Redis 2.4:后台线程如何解决aof缺陷?【转】
来源:互联网 发布:重生之网络大亨txt下载 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 07:12
转自:http://tech.it168.com/a2011/1219/1290/000001290827.shtml
Redis终于在2.4版本里引入了除主线程之外的后台线程,这个事情由来已久.早在2010年2月就有人提出aof的缺陷,提及的问题主要有:
① 主线程aof的每次fsync(everysecond模式)在高并发下时常出现100ms的延时,这源于fsync必不可少的磁盘操作,即便已经优化多次请求的离散小io转化成一次大的连续io(sina的同学也反映过这个问题).
② 主线程里backgroundRewriteDoneHandler函数在处理bgrewriteaof后台进程退出的时候存在一个rename new-aof-file old-aof-file,然后再close old-aof-file的操作, close是一个unlink的操作(最后的引用计数), unlink消耗的时间取决于文件的大小,是个容易阻塞的系统调用.
③ 当发生bgsave或者bgrewriteaof的时候主线程和子进程同时写入不同的文件,这改变了原有连续写模式,不同写入点造成了磁盘磁头的寻道时间加长(其实一个台物理机多实例也有这个问题, 要避免同一时间点做bgrewriteaof), 这又加长了fsync时间.
经过漫长的设计和交流,antirez终于在2.4版里给出了实现, 这个设计保持了Redis原有的keep it simple的风格,实现的特别简单且有效果,实现的主要原理就是把fsync和close操作都移动到background来执行.
后台线程
2.4.1版本引入新的文件bio.c,这个文件包含了后台线程的业务逻辑.如图.
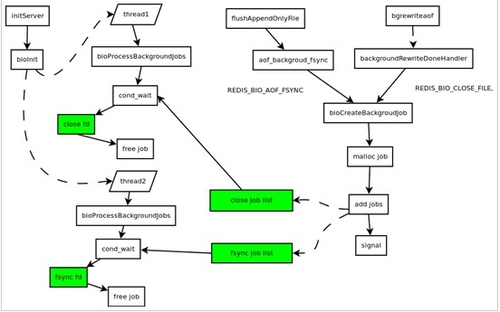
bioInit在Redis启动的时候被调用,默认启动2个后台线程(如图中的thread1,2),其一负责fsync fd的任务(解决缺陷1),其二负责close fd的任务(解决缺陷2).这两个线程条件等待各自独立的2个链表(close job,fsync job)上,看是否有新任务的加入,有则进行fsync或者close.
解决问题1
主线程仅仅把aofbuf的数据刷新到aof文件里,然后通过bioCreateBackgroundJob函数往这队列里插入fsync job,于是原有主线程的fsync工作被转移到后台线程来做,这样主线程阻塞问题就异步的解决了.
但这又引发了一个问题,主线程对同一个fd如果有write操作,后台线程同时在fsync,这两个线程会互相影响. antirez为此做了一定研究,并给出了简单的解决方案.
为了避免线程的互相影响,主线程每次write之前都要检测一下后台线程任务队列里是否有fsync操作,如果有则延迟这次aofbuf的flush,延迟flush这个功能,当然会增大丢数据的可能,我们来看看实现.
=======
78 void flushAppendOnlyFile(int force) {
.......
84 if (server.appendfsync== APPENDFSYNC_EVERYSEC)
85 sync_in_progress= bioPendingJobsOfType(REDIS_BIO_AOF_FSYNC)!= 0;
86
87 if (server.appendfsync== APPENDFSYNC_EVERYSEC&& !force) {
88 /* With this append fsync policy we do background fsyncing.
89 * If the fsync is still in progress we can try to delay
90 * the write for a couple of seconds. */
91 if (sync_in_progress) {
92 if (server.aof_flush_postponed_start== 0) {
93 /* No previous write postponinig, remember that we are
94 * postponing the flush and return. */
95 server.aof_flush_postponed_start= server.unixtime;
96 return;
97 }else if (server.unixtime- server.aof_flush_postponed_start< 2) {
98 /* We were already waiting for fsync to finish, but for less
99 * than two seconds this is still ok. Postpone again. */
100 return;
101 }
102 /* Otherwise fall trough, and go write since we can't wait
103 * over two seconds. */
104 redisLog(REDIS_NOTICE,"Asynchronous AOF fsyncis taking toolong (diskis busy?). Writing the AOF buffer without waiting for fsyncto complete, this may slow down Redis.");
105 }
106 }
我们来解读一下这段代码, force这个参数如果为1,则为强制flush,为0否则允许延迟flush.
85行:这段就是判断后台线程是否有fsync任务,如果存在则会出现主线程write,后台线程fsync的并发行为.sync_in_process就表示存在冲突的可能性,则开始延迟flush.
92行:如果当前未发生延迟,现在开始延迟flush,记录一下时间就立即返回,这就发生了延迟flush,aofbuf里的信息未被刷出去.
97行:当再次进入该函数之后,如果距离开始延迟时间仍然小于2s,则允许继续延迟.
104行:距离开始延迟事件已经超过2s了,必须强制flush了,否则丢数据可能超过2s.
解决了冲突之后就是加入后台任务了,以前是fsync现在改成了加入队列
========
151 }else if ((server.appendfsync== APPENDFSYNC_EVERYSEC&&
152 server.unixtime> server.lastfsync)) {
153 if (!sync_in_progress) aof_background_fsync(server.appendfd);
154 server.lastfsync= server.unixtime;
155 }
好了缺陷1解决了.
解决缺陷2backgroundRewriteDoneHandler里同样的把close old-aof-file的工作交给backgroud thread来执行.
=========
856/* Asynchronously close the overwritten AOF.*/
857if (oldfd != -1) bioCreateBackgroundJob(REDIS_BIO_CLOSE_FILE,(void*)(long)oldfd,NULL
这样关闭old-aof-file的工作被移交到后台任务执行,不再阻塞主线程了,不过没那么简单,如下的特殊场景需要额外处理.
bgrewriteaof start
aof disbled
bgrewriteaof stop
bgrewriteaof handler
在bgrewriteaof触发之后,关闭了aof功能,这样由于server.appendfd对应old-aof-file文件未被打开, 一旦rename new-aof old-aof, 则会触发一个unlink old-aof-file的行为, 而不是上面说的close才触发unlink行为.为了跳过这种状况,如果发现aof被关闭,通过打开old-aof-file文件增加引用计数的方法解决这个问题.
==========
810 if (server.appendfd== -1) {
811 /* AOF disabled*/
812
813 /* Don't care if this fails: oldfd will be -1 and we handle that.
814 * One notable case of -1 return is if the old file does
815 * not exist. */
816 oldfd= open(server.appendfilename,O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK);
817 }else {
818 /* AOF enabled*/
819 oldfd= -1;/* We'll set this to the current AOF filedes later.*/
820 }
816行:如果处于aof关闭状态,则打开old-aof-file.
819行:aof已经是激活状态,不做任何操作.
这样rename就不再引发unlink old-aof-file, 不会再阻塞主线程.
处理完rename之后就要来处理old-aof-file了.如果aof是非激活状态,对于new-aof-file文件,我们关闭他即可不需要其它操作,这个close不会引发阻塞,因为这个文件的已经在生成new-aof-file文件的时候做过fsync了.
如果aof是激活状态, fsync行为递给后台去执行,这块的行为和缺陷1一样.
===========
840 if (server.appendfsync== APPENDFSYNC_ALWAYS)
841 aof_fsync(newfd);
842 else if (server.appendfsync== APPENDFSYNC_EVERYSEC)
843 aof_background_fsync(newfd);
解决缺陷3
引入了延迟bgrewriteaof来避免与bgsave同时写文件,而server.no_appendfsync_on_rewrite参数的设置又避免了bgrewriteaof时主线程出现fsync.
测试2.4.1的性能确实较之前版有较大的提升,以后会给出测试数据.
- Redis 2.4:后台线程如何解决aof缺陷?【转】
- 解决redis下没有appendonly.aof文件
- redis如何利用appendonly.aof恢复数据
- redis aof
- redis aof
- redis-AOF
- redis-aof
- 【Redis】redis的AOF
- redis如何后台启动
- redis如何后台启动
- REDIS AOF的实现
- Redis源码分析:AOF
- Redis的AOF功能
- Redis的AOF功能
- Redis源码学习-AOF
- Redis AOF持久化
- Redis RDB/AOF
- REDIS的AOF实现
- 通用版登录login_委托
- linux top命令
- android usb挂载分析----vold启动
- poj1734 - Sightseeing trip
- 防止独立ip虚拟主机被恶意解析的方法 canonical标签 百度
- Redis 2.4:后台线程如何解决aof缺陷?【转】
- myeclipse安装svn
- 风柔月清,吾爱在浅秋
- SQLite可视化管理工具汇总
- android开发面试题 及答案
- 随笔2 - C#的JSON
- 随便写写....
- 我做华为机试题
- gcc


