字符串指针与char型指针数组
来源:互联网 发布:诸暨企业网络综合布线 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/23 17:43
一、字符串指针
字符串是一种特殊的char型数组,指向char类型数组的指针,就是字符串指针。与普通指针一样,字符串指针在使用前也必须定义。字符串与char数组的区别在于长度,字符会自动在尾部加上一个长度‘\0’,而char型数组的长度就是其字符的个数。字符串长度是字符个数+1。例:
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ char str[]="hello world"; char *p=str; cout<<str<<endl; cout<<p<<endl; cout<<*p<<endl; system("pause"); }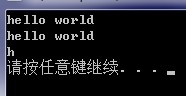
二、char型指针数组
指针数组的元素是指针。与普通指针类似,指针数组在使用前也必须先赋值,否则可能指向没有意义的值,这是比较危险的。以char型指针数组为例。
int main(){ char *p[5]={"abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno"}; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) puts(p[i]); system("pause"); }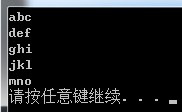
对于int型数据,如下:
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ int a=1,b=2,c=3; int *p[]={&a,&b,&c};//不能写成int *p[]={1,2,3},这是不合法的。因为p与[]先结合,是一个指针数组,数组的数据元素是int型指针,而不是int型数据。 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) cout<<p[i]<<endl;//打印出地址(指针) system("pause"); }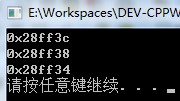
三、对比int型和char型数组的数组名和取地址
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ int a[]={1,2,3}; char b[]={'a','b','c'}; cout<<a<<endl; cout<<&a<<endl; cout<<b<<endl; cout<<&b<<endl; system("pause"); }
- 字符串指针与char型指针数组
- 字符串指针与char型指针数组
- 字符串与char数组的指针表示
- char* ,char[],指针与数组
- char数组与char指针
- char数组与char指针
- char数组 、char指针与字符串常量的比较
- char数组 、char指针与字符串常量的比较
- 二维char数组与二维char指针
- char *指针与char 数组的区别
- 字符串数组与指针
- 字符串数组与指针
- 数组、指针与字符串
- 数组、指针与字符串
- 数组、字符串与指针
- 字符串数组与指针
- 数组字符串与指针字符串的区别 char s[]="***" 和char *s="***"的区别
- char型指针数组与字符数组的区别
- 关于空类 含有虚函数类 占有空间大小
- 内向者怎样成为社交达人
- javascript变量作用域一点总结
- c# int数组与string数组一样定义
- 利用Hog特征和SVM分类器进行行人检测(自己收集正反例样本训练分类器)
- 字符串指针与char型指针数组
- DFLASH 配置
- 利用JAXP方式对XML解析
- cocos2d如何使用Texture Packer并优化spritesheet
- 装饰器模式(Decorator)
- 第05章 数组 08 练习6
- Java实现链表结构
- Project Euler Problem 47
- js url传值中文乱码之解决之道


