memcached内存管理(2) ----------------items
来源:互联网 发布:上古卷轴5帧数优化mod 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/01 10:26
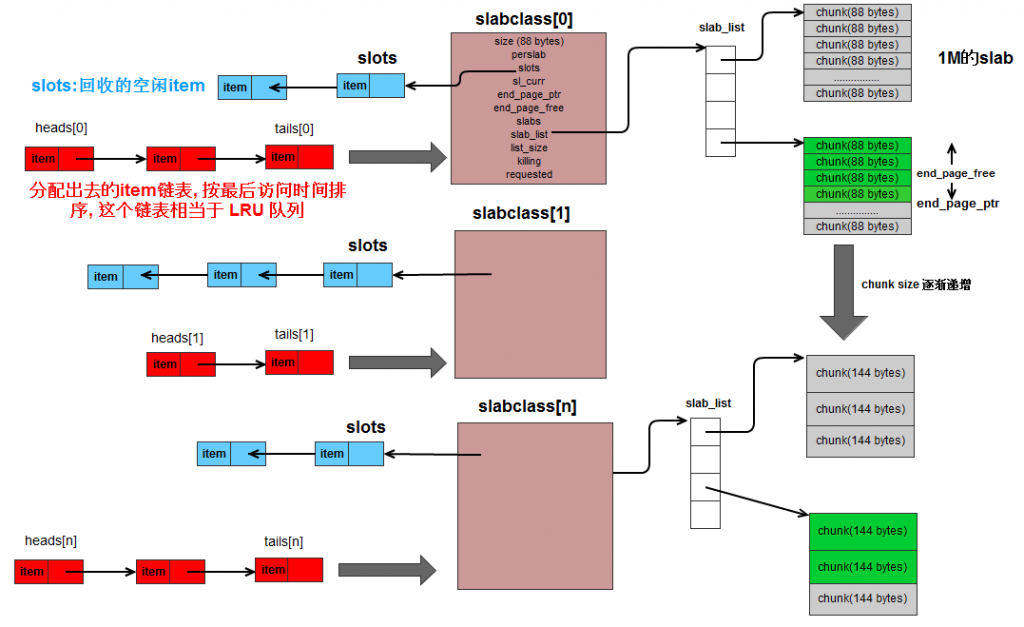
memcached.h中item的声明
/** * Structure for storing items within memcached. */typedef struct _stritem { struct _stritem *next; struct _stritem *prev; struct _stritem *h_next; /* hash chain next */ rel_time_t time; /* least recent access */ rel_time_t exptime; /* expire time */ int nbytes; /* size of data */ unsigned short refcount; uint8_t nsuffix; /* length of flags-and-length string */ uint8_t it_flags; /* ITEM_* above */ uint8_t slabs_clsid;/* which slab class we're in */ uint8_t nkey; /* key length, w/terminating null and padding */ /* this odd type prevents type-punning issues when we do * the little shuffle to save space when not using CAS. */union { uint64_t cas; char end; } data[];} item;next,pre是双向链表使用的,用于slots,heads和tails,h_next则用于hash表
time 是最近访问时间,time=current_time, 新的item都会放在对应id双向链表的开头,而do_item_alloc会从链表尾开始搜链表,变相的实现了LRU
exptime 过期时间
nbytes 实际数据的字节数
refcount 引用次数
nsuffix 后缀的长度,以下代码赋值
*nsuffix = (uint8_t) snprintf(suffix, 40, " %d %d\r\n", flags, nbytes - 2);即通过snprintf返回的值
it_flags
slab_clsid 所属的slabclass的id
nkey 键长
union { uint64_t cas; char end; } data[];变长数组,真正存放key-value的地方具体的内容为 cas + key + suffix + data
cas 是一个编号,不一定会使用
key是键
suffix是后缀,由前面的snprintf赋值
data就是我们的数据了
一组调用的宏,位于memcached.h
#define ITEM_get_cas(i) (((i)->it_flags & ITEM_CAS) ? \ (i)->data->cas : (uint64_t)0)#define ITEM_set_cas(i,v) { \ if ((i)->it_flags & ITEM_CAS) { \ (i)->data->cas = v; \ } \}#define ITEM_key(item) (((char*)&((item)->data)) \ + (((item)->it_flags & ITEM_CAS) ? sizeof(uint64_t) : 0))#define ITEM_suffix(item) ((char*) &((item)->data) + (item)->nkey + 1 \ + (((item)->it_flags & ITEM_CAS) ? sizeof(uint64_t) : 0))#define ITEM_data(item) ((char*) &((item)->data) + (item)->nkey + 1 \ + (item)->nsuffix \ + (((item)->it_flags & ITEM_CAS) ? sizeof(uint64_t) : 0))#define ITEM_ntotal(item) (sizeof(struct _stritem) + (item)->nkey + 1 \ + (item)->nsuffix + (item)->nbytes \ + (((item)->it_flags & ITEM_CAS) ? sizeof(uint64_t) : 0))用于获取具体item的cas,key,suffix和data的起始地址。
从宏ITEM_ntotal可以看出一个item 的实际长度为 sizeof(item) + nkey + 1 + nsuffix + nbytes ( + sizoef(uint64_t), 如果使用了cas)
上面的数据结构就是item的大概,下面就看看item是如何获取内存和释放内存
item.c中的重要全局变量
static item *heads[LARGEST_ID];static item *tails[LARGEST_ID];为对应的slabclass中从slots获取而来空间(以item方式组织的双向链表),分别指向链表的头尾,LRU。
do_item_alloc函数
/** * Generates the variable-sized part of the header for an object. * * key - The key * nkey - The length of the key * flags - key flags * nbytes - Number of bytes to hold value and addition CRLF terminator * suffix - Buffer for the "VALUE" line suffix (flags, size). * nsuffix - The length of the suffix is stored here. * * Returns the total size of the header. */static size_t item_make_header(const uint8_t nkey, const int flags, const int nbytes, char *suffix, uint8_t *nsuffix) { /* suffix is defined at 40 chars elsewhere.. */ *nsuffix = (uint8_t) snprintf(suffix, 40, " %d %d\r\n", flags, nbytes - 2); return sizeof(item) + nkey + *nsuffix + nbytes;}给suffix赋值,并返回item总的长度(除去cas的)。总长度用于决定该item属于哪个slabclass/*@null@*/item *do_item_alloc(char *key, const size_t nkey, const int flags, const rel_time_t exptime, const int nbytes) { uint8_t nsuffix; item *it = NULL; char suffix[40]; size_t ntotal = item_make_header(nkey + 1, flags, nbytes, suffix, &nsuffix); if (settings.use_cas) { ntotal += sizeof(uint64_t); } unsigned int id = slabs_clsid(ntotal); if (id == 0) return 0; mutex_lock(&cache_lock); /* do a quick check if we have any expired items in the tail.. */ item *search; rel_time_t oldest_live = settings.oldest_live; //从尾部开始搜索,因为尾部的time总是最早的,所以就是一种LRU实现 search = tails[id]; if (search != NULL && (refcount_incr(&search->refcount) == 2)) { if ((search->exptime != 0 && search->exptime < current_time) || (search->time <= oldest_live && oldest_live <= current_time)) { // dead by flush //如果尾部的item已经超时,那么就替换掉 STATS_LOCK(); stats.reclaimed++; STATS_UNLOCK(); itemstats[id].reclaimed++; if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) { STATS_LOCK(); stats.expired_unfetched++; STATS_UNLOCK(); itemstats[id].expired_unfetched++; } //替换掉已经超时的item it = search; slabs_adjust_mem_requested(it->slabs_clsid, ITEM_ntotal(it), ntotal); //虽然属于同一个slabclass,但是长度仍可能不一样,需要修改一下 do_item_unlink_nolock(it, hash(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, 0)); //将超时的item从双向链表和hash表中除去 /* Initialize the item block: */ it->slabs_clsid = 0; //slab_clsid设为0 } else if ((it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id)) == NULL) {//没有超时,则从slabclass中的slots获取空间,还是失败的话 if (settings.evict_to_free == 0) { //evict_to_free = 0 的话则直接返回null,否则强行将最后一个item替换掉 itemstats[id].outofmemory++; mutex_unlock(&cache_lock); return NULL; } itemstats[id].evicted++; itemstats[id].evicted_time = current_time - search->time; if (search->exptime != 0) itemstats[id].evicted_nonzero++; if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) { STATS_LOCK(); stats.evicted_unfetched++; STATS_UNLOCK(); itemstats[id].evicted_unfetched++; } STATS_LOCK(); stats.evictions++; STATS_UNLOCK(); it = search; slabs_adjust_mem_requested(it->slabs_clsid, ITEM_ntotal(it), ntotal); do_item_unlink_nolock(it, hash(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, 0)); /* Initialize the item block: */ it->slabs_clsid = 0; /* If we've just evicted an item, and the automover is set to * angry bird mode, attempt to rip memory into this slab class. * TODO: Move valid object detection into a function, and on a * "successful" memory pull, look behind and see if the next alloc * would be an eviction. Then kick off the slab mover before the * eviction happens. */ if (settings.slab_automove == 2) slabs_reassign(-1, id); } else { refcount_decr(&search->refcount); } } else { /* If the LRU is empty or locked, attempt to allocate memory */ it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id); if (search != NULL) refcount_decr(&search->refcount); } if (it == NULL) { itemstats[id].outofmemory++; /* Last ditch effort. There was a very rare bug which caused * refcount leaks. We leave this just in case they ever happen again. * We can reasonably assume no item can stay locked for more than * three hours, so if we find one in the tail which is that old, * free it anyway. */ if (search != NULL && search->refcount != 2 && search->time + TAIL_REPAIR_TIME < current_time) { itemstats[id].tailrepairs++; search->refcount = 1; do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hash(ITEM_key(search), search->nkey, 0)); } mutex_unlock(&cache_lock); return NULL; } assert(it->slabs_clsid == 0); assert(it != heads[id]); /* Item initialization can happen outside of the lock; the item's already * been removed from the slab LRU. */ //初始化一些item属性,可以看出这里只是申请了data所需要的空间,而未给data真正的赋值,并且将其连入到LRU和hash表的操作也不在这 it->refcount = 1; /* the caller will have a reference */ mutex_unlock(&cache_lock); it->next = it->prev = it->h_next = 0; it->slabs_clsid = id; DEBUG_REFCNT(it, '*'); it->it_flags = settings.use_cas ? ITEM_CAS : 0; it->nkey = nkey; it->nbytes = nbytes; memcpy(ITEM_key(it), key, nkey); it->exptime = exptime; memcpy(ITEM_suffix(it), suffix, (size_t)nsuffix); it->nsuffix = nsuffix; return it;}上面代码如果要替换掉最后的item时会将其从LRU和hash表中除掉
void do_item_unlink(item *it, const uint32_t hv) { MEMCACHED_ITEM_UNLINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes); mutex_lock(&cache_lock); if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) { it->it_flags &= ~ITEM_LINKED; STATS_LOCK(); stats.curr_bytes -= ITEM_ntotal(it); stats.curr_items -= 1; STATS_UNLOCK(); assoc_delete(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, hv); //从hash表中删除,在assoc.c中再解释 item_unlink_q(it); //从LRU中删除 do_item_remove(it); //返回item的空间 } mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);}item_unlink_q函数
static void item_unlink_q(item *it) { item **head, **tail; assert(it->slabs_clsid < LARGEST_ID); head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid]; tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid]; if (*head == it) { assert(it->prev == 0); *head = it->next; } if (*tail == it) { assert(it->next == 0); *tail = it->prev; } assert(it->next != it); assert(it->prev != it); if (it->next) it->next->prev = it->prev; if (it->prev) it->prev->next = it->next; sizes[it->slabs_clsid]--; return;}还是很好懂的,就是普通的双向链表操作。do_item_remove函数
void do_item_remove(item *it) { MEMCACHED_ITEM_REMOVE(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes); assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0); if (refcount_decr(&it->refcount) == 0) { item_free(it); }}如果refcount为0则调用item_free返还item占用的空间void item_free(item *it) { size_t ntotal = ITEM_ntotal(it); unsigned int clsid; assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) == 0); assert(it != heads[it->slabs_clsid]); assert(it != tails[it->slabs_clsid]); assert(it->refcount == 0); /* so slab size changer can tell later if item is already free or not */ clsid = it->slabs_clsid; it->slabs_clsid = 0; DEBUG_REFCNT(it, 'F'); slabs_free(it, ntotal, clsid);}实际就是调用slabs_free将item占用的内存放回到slabclass的slots中。还有几个重要的函数
do_item_link 就是将item放入对用的LRU和hash表中
int do_item_link(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_LINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
assert((it->it_flags & (ITEM_LINKED|ITEM_SLABBED)) == 0);
mutex_lock(&cache_lock);
it->it_flags |= ITEM_LINKED;
it->time = current_time;
STATS_LOCK();
stats.curr_bytes += ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats.curr_items += 1;
stats.total_items += 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
/* Allocate a new CAS ID on link. */
ITEM_set_cas(it, (settings.use_cas) ? get_cas_id() : 0);
assoc_insert(it, hv);
item_link_q(it);
refcount_incr(&it->refcount);
mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);
return 1;
}
item_link_q函数,就是将item加入到LRU中
static void item_link_q(item *it) { /* item is the new head */
item **head, **tail;
assert(it->slabs_clsid < LARGEST_ID);
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
assert(it != *head);
assert((*head && *tail) || (*head == 0 && *tail == 0));
it->prev = 0;
it->next = *head;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it;
*head = it;
if (*tail == 0) *tail = it;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]++;
return;
}
do_item_update函数,就是改变其最后访问时间,反映到链表上就是将其移到链表头
void do_item_update(item *it) { MEMCACHED_ITEM_UPDATE(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes); if (it->time < current_time - ITEM_UPDATE_INTERVAL) { assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0); mutex_lock(&cache_lock); if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) { item_unlink_q(it); it->time = current_time; item_link_q(it); } mutex_unlock(&cache_lock); }}do_item_touch函数,改变exptimeitem *do_item_touch(const char *key, size_t nkey, uint32_t exptime, const uint32_t hv) { item *it = do_item_get(key, nkey, hv); if (it != NULL) { it->exptime = exptime; } return it;}do_item_get函数:通过hash表(key)来找到所要的所要的item ,其实就是调用assoc_find函数,将在后面再讲
/** wrapper around assoc_find which does the lazy expiration logic */item *do_item_get(const char *key, const size_t nkey, const uint32_t hv) { mutex_lock(&cache_lock); item *it = assoc_find(key, nkey, hv); if (it != NULL) { refcount_incr(&it->refcount); /* Optimization for slab reassignment. prevents popular items from * jamming in busy wait. Can only do this here to satisfy lock order * of item_lock, cache_lock, slabs_lock. */ if (slab_rebalance_signal && ((void *)it >= slab_rebal.slab_start && (void *)it < slab_rebal.slab_end)) { do_item_unlink_nolock(it, hv); do_item_remove(it); it = NULL; } } mutex_unlock(&cache_lock); int was_found = 0; if (settings.verbose > 2) { if (it == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "> NOT FOUND %s", key); } else { fprintf(stderr, "> FOUND KEY %s", ITEM_key(it)); was_found++; } } if (it != NULL) { if (settings.oldest_live != 0 && settings.oldest_live <= current_time && it->time <= settings.oldest_live) { do_item_unlink(it, hv); do_item_remove(it); it = NULL; if (was_found) { fprintf(stderr, " -nuked by flush"); } } else if (it->exptime != 0 && it->exptime <= current_time) { do_item_unlink(it, hv); do_item_remove(it); it = NULL; if (was_found) { fprintf(stderr, " -nuked by expire"); } } else { it->it_flags |= ITEM_FETCHED; DEBUG_REFCNT(it, '+'); } } if (settings.verbose > 2) fprintf(stderr, "\n"); return it;}大概就这样了吧。
再盗一张图
- memcached内存管理(2) ----------------items
- memcached 内存管理 分析
- memcached内存管理
- memcached内存管理
- Memcached内存管理分析
- Memcached内存管理
- memcached 中内存管理
- Memcached内存管理slabclass
- memcached-items操作
- Memcached 内存管理(一)
- memcached内存管理(1) ----------------slabs
- memcached内存管理(3) ----------------assoc
- Memcached内存管理源码阅读
- memcached 内存管理 分析(转)
- Memcached 内存管理(一)
- memcached源码学习-items操作
- python内存管理与Memcached内存管理的理解
- memcached 内存管理的一点变化
- 网络编程:优雅关闭socket/TIME_WAIT/CLOSE_WAIT/SoLinger
- 苹果为什么收购AuthenTec:“神秘技术”将用于下一代iPhone
- Spring集成CXF
- QTextCodec类更换中文编码环境出错问题
- reinterpret_cast,const_cast,static_cast,dynamic_cast 总结
- memcached内存管理(2) ----------------items
- Android真机如何开启logcat
- performSelector延时调用导致的内存泄露
- Clone 分浅拷贝和深拷贝
- oracle 权限管理
- $.each()遍历数组和集合对象
- 变焦与调焦的区别
- 读取xml档测试
- 关于设计模式----单例模式


