黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(对象序列化和字符编码)
来源:互联网 发布:电话软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 07:25
一、IO流(对象的序列化)
对象流:ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream(实现对象序列化)
序列化就是一种用来处理对象流的机制,所谓对象流也就是将对象的内容进行流化,流的概念这里不用多说(就是I/O),我们可以对流化后的对象进行读写操作,也可将流化后的对象传输于网络之间(注:要想将对象传输于网络必须进行流化)!在对对象流进行读写操作时会引发一些问题,而序列化机制正是用来解决这些问题的!
1.需要序列化的类需要实现Serializable接口或者Externalizable接口;
2.实现Serializable接口时,默认所有的属性都要被保存,若不想保存某些属性,有两种办法:
一是在不想保存的属性前面加上transient关键字;
二是在该类中实现下面两个方法,在该方法中自行选择需要保存哪些属性;
3.实现Externalizable接口时,默认所有的属性都不被保存,而是需要该类在实现Externalizable接口时,自行决定需要保存哪些属性(writeExternal和readExternal方法);
4.类的静态变量在序列化时是不保存的,如需要保存,则只能手动保存(即显示的将静态变量的值写入对象输出流);
更加详细的对象序列化,请参照这篇文章。
/*Person.java*/import java.io.*;class Person implements Serializable//类通过实现java.io.Serializable接口以启用其序列化功能。{static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;//自定义serialVersionUIDString name;transient int age;//transient修饰的成员不能被序列化static String country="cn";//static修饰的成员不能被序列化Person(String name,int age,String country){this.name=name;this.age=age;this.country=country;}public String toString(){return "姓名:"+name+"\t年龄:"+age+"\t国家:"+country;}}/*ObjectStreamDemo.java*/import java.io.*;class ObjectStreamDemo{public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{//writeObj();//1.readObj();//2 }public static void readObj()throws Exception{ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.txt"));Person p=(Person)ois.readObject();System.out.println(p);for(int i=0;i<2;i++){System.out.println((Person)ois.readObject());}ois.close();}public static void writeObj()throws Exception{ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("obj.txt"));oos.writeObject(new Person("lisi",30,"kr"));oos.writeObject(new Person("zhangsan",25,"cn"));oos.writeObject(new Person("wangwu",20,"kr"));oos.flush();oos.close();}}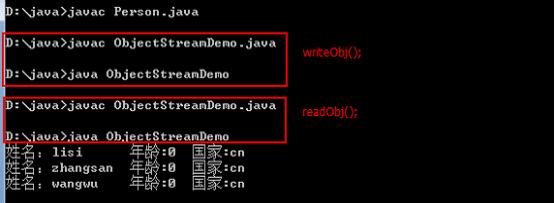
二、IO流(管道流)
/*IO流(管道流):PipedInputStream和PipedOutStream输入输出可以直接进行连接,通过结合线程使用。*/import java.io.*;class Read implements Runnable{private PipedInputStream in;Read(PipedInputStream in){this.in=in;}public void run(){try{byte[] buf=new byte[1024];System.out.println("读取前....没有数据,阻塞...");int len=in.read(buf);System.out.println("读取后....阻塞结束...");String s=new String(buf,0,len);System.out.println(s);in.close();}catch (IOException e){throw new RuntimeException("管道读取流失败");}}}class Write implements Runnable{private PipedOutputStream out;Write(PipedOutputStream out){this.out=out;}public void run(){try{System.out.println("开始写入数据,等待3秒...");Thread.sleep(3000);out.write("管道流示例。。。。。".getBytes());out.close();}catch (Exception e){throw new RuntimeException("管道输出流失败");}}}class PipedStream{public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{PipedInputStream in=new PipedInputStream();PipedOutputStream out=new PipedOutputStream();in.connect(out);Read r=new Read(in);Write w=new Write(out);new Thread(r).start();new Thread(w).start();}}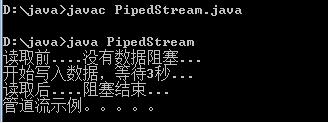
三、IO流(RandomAccessFile)
随机访问文件,自身具备读写的方法。
通过skipBytes(int x),seek(int x)来达到随机访问。
/*RandomAccessFile:该类不算是IO体系中的子类,而是直接继承自Object,但它是IO包中成员,因为它具备读和写功能。内部封装了一个数组,通过指针对数组的元素进行操作,通过getFilePointer获取指针的位置,同时可以通过seek改变指针的位置。其实完成读写的原理就是内部封装了字节输入流和输出流。public RandomAccessFile(File file, String mode) throws FileNotFoundException通过构造函数可以看出,该类只能操作文件。而且操作文件还有mode(模式): "r" 以只读方式打开。调用结果对象的任何 write 方法都将导致抛出 IOException。 "rw" 打开以便读取和写入。如果该文件尚不存在,则尝试创建该文件。 "rws" 打开以便读取和写入,对于 "rw",还要求对文件的内容或元数据的每个更新都同步写入到底层存储设备。 "rwd" 打开以便读取和写入,对于 "rw",还要求对文件内容的每个更新都同步写入到底层存储设备。 如果模式是"r"的话,不会创建文件,会去读取已存在的文件,如果不存在会出现异常。如果模式是"rw"的话,操作的文件不存在会自动创建,如果存在不会覆盖。*/import java.io.*;class RandomAccessFileDemo {public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {writeFile();readFile();//readFile_2();}/*public static void readFile_2()throws IOException {RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","rw");raf.seek(8*1);raf.write("周期".getBytes());raf.writeInt(102);raf.close();}*/public static void readFile()throws IOException {RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","r");raf.seek(8*1);//调整对象中的指针。往前和往后均可。//raf.skipBytes(8);//跳过指定的字节数。只能往后,不能往前byte[] buf=new byte[4];raf.read(buf);String name=new String(buf);int age=raf.readInt();System.out.println("name:"+name+"\tage:"+age);raf.close();}public static void writeFile()throws IOException{RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","rw");raf.write("李四".getBytes());//raf.write(97);//只能写一个字节,97存入错误。raf.writeInt(98);//写4个字节,98完美写入raf.write("王五".getBytes());raf.writeInt(97);raf.close();}}
四、IO流(操作基本数据类型的流对象DataStream)
操作基本数据类型:
DataInputStream与DataOutputStream
/*DataInputStream与DataOutputStream:可以用于操作基本数据类型的数据的流对象。*/import java.io.*;class DataStreamDemo{public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{writeData();readData();writeUTFDemo();readUTFDemo();}public static void readUTFDemo()throws IOException{DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("utfdata.txt"));String s=dis.readUTF();System.out.println(s);dis.close();}public static void writeUTFDemo()throws IOException{DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("utfdata.txt"));dos.writeUTF("你好");dos.close();}public static void readData()throws IOException{DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt"));int num=dis.readInt();boolean b=dis.readBoolean();double d=dis.readDouble();System.out.println("num:"+num);System.out.println("b:"+b);System.out.println("d:"+d);dis.close();}public static void writeData()throws IOException{DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt"));dos.writeInt(123);dos.writeBoolean(true);dos.writeDouble(213.345);dos.close();}}
五、IO流(ByteArrayStream)
操作字节数组:
ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream
/*用于操作字节数组的流对象。ByteArrayInputStream:在构造的时候需要接受数据源,而且数据源是一个字节数组。ByteArrayOutputStream:在构造的时候不用定义数据目的,因为该对象中已经内部封装了可变长度的字节数组。这就是数据目的地。因为这两个流对象都操作的是数组,并没有使用系统资源,所以不用进行close关闭资源。在流操作规律讲解时:源设备:键盘 System.in ,硬盘 FileStream ,内存 ArrayStream目的设备:控制台 System.out,硬盘 FileStream,内存 ArrayStream用流的读写思想来操作数组。*/import java.io.*;class ByteArrayStream{public static void main(String[] args) {ByteArrayInputStream bis=new ByteArrayInputStream("abcde".getBytes());//数据源ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();//明确数据目的int by=0;while((by=bis.read())!=-1){bos.write(by);}System.out.println(bos.toString());//bos.writeTo(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));}}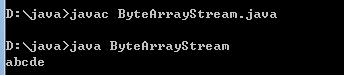
六、IO流(转换流的字符编码)
字符流的出现方便了操作字符,更重要的是加入了编码转换。通过子类转换流来完成:
InputStreamReader
OutputStreamWriter
在两个对象进行构造的时候可以加入字符集。
编码表:
计算机只能识别二进制数据,早期由来是电信号。为了方便应用计算机,让它可以识别各个国家的文字,就将各个国家的文字用数字来表示,并一一对应形成一张表,这就是编码表。
常见的编码表:
ASCII:美国标准信息交换码。用一个字节的7位来表示。
ISO8859-1:拉丁码表。欧洲码表。用一个字节的8位来表示。
GB2312:中国的中文编码表。占两个字节。
GBK:中国的中文编码的表升级,融合了更多中文的字符符号。占两个字节。
Unicode:国际标准码,融合了多种文字。所有文字都用2个字节来表示,Java语言使用的就是 Unicode。
UTF-8:最多用3个字节来表示一个字符。
/*转换流的字符编码:*/import java.io.*;class EncodeStream {public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {writeTest();readText();}public static void writeTest()throws IOException{OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk.txt"),"UTF-8");//默认GBK编码osw.write("你好");osw.close();}public static void readText()throws IOException{InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("gbk.txt"),"GBK");//默认GBK编码char[] buf=new char[10];int len=isr.read(buf);String str=new String(buf,0,len);System.out.println(str);isr.close();}}
七、字符编码
/*编码:字符串变成字节数组。String-->byte[]; str.getBytes(charsetName);解码:字节数组变成字符串byte[]-->String; new String(byte[],charsetName);*/import java.util.*;class EncodeDemo {public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {String s="你好";byte[] b1=s.getBytes("GBK");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b1));String s1=new String(b1,"ISO8859-1");System.out.println("s1="+s1);//对s1进行ISO8859-1编码byte[] b2=s1.getBytes("ISO8859-1");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b2));String s2=new String(b2,"gbk");System.out.println("s2="+s2);}}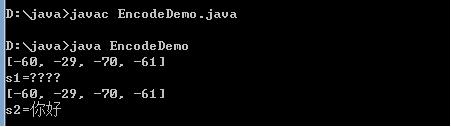
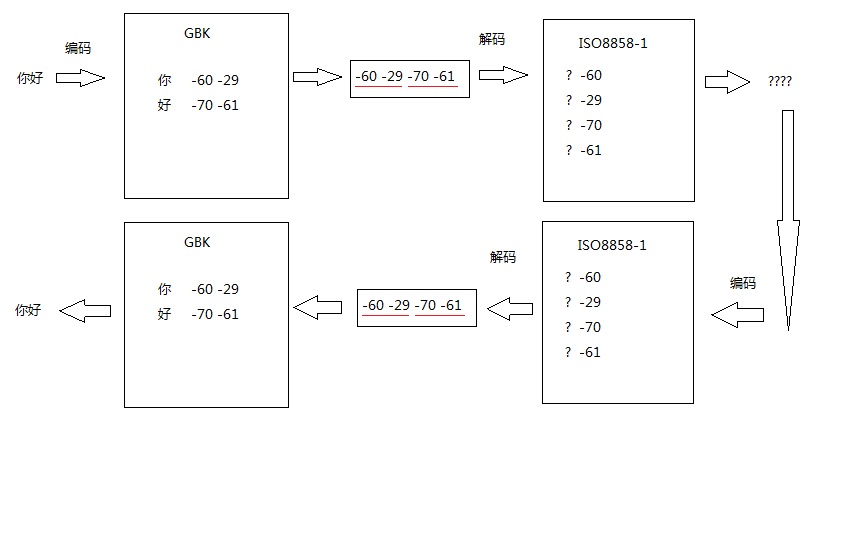
注意:
/*编码:字符串变成字节数组。String-->byte[]; str.getBytes(charsetName);解码:字节数组变成字符串byte[]-->String; new String(byte[],charsetName);*/import java.util.*;class EncodeDemo {public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {String s="你好";byte[] b1=s.getBytes("GBK");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b1));String s1=new String(b1,"UTF-8");System.out.println("s1="+s1);byte[] b2=s1.getBytes("UTF-8");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b2));String s2=new String(b2,"GBK");System.out.println("s2="+s2);}}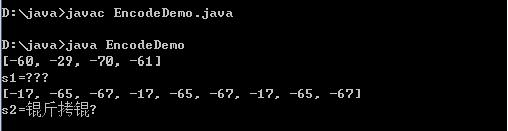
八、字符编码-联通
/*联通:*/class EncodeDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{String s="联通";byte[] by=s.getBytes("GBK");for(byte b:by){System.out.print(Integer.toBinaryString(b&255)+"\t");}System.out.println("\n"+new String(by,"UTF-8"));}}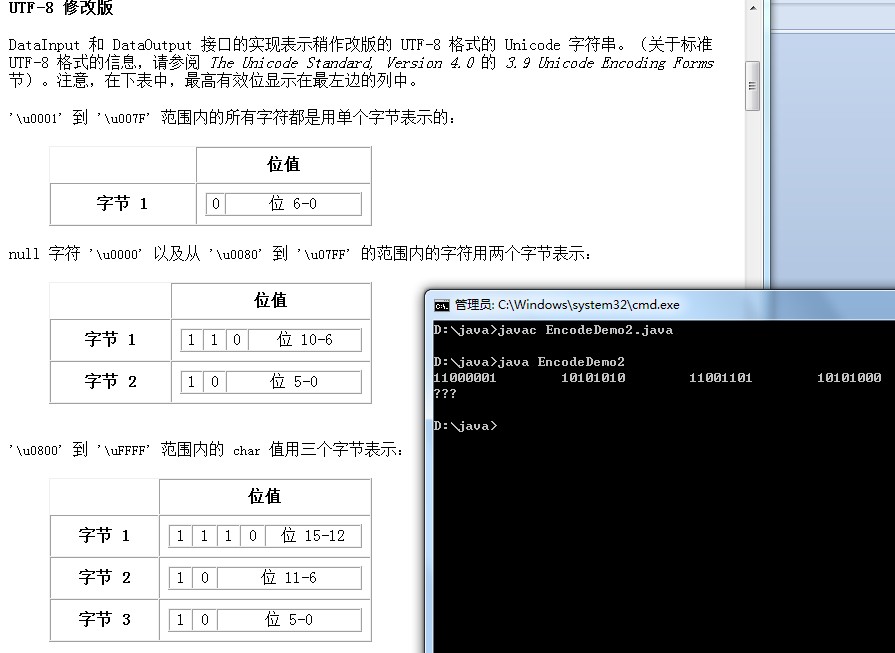
九、练习
/*有5个学生,每个学生有3门课的成绩。从键盘输入以上数据(姓名,三门课成绩)输入的格式:如:zhangsan,80,90,89 计算出总成绩并把学生的信息和计算出的总分数按由高到低顺序存放在磁盘文件"stud.txt"中。1.描述学生对象。2.定义一个可以操作学生对象的工具类。思想:1.通过获取键盘录入的一行数据,并将该行的信息取出封装成学生对象。2.因为学生对象有很多,那么需要存储,使用集合。因为要对学生成绩的总分排序,所以可以使用TreeSet集合。3.将集合的信息写入到一个文件中。*/import java.io.*;import java.util.*;class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private String name;private int ma,cn,en;private int sum;Student(String name,int ma,int cn,int en){this.name=name;this.ma=ma;this.cn=cn;this.en=en;sum=ma+cn+en;}public int compareTo(Student s){int num=new Integer(this.sum).compareTo(new Integer(s.sum));if(num==0)return this.name.compareTo(s.name);return num;}public String getName(){return name;}public int getSum(){return sum;}public int hashCode(){return name.hashCode()+sum*67;}public boolean equals(Object obj){if((obj instanceof Student))throw new ClassCastException("类型不匹配");Student s=(Student)obj;return this.name.equals(s.name)&&this.sum==s.sum;}public String toString(){return "student["+name+", "+ma+", "+cn+", "+en+"]";}}class StudentInfoTool{public static Set<Student> getStudent()throws IOException{return getStudent(null);}public static Set<Student> getStudent(Comparator<Student> cmp)throws IOException{BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String line=null;Set<Student> stus=new TreeSet<Student>();if(cmp==null)stus=new TreeSet<Student>();elsestus=new TreeSet<Student>(cmp);while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){if("over".equals(line))break;String[] info=line.split(",");Student stu=new Student(info[0],Integer.parseInt(info[1]),Integer.parseInt(info[2]),Integer.parseInt(info[3]));stus.add(stu);}bufr.close();return stus;}public static void write2File(Set<Student> stus)throws IOException{BufferedWriter bufw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("stuinfo.txt"));for(Student stu:stus){bufw.write(stu.toString()+"\t");bufw.write(stu.getSum()+"");//注意:在BufferedWriter复写的write(int a)中,有个(char)a的动作。bufw.newLine();bufw.flush();}bufw.close();}}class StudentInfoTest {public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {Comparator<Student> cmp=Collections.reverseOrder();Set<Student> stu=StudentInfoTool.getStudent(cmp);StudentInfoTool.write2File(stu);}}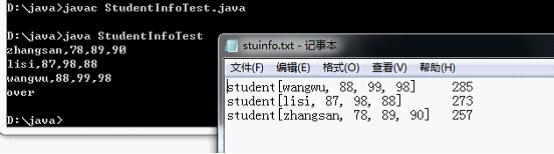
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(对象序列化和字符编码)
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(字符流缓冲区和字节流相关操作以及相关操作技巧)
- 黑马程序员_JAVA基础_IO流(一)
- 黑马程序员_JAVA基础_IO流(二)
- 黑马程序员_java基础_IO流
- 黑马程序员_java基础_io流
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(二)_19
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(四)_21
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO
- 黑马程序员_IO流(对象的序列化和反序列化)
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流_字符流,带缓冲区的字符流,文本文件读写
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(File类和properties类相关操作)
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(File类和properties类相关操作)
- 黑马程序员_java基础10--IO(2)和字符编码
- 黑马程序员_毕向东_Java基础_DAY18-19_IO基础、字符流
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_其它对象和IO流(字符流)
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流_编码表,编码与解码
- 黑马程序员_Java语言_IO流(序列流)
- Def和__declspec(dllexport)
- java多线程的几种实现方法
- 各种文件之间的转换
- Android开发环境搭建
- POJ 1375 Intervals(解析几何)
- 黑马程序员_Java基础_IO流(对象序列化和字符编码)
- 《Unix & Linux 大学教程》 - 第十八章 学习笔记
- 为什么打开网页速度慢,或者很难打开网页,无法收发邮件?
- zf多种页面跳转
- 未能加载文件或程序集“”或它的某一个依赖项。系统找不到指定的文件
- vs2008编译环境opengl的glut函数库安装
- OpenGL的函数
- linux下的权限设置
- 要素外接矩形的四个角点坐标、长度、宽度、面积如何计算到要素属性表中?


