size | Max NUMBER size | Min DATE value | Max DATE value | Max column name size | Note (1): Firebird 2.x maximum database size is effectively unlimited with the largest known database size >980 GB.[35] Firebird 1.5.x maximum database size: 32 TB.
Note (2): limit is 1038usingDECIMAL datatype[36]
Note (3): InnoDB is limited to 8,000 bytes (excludingVARBINARY, VARCHAR, BLOB, or TEXT columns)[37]
Note (4): InnoDB is limited to 1,000 columns[37]
Note (6): UsingVARCHAR (MAX) in SQL 2005 and later[38]
Note (7): When using a page size of 32 kB, and when BLOB/CLOB data is stored in the database file.
Note (8): Java array size limit of 2,147,483,648 (231) objects per array applies. This limit applies to number of characters in names, rows per table, columns per table, and characters per CHAR/VARCHAR.
Note (9): Despite the lack of a date datatype, SQLite does include date and time functions,[39] which work for timestamps between 0000-01-01 00:00:00 and 5352-11-01 10:52:47.
Note (10): Informix DATETIME type has adjustable range from YEAR only through 1/10000th second. DATETIME date range is 0001-01-01 00:00:00.00000 through 9999-12-31 23:59:59.99999.
Tables and views
Information about what tables and views (other than basic ones) are supported natively.
4th Dimension | YesPlanned for inclusion in next major releaseADABAS | ??Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes1NoAdvantage Database Server | YesNo (only common views)Altibase | YesYesApache Derby | YesNoCUBRID | NoNoDrizzle | YesNo4DB2 | YesYesEmpress Embedded Database | YesYesFirebird | YesNo (only common views)HSQLDB | YesNoH2 | YesNoInformix Dynamic Server | YesNo2Ingres | YesPlanned for inclusion in next major releaseInterBase | YesNoLinter SQL RDBMS | YesYesLucidDB | NoNoMaxDB | YesNoMicrosoft Access (JET) | NoNoMicrosoft Visual Foxpro | YesYesMicrosoft SQL Server | YesYes3Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | YesNoMonetDB/SQL | YesNoMySQL | YesNo4OpenBase SQL | YesYesOracle | YesYesOracle Rdb | YesYesOpenLink Virtuoso | YesYesPolyhedra DBMS | NoNo (only common views)PostgreSQL | YesNo5RDM Embedded | YesNoRDM Server | YesNoSQL Anywhere | YesYesScimoreDB | NoNoSQLite | YesNoTeradata | YesYesUniData | YesNoUniVerse | YesNoXeround Cloud Database | YesNoNote (1): Server provides tempdb, which can be used for public and private (for the session) temp tables.[40]
Note (2): Materialized views are not supported in Informix; the term is used in IBM’s documentation to refer to a temporary table created to run the view’s query when it is too complex, but one cannot for example define the way it is refreshed or build an index on it. The term is defined in the Informix Performance Guide.[41]
Note (3):Query optimizer support only in Developer and Enterprise Editions. In other versions, a direct reference to materialized view and a query hint are required.[42]
Note (4): Materialized views can be emulated usingstored procedures and triggers.[43]
Note (5): Materialized views can be emulated with stored procedures and triggers usingPL/pgSQL, PL/Perl, PL/Python, or other procedural languages.[44]
Indexes
Information about what indexes (other than basic B-/B+ tree indexes) are supported natively.
4th Dimension | ?Cluster????????ADABAS | ??????????Adaptive Server Enterprise | NoNoYesNoYesNoNoNoYes?Advantage Database Server | NoNoYesNoYesYesNoNoYes?Apache Derby | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo[45]?CUBRID | NoNoNoNoYesNoNoNo??Drizzle | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo?DB2 | No?YesNoYesYesNoNoYes[46]?Empress Embedded Database | YesNoNoYesNoYesNoNoNo?Firebird | NoNoYesNoYes 1NoNoNoNo[47]?HSQLDB | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo?H2 | NoYesNoNoNoNoNoNoYes[48]?Informix Dynamic Server | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesIngres | YesYesIngres v10NoNoIngres v10NoNoNo?InterBase | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo?Linter SQL RDBMS10 | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoYes[49]?LucidDB | NoNoNoNoNoYesNoNoNo?MaxDB | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo?Microsoft Access (JET) | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo[50]?Microsoft Visual Foxpro | NoNoYesYesYes2YesNoNoNo?Microsoft SQL Server | ?Non/Cluster & fill factorYes3Yes4No3NoNoNoYes[51]Yes[52]Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo[53]?MonetDB/SQL | NoYesNoNoNoNoNoNo??MySQL | MyISAM tables onlyMEMORY, Cluster (NDB), InnoDB,5 tables onlyNo[54]NoNoNoNoNoMyISAM tables only[55]MyISAM tables only[56]?Oracle | Yes 11Cluster TablesYesYes 6YesYesNoNoYes[57]Yes[58]Oracle Rdb | NoYes?NoNo?NoNo??OpenLink Virtuoso | YesClusterYesYesNoYesNoNoYes?Polyhedra DBMS | NoYesNoNoNoNoNoNo??PostgreSQL | YesYesYesYesYes7Yes8YesYesYes[59]PostGIS[60]RDM Embedded | NoYesNoYesYesNoNoNoNoNoNoRDM Server | NoNoNoYesYesNoNoNoNoNoNoScimoreDB | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoYes[61]?SQL Anywhere | NoNoNoNoNoNoNoNoYes?SQLite | Yes[62]NoNoNoYesNoNoNoYes[63]SpatiaLite[64]Teradata | NoYesYesYesNoYesNoNo?[65]?UniVerse | YesYesYes3Yes3Yes3NoNoNo??Xeround Cloud Database | NoYesNoNoNoNoNoNoNoNo | R-/R+ tree | Hash | Expression | Partial | Reverse | Bitmap | GiST | GIN | Full-text | Spatial | FOT | Note (1): The users need to use a function from freeAdhocUDF library or similar.[66]
Note (2): Can be implemented for most data types using expression-based indexes.
Note (3): Can be emulated by indexing a computed column[67] (doesn't easily update) or by using an "Indexed View"[68] (proper name not just any view works[69])
Note (4): Can be implemented by using an indexed view.[70]
Note (5): InnoDB automatically generates adaptive hash index[71] entries as needed.
Note (6): Can be implemented using Function-based Indexes in Oracle 8i and higher, but the function needs to be used in the sql for the index to be used.
Note (7): A PostgreSQL functional index can be used to reverse the order of a field.
Note (8): PostgreSQL will likely support on-disk bitmap indexes in a future version. Version 8.2 supports a related technique known as "in-memory bitmap scans".
Note (10): B+ tree and full-text only for now.
Note (11): R-Tree indexing available in base edition with Locator but some functionality requires Personal Edition or Enterprise Edition with Spatial option
Database capabilities
4th Dimension | YesYesYesYesYesNoNoYes???ADABAS | Yes??????????Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes??YesYesYesYesYes??YesAdvantage Database Server | YesNoNoYesYesYesYesYes?No?Altibase | Yes??YesYesYesYesYes???Apache Derby | YesYesYesYesYes??YesNoNo?CUBRID | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesNoNo?Drizzle | YesNoNoYesYesYesNoYesNoNoNo[72]DB2 | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYes[73]Empress Embedded Database | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYes???Firebird | Yes??YesYesYesYesYesYesYes?HSQLDB | YesYesYesYesYesYesYes[74]YesYesNoYes[75]H2 | YesYesYesYesYesYesNoYesexperimental[76]No[77]?Informix Dynamic Server | Yes?Yes, via MINUSYesYesYesYesYesYes?Yes[78]Ingres | YesNoNoYesYesYesYesYesNoNo?InterBase | Yes??YesYes??Yes???Linter SQL RDBMS | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesNoYes?LucidDB | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesNo???MaxDB | Yes??YesYesYesNoYes???Microsoft Access (JET) | YesNoNoYesYesYesNoYesNoNo?Microsoft Visual Foxpro | Yes??YesYesYes?Yes???Microsoft SQL Server | YesYes (2005 and beyond)Yes (2005 and beyond)YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYes[79]Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | YesNoNoYesYes?NoYesNoNo?MonetDB/SQL | ???????????MySQL | YesNoNoYesYesYesNoYesNo[80]NoNo[81]OpenBase SQL | NoNoNoYesYesYesYesYes???Oracle | YesYesYes, via MINUSYesYesYesYesYesYes 1YesYes[82]Oracle Rdb | Yes??YesYesYesYesYes???OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes??YesYesYes?Yes???Polyhedra DBMS | YesYesYesYesNo??Yes???PostgreSQL | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesNo[83]RDM Embedded | NoNoNoYesYesNoNoYesNoNoNoRDM Server | YesNoNoYesYesYesNoYesNoNoNoScimoreDB | Yes??YesLEFT onlyYesYesYes???SmallSQL | ???????????SQL Anywhere | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesSQLite | YesYesYesYesLEFT onlyYes?YesNoNo?Teradata | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesYesNoYesYesUniVerse | YesYesYesYesYesYesYesNoNoNo?Xeround Cloud Database | YesNoNoYesYesYesNoYesNoNoNo | Union | Intersect | Except | Inner joins | Outer joins | Inner selects | Merge joins | Blobs andClobs | Common Table Expressions | Windowing Functions | Parallel Query | Note (1): Recursive CTEs introduced in 11gR2 supersedes similar construct called CONNECT BY
Data types
CUBRID[84] | StaticSMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)FLOAT, REAL(32-bit), DOUBLE(64-bit)DECIMAL, NUMERICCHAR, VARCHAR, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, CLOBBLOBDATE, DATETIME, TIME, TIMESTAMPBITMONETARY, BIT VARYING, SET, MULTISET, SEQUENCEDrizzle[85] | StaticINT (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)DOUBLE (aka REAL) (64-bit)DECIMALBINARY, VARCHAR, VARBINARY, TEXT,BLOBDATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP ENUM, SERIALEmpress Embedded Database | StaticTINYINT, SQL_TINYINT or INTEGER8SMALLINT, SQL_SMALLINT or INTEGER16 INTEGER, INT, SQL_INTEGER or INTEGER32 BIGINT, SQL_BIGINT or INTEGER64
REAL, SQL_REAL or FLOAT32DOUBLE PRECISION, SQL_DOUBLE or FLOAT64 FLOAT or SQL_FLOAT EFLOAT
DECIMAL, DEC, NUMERIC, SQL_DECIMAL or SQL_NUMERICDOLLAR
CHARACTER,ECHARACTER, CHARACTER VARYING, NATIONAL CHARACTER, NATIONAL CHARACTER VARYING and NLSCHARACTER
CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT, TEXT, NATIONAL CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT, and NLSTEXT
BINARY LARGE OBJECT or BLOBBULK
DATE,EDATE, TIME, ETIME, EPOCH_TIME, TIMESTAMP, MICROTIMESTAMP
BOOLEANSEQUENCE 32SEQUENCE
HSQLDB[86] | StaticTINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)DOUBLE (64-bit)DECIMAL, NUMERICCHAR, VARCHAR, LONGVARCHAR, CLOBBINARY, VARBINARY, LONGVARBINARY, BLOBDATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP, INTERVALBOOLEANOTHER (object), BIT, BIT VARYING, ARRAYInformix Dynamic Server[87] | StaticSMALLINT (16-bit), INT (32-bit), INT8 (64-bit proprietary), BIGINT (64-bit)SMALLFLOAT (32-bit), FLOAT (64-bit)DECIMAL (32 digits float/fixed), MONEYCHAR, VARCHAR, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, LVARCHAR, CLOB, TEXTTEXT, BYTE, BLOB, CLOBDATE, DATETIME, INTERVALBOOLEANSET, LIST, MULTISET, ROW, TIMESERIES, SPATIAL, USER DEFINED TYPESIngres[88] | StaticTINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)FLOAT4 (32-bit), FLOAT (64-bit)DECIMALC, CHAR, VARCHAR, LONG VARCHAR, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, LONG NVARCHAR, TEXTBYTE, VARBYTE, LONG VARBYTE (BLOB)DATE, ANSIDATE, INGRESDATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP, INTERVALN/AMONEY, OBJECT_KEY, TABLE_KEY, USER-DEFINED DATA TYPES (via OME)Microsoft SQL Server[89] | StaticTINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINTFLOAT, REALNUMERIC, DECIMAL, SMALLMONEY, MONEYCHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, NTEXTBINARY, VARBINARY, IMAGE, FILESTREAMDATE, DATETIMEOFFSET, DATETIME2, SMALLDATETIME, DATETIME, TIMEBITCURSOR, TIMESTAMP, HIERARCHYID, UNIQUEIDENTIFIER, SQL_VARIANT, XML, TABLEMicrosoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database)[90] | StaticTINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINTFLOAT, REALNUMERIC, DECIMAL, MONEYNCHAR, NVARCHAR, NTEXTBINARY, VARBINARY, IMAGEDATETIMEBITTIMESTAMP, ROWVERSION, UNIQUEIDENTIFIER, IDENTITY, ROWGUIDCOLMySQL[91] | StaticTINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), MEDIUMINT (24-bit), INT (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)FLOAT (32-bit), DOUBLE (aka REAL) (64-bit)DECIMALCHAR, BINARY, VARCHAR, VARBINARY, TEXT, TINYTEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXTTINYBLOB, BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, LONGBLOBDATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP, YEARBOOLEAN (aka BOOL) = synonym for TINYINTENUM, SET, GIS data types (Geometry, Point, Curve, LineString, Surface, Polygon, GeometryCollection, MultiPoint, MultiCurve, MultiLineString, MultiSurface, MultiPolygon)Oracle[92] | Static + Dynamic (through ANYDATA)NUMBERBINARY_FLOAT, BINARY_DOUBLENUMBERCHAR, VARCHAR2, CLOB, NCLOB, NVARCHAR2, NCHARBLOB, RAW, LONGRAW, BFILEDATE, TIMESTAMP (with/without TIMEZONE), INTERVALN/ASPATIAL, IMAGE, AUDIO, VIDEO, DICOM, XMLTypePolyhedra | StaticINTEGER8 (8-bit), INTEGER(16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit)FLOAT32 (32-bit), FLOAT (aka REAL; 64-bit)N/AVARCHAR, LARGE VARCHAR (aka CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT)LARGE BINARY (aka BINARY LARGE OBJECT)DATETIMEBOOLEANN/APostgreSQL[93] | StaticSMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)REAL (32-bit), DOUBLE PRECISION (64-bit)DECIMAL, NUMERICCHAR, VARCHAR, TEXTBYTEADATE, TIME (with/without TIMEZONE), TIMESTAMP (with/without TIMEZONE), INTERVALBOOLEANENUM, POINT, LINE, LSEG, BOX, PATH, POLYGON, CIRCLE, CIDR, INET, MACADDR, BIT, UUID, XML, arraysRDM Embedded[94] | Statictinyint, smallint, integer, bigintreal, float, doubleN/Achar, varchar, wchar, varwchar, long varchar, long varwcharbinary, varbinary, long varbinarydate, time, timestampbitN/ARDM Server[95] | Statictinyint, smallint, integer, bigintreal, float, doubledecimal, numericchar, varchar, wchar, varwchar, long varchar, long varwcharbinary, varbinary, long varbinarydate, time, timestampbitrowidSQLite[96] | DynamicINTEGER (64-bit)REAL (aka FLOAT, DOUBLE) (64-bit)N/ATEXT (aka CHAR, CLOB)BLOBN/AN/AN/AUniData | DynamicN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AUniVerse | DynamicN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AN/AXeround Cloud Database | StaticTINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), MEDIUMINT (24-bit), INT (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit)FLOAT (32-bit), DOUBLE (aka REAL) (64-bit)DECIMALCHAR, BINARY, VARCHAR, VARBINARY, TEXT, TINYTEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXTTINYBLOB, BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, LONGBLOBDATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP, YEARBOOLEAN (aka BOOL) = synonym for TINYINTENUM, SET | Type system | Integer | Floating point | Decimal | String | Binary | Date/Time | Boolean | Other | Other objects
Information about what other objects are supported natively.
4th Dimension | YesNoYesYesYesYesADABAS | ?Yes?Yes?Yes??Adaptive Server Enterprise | YesYesYesYesYesYesAdvantage Database Server | YesYesYesYesYesYesApache Derby | NoYesYesYes 2Yes 2Yes 2CUBRID | YesYesYesYesYes 2YesDrizzle | YesYesYes 4Yes 4Yes 4Yes 4Empress Embedded Database | Yes via RANGE CHECKYesYesYesYesYesDB2 | Yes via CHECK CONSTRAINTYesYesYesYesYesFirebird | YesYesYesYesYesYesHSQLDB | YesNoYesYesYesYesH2 | YesNoYes 2Yes 2Yes 2YesInformix Dynamic Server | Yes via CHECKYesYesYesYesYesIngres | YesYesYesYesYesYesInterBase | YesYesYesYesYesYesLinter SQL RDBMS | NoYesYesYesYesNoLucidDB | NoYesNoYes 2Yes 2Yes 2MaxDB | YesYesYesYesYes?Microsoft Access (JET) | YesNoNoNoYes, But single DML/DDL OperationYesMicrosoft Visual Foxpro | NoYesYesYesYesYesMicrosoft SQL Server | Yes (2000 and beyond)YesYesYesYesYesMicrosoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | NoYesNoNoNoNoMonetDB | NoNoYesYesYesYesMySQL | No 3YesYesYesYesYesOpenBase SQL | YesYesYesYesYesYesOracle | YesYesYesYesYesYesOracle Rdb | YesYesYesYesYesYesOpenLink Virtuoso | YesYesYesYesYesYesPolyhedra DBMS | NoNoYesYesYesYesPostgreSQL | YesYesYesYesYesYesRDM Embedded | NoYesNoNoYesYesRDM Server | NoYesYesNoYesYesScimoreDB | NoNoNoNoYesYesSQL Anywhere | YesYesYesYesYesYesSQLite | NoNoYesNoNoYesTeradata | NoYesYesYesYesYesUniData | NoNoYesYesYesYesUniVerse | NoNoYesYesYesYesXeround Cloud Database | No 3YesYesYesYesNo | Data Domain | Cursor | Trigger | Function 1 | Procedure 1 | External routine 1 | Note (1): Bothfunction and procedure refer to internal routines written in SQL and/or procedural language likePL/SQL. External routine refers to the one written in the host languages, such as C, Java, Cobol, etc. "Stored procedure" is a commonly used term for these routine types. However, its definition varies between different database vendors.
Note (2): In Derby, H2, LucidDB, and CUBRID, users codefunctions and procedures in Java.
Note (3): ENUM datatype exist. CHECK clause is parsed, but not enforced in runtime.
Note (4): In Drizzle the user codesfunctions and procedures in C++.
Partitioning
Information about what partitioning methods are supported natively.
4th Dimension | ????ADABAS | ????Adaptive Server Enterprise | YesYesNoYesAdvantage Database Server | NoNoNoNoApache Derby | NoNoNoNoCUBRID | YesYesNoYesIBM DB2 | YesYesYesYesEmpress Embedded Database | NoNoNoNoFirebird | NoNoNoNoHSQLDB | NoNoNoNoH2 | NoNoNoNoInformix Dynamic Server | YesYesYesYesYesIngres | YesYesYesYesInterBase | NoNoNoNoLinter SQL RDBMS | NoNoNoNoMaxDB | NoNoNoNoMicrosoft Access (JET) | NoNoNoNoMicrosoft Visual Foxpro | NoNoNoNoMicrosoft SQL Server | YesNoNoNoMicrosoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | NoNoNoNoMonetDB | Yes (M5)Yes (M5)Yes (M5)NoMySQL | YesYesYesYesOpenBase SQL | ????Oracle | YesYesYesYesOracle Rdb | YesYes??OpenLink Virtuoso | YesNoNoNoPolyhedra DBMS | NoNoNoNoPostgreSQL | Yes1Yes1Yes1Yes1RDM Embedded | Yes2Yes2Yes2NoRDM Server | NoNoNoNoScimoreDB | NoYesNoNoSQL Anywhere | NoNoNoNoSQLite | NoNoNoNoTeradata | YesYesYesYesUniVerse | YesYesYesYesXeround Cloud Database | N/A - partitioning provided transparentlyN/A - partitioning provided transparentlyN/A - partitioning provided transparentlyN/A - partitioning provided transparently | Range | Hash | Composite (Range+Hash) | List | Note (1): PostgreSQL 8.1 provides partitioning support through check constraints. Range, List and Hash methods can be emulated with PL/pgSQL or other procedural languages.[97]
Note (2): RDM Embedded 10.1 requires the application programs to select the correct partition (using range, hash or composite techniques) when adding data, but the database union functionality allows all partitions to be read as a single database.[98]
Access control
Information about access control functionalities (work in progress).
Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes (optional; to pay)YesYes (optional ?)YesPartial (need to register; depend on which product)[99]YesYesYesYesYes (EAL4+ 1)Advantage Database Server | YesNoNoNo?YesNoNoYes?DB2 | Yes?Yes (LDAP, Kerberos…)Yes?YesYesYesYesYes (EAL4+6)Empress Embedded Database | ??NoNoYesYesYesNoYesNoFirebird | NoYes[100]Yes (Windows trusted authenification)NoPartial (no security page)[101]YesNoNoNo7?HSQLDB | YesNoYesYesYesYesNoNoYesNoH2 | YesYes?No?Yes?YesYesNoInformix Dynamic Server | Yes?Yes10?10YesYesYesYesYes?Linter SQL RDBMS | Yes (with SSL)YesNoYes (length only)NoYesYesYesYesYesMySQL | Yes (SSL with 4.0)NoYes (with 5.5)NoPartial (no security page)[102]Yes???8NoOpenBase SQL | Yes?Yes (Open Directory, LDAP)No??????Microsoft SQL Server | Yes?Yes (Microsoft Active Directory)YesYesYesYes (From 2008)YesYesYes (EAL1+1)Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | No (not relevant, only file permissions)No (not relevant)No (not relevant)No (not relevant)YesYes (file access)YesYesNo?Oracle | YesYesYesYes?YesYesYesYesYes (EAL4+1)PostgreSQL | YesYes (for 9.1)Yes (LDAP, Kerberos…9)Yes (as of 9.0 with passwordcheck module)Yes[103]YesNoYesYesYes (EAL11)RDM Embedded | NoNoNoNoNoYesNoNoNoNoRDM Server | YesNoNoNoNoYesYesNoYesNoSQL Anywhere | Yes?Yes (Kerberos)Yes?YesYesNoYesYes (EAL3+1 as Adaptive Server Anywhere)SQLite | No (not relevant, only file permissions)No (not relevant)No (not relevant)No (not relevant)Partial (no security page)[104]Yes (file access)YesYesNoNoXeround Cloud Database | Yes (SSL with 4.0)NoNoNoN/A - database as a serviceYesNoNoNoNo | Native network encryption1 | Brute-force protection | Enterprise directory compatibility | Password complexity rules2 | Patch access3 | Run unprivileged4 | Audit | Resource limit | Separation of duties (RBAC)5 | Security Certification | Note (1): Network traffic could be transmitted in a secure way (not clear-text, en general SSL encryption). Precise if option is default, included option or an extra modules to buy.
Note (2): Options are present to set a minimum size for password, respect complexity like presence of numbers or special characters.
Note (3): How do you get security updates? Is it free access, do you need a login or to pay? Is there easy access through a Web/FTP portal or RSS feed or only through offline access (mail CD-ROM, phone).
Note (4): Does database process run as root/administrator or unprivileged user? What is default configuration?
Note (5): Is there a separate user to manage special operation like backup (only dump/restore permissions), security officer (audit), administrator (add user/create database), etc.? Is it default or optional?
Note (6): Common Criteria certified product list[105]
Note (7): FirebirdSQL seems to only have SYSDBA user and DB owner. There are no separate roles for backup operator and security administrator.
Note (8): User can define a dedicated backup user but nothing particular in default install[106]
Note (9): Authentication methods[107]
Note (10): Informix Dynamic Server supports PAM and other configurable authentication. By default uses OS authentication.
Databases vs schemas (terminology)
This section may contain original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding references. Statements consisting only of original research may be removed. More details may be available on thetalk page. (June 2010)The SQL specification makes clear what an "SQL schema" is; however, different databases implement it incorrectly. To compound this confusion the functionality can, when incorrectly implemented, overlap with that of the parent-database. An SQL schema is simply a namespace within a database, things within this namespace are addressed using the memberoperator dot ".". This seems to be a universal amongst all of the implementations.
A true fully (database, schema, and table) qualified query is exemplified as such: SELECT * FROM database.schema.table
Now, the issue, both a schema and a database can be used to isolate one table, "foo" from another like named table "foo". The following is pseudo code:
SELECT * FROM db1.foo vs. SELECT * FROM db2.foo (no explicit schema between db and table)SELECT * FROM [db1.]default.foo vs. SELECT * FROM [db1.]alternate.foo (no explicit db prefix)
The problem that arises is that former MySQL users will create multiple databases for one project. In this context, MySQL databases are analogous in function to Postgres-schemas, insomuch as Postgres lacks off-the-shelf cross-database functionality that MySQL has. Conversely,PostgreSQL has applied more of the specification implementing cross-table, cross-schema, and then left room for future cross-database functionality.
MySQL aliases schema with database behind the scenes, such thatCREATE SCHEMA and CREATE DATABASE are analogs. It can therefore be said that MySQL has implemented cross-table functionality, skipped schema functionality entirely, and provided similar functionality into their implementation of a database. In summary, Postgres fully supports schemas but lacks some functionality MySQL has with databases, while MySQL does not even attempt to support true schemas.
Oracle has its own spin where creating a user is synonymous with creating a schema. Thus a database administrator can create a user called PROJECT and then create a table PROJECT.TABLE. Users can exist without schema objects, but an object is always associated with an owner (though that owner may not have privileges to connect to the database). With the Oracle 'shared-everything' RAC architecture, the same database can be opened by multiple servers concurrently. This is independent of replication, which can also be used, whereby the data is copied for use by different server. In the Oracle view, the 'database' is a set of files which contains the data while the 'instance' is a set of processes (and memory) through which a database is accessed.
Informix supports multiple databases in a server instance, like MySQL. It supports the CREATE SCHEMA syntax as a way to group DDL statements into a single unit creating all objects created as a part of the schema as a single owner. Informix supports a database mode called ANSI mode which supports creating objects with the same name but owned by different users.
The end result is confusion between the database factions. The Postgres and Oracle communities maintain that one database is all that is needed for one project, per the definition of database. MySQL and Informix proponents maintain that schemas have no legitimate purpose when the functionality can be achieved with databases. Postgres adheres to the SQL specification, in a more intuitive fashion (bottom-up), while MySQL’spragmatic counterargument allows their users to get the job done while creating conceptual confusion.
See also
- List of relational database management systems
- Comparison of object-relational database management systems
- Comparison of database tools
- Object Database - some of which have relational (SQL/ODBC) interfaces.
References
- ^Altibase.
- ^NHN Corp.
- ^Empress.
- ^FileMaker.
- ^Firebird SQL.
- ^IPL, Firebird SQL.
- ^IDPL, Firebird SQL.
- ^hsqldb
- ^Eigenbase.
- ^"MariaDB 5.5.23 Release Notes".AskMonty KnowledgeBase. Retrieved 2012-04-18.
- ^ a b VisualFoxPro.
- ^MonetDB Public License, CWI.
- ^mSQL, Products, AU: Hughes.
- ^Nexus DB.
- ^Omnis.
- ^OpenBase.
- ^OpenLink Software.
- ^Oracle Rdb Product Family Compatibility Matrix, Oracle Corporation.
- ^Corel.
- ^PostgreSQL development group, PostgreSQL community.
- ^PostgreSQL 2012-02-27 Security Update, Documentation, PostgreSQL Community.
- ^License, PostgreSQL Community.
- ^r:Base.
- ^RDM Embedded, Raima Inc.
- ^RDM Server, Raima Inc..
- ^Scimore.
- ^SQLBase, Products, Unify.
- ^SQLite Release History, SQLite.
- ^"Building MariaDB on Mac OS X using Homebrew".AskMonty KnowledgeBase. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ^a b Transactional DDL in PostgreSQL: A Competitive Analysis
- ^SQLite Full Unicode support is optional and not installed by default in most systems (likeAndroid, Debian…)
- ^"MySQL - The InnoDB Storage Engine".
- ^"InnoDB - Oracle Wiki".
- ^"MySQL 5.6 Reference Manual".
- ^Technical Specifications, Guide, Firebird SQL.
- ^Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^ a b "Column count limit",Reference Manual, MySQL Documentation, Oracle.
- ^"Row-Overflow Considerations",TechNet Library, SQL Server Documentation, Microsoft.
- ^"Date functions",Language, SQLite.
- ^Online books, Sybase.
- ^Informix Performance Guide, Info Centre, IBM.
- ^"SQL",Prod Technol, Tech Net, Microsoft.
- ^Archives, Pure, Red Noize.
- ^"Materialized Views",PostgreSQL, Jonathan Gardner.
- ^"Derby",Full Text Indexing, Search, Issues, Apache.
- ^Full-text search with DB2 Text Search, Developer Works, IBM.
- ^Does Firebird support full-text search?, Firebird FAQ.
- ^Fulltext Search, Tutorial, H2 Database.
- ^(PDF) Full Text Search Functions, Documentation, RU: Linter.
- ^Does Microsoft Access have Full Text Search?, Questions, Stack Overflow.
- ^"Microsoft SQL Server Full-Text Search",Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^"Spatial Indexing Overview",Library, Tech Net, Microsoft.
- ^"Microsoft SQL Server Compact Full-text search is not available",Forums, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^"Feature request #4990: Functional Indexes",Bugs, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^"Feature request #13979: InnoDB engine doesn't support FULLTEXT",Bugs, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^Creating Spatial Indexes, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^Does Oracle support full text search?, Questions, Stack Overflow
- ^"Location Features for Database 11g",Spatial & Locator, Tech Network, Oracle.
- ^Full Text Search], Documentation, PostgreSQL community,http://www.postgresql.org/docs/8.4/static/textsearch.html.
- ^"4",Manual, PostGIS, Refractions.
- ^Free text search queries in SQL, ScimoreDB.
- ^The SQLite R*Tree Module
- ^SQLite FTS3 Extension
- ^SpatiaLite, IT: Gaia GIS.
- ^Full-Text Search, Online Publications, Teradata.
- ^UDF, Ad Hoc Data.
- ^"Create DB",Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^"SQL",Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^Petkovic, Dusan (2005). Microsoft SQL Server 2005: A Beginner’s Guide. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 300.ISBN 978-0-07-226093-9.
- ^"Indexed Views",Library, MSDN.
- ^"InnoDB adaptive Hash",Reference manual, Development documentation, Oracle.
- ^How does Drizzle handle parallel "things"?
- ^"Article",Library, Developer Works, IBM.
- ^New Features in HyperSQL 2.2
- ^New Features in HyperSQL 2.2
- ^H2 > Advanced > Recursive Queries
- ^H2 Roadmap
- ^Informix parallel data query (PDQ)
- ^"SQL Server Parallel Query Processing",Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^"Feature request #16244: SQL-99 Derived table WITH clause (CTE)",Bugs, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^"Feature request #1542: Parallel query",Bugs, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^Parallel Query, Wiki, Ora FAQ
- ^PostgreSQL lacks parallel query processing, Mark Mail.
- ^"Data Types",CUBRID SQL Guide, Reference Manual, CUBRID.
- ^Built-in Column Types, Documents, Drizzle.
- ^"General: HSQLDB data types",Guide, Documents, HSQLDB.
- ^, Publications, IBM, http://www.ibm.com/shop/publications/order?CTY=US&FNC=SRX&PBL=SC23-7750-04.
- ^"3: Understanding SQL Data Types",SQL Reference Guide, Doucments, Ingres.
- ^"SQL Server Data Types",Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^"SQL Server Compact Data Types",Library, MSDN, Microsoft.
- ^"10. Data Types",Reference manual, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^"Data Types",SQL Reference, Server documents, Oracle
- ^"Data Types",Manual, Documents, PostgreSQL community.
- ^"Defining a Database",SQL Reference, Raima
- ^"Defining Table Columns",SQL Reference, Raima
- ^Datatypes, SQLite.
- ^"Release",Documents, Developer, PostgreSQL community.
- ^"5.11 Database Unions",User's Guide, Raima.
- ^Support, Downloads, Sybase.
- ^"Release",Engine, Development, Firebird SQL.
- ^Files, Firebird SQL.
- ^"Downloads",Development, MySQL, Oracle.
- ^Security, Support, PostgreSQL community.
- ^Download, SQLite.
- ^DB, Products, Common Criteria Portal.
- ^Backup MySQL, How to, Gentoo wiki.
- ^Authentication methods, Documents, PostgreSQL community.