HDU 1022 Train Problem I
来源:互联网 发布:剑三成女捏脸数据图片 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 19:06
Train Problem I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 11821 Accepted Submission(s): 4332
Problem Description
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves, train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
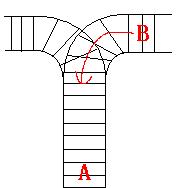
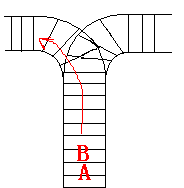
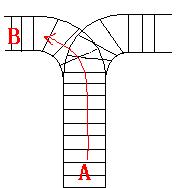



Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file. More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out" for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 3213 123 312
Sample Output
Yes.inininoutoutoutFINISHNo.FINISHFor the first Sample Input, we let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3.So now train 3 is at the top of the railway, so train 3 can leave first, then train 2 and train 1.In the second Sample input, we should let train 3 leave first, so we have to let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3.Now we can let train 3 leave.But after that we can't let train 1 leave before train 2, because train 2 is at the top of the railway at the moment.So we output "No.".HintHint
Author
Ignatius.L
分析:很典型的堆栈的题目,若图方便直接用STL或者用数组模拟出一个堆栈都可以
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
stack<char>s;
string stra,strb;
int i,j,k,n;
int result[9];
int main()
{
while(cin>>n>>stra>>strb)
{
i=j=k=0;
s.push(stra[i]);
result[k++]=1;
while(i<n&&j<n)
{
if(s.size()&&s.top()==strb[j])
{
s.pop();
result[k++]=0;
j++;
}
else
{
i++;
if(i==n)
break;
s.push(stra[i]);
result[k++]=1;
}
}
while(!s.empty())
s.pop();
if(i==n)
cout<<"No."<<endl;
else
{
cout<<"Yes."<<endl;
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
{
if(result[i])
cout<<"in"<<endl;
else
cout<<"out"<<endl;
}
}
cout<<"FINISH"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
代码2:C语言数组模拟
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>int main(){ int n; char a1[10]; char a2[10]; int b[10]; int c[1000]; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { memset(c,0,sizeof(c)); int i=0,j=0,k=0,m=0; getchar(); scanf("%s",a1); scanf("%s",a2); b[0]=0; while(j<n) { if(b[0]==0) { m=0; b[m]=a1[i]-'0'; c[k++]=1; i++; m++; } else { if(b[m-1]==(a2[j]-'0')) { b[m-1]=0; m--; j++; k++; } else { if(i==n) break; b[m]=a1[i]-'0'; c[k++]=1; i++; m++; } } } if(b[0]==0) { printf("Yes.\n"); for(i=0;i<k;i++) { if(c[i]) printf("in\n"); else printf("out\n"); } printf("FINISH\n"); } else { printf("No.\n"); printf("FINISH\n"); } } return 0;}
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU-1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022 ( Train Problem I )
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- Hdu 1022 - Train Problem I
- HDU-1022:Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- hdu-Train Problem I-1022
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- hdu 1022 Train Problem I
- HDU 1022Train Problem I
- 加密与解密
- ANSI,ASCII,Unicode的区别与联系
- 动态绑定
- SAP Project 期初数据导入
- 数字证书
- HDU 1022 Train Problem I
- C1189 rpcndr.h 错误
- python 单例模式的探究
- IAR for AVR 学习笔记
- 下载官方谷歌Chrome浏览器 离线包的方法
- OpenGL中的缓冲区对象
- Java程序员应该知道的10个调试技巧
- 拼命编码,老板会因此感谢你吗?
- 对于Java内存使用情况


