由浅入深 Core Data 详解
来源:互联网 发布:广州市梦享网络 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 11:01
from:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4cd8dd1301019487.html
第一节 core data框架
Core data 是 Cocoa 中处理数据,绑定数据的关键特性,其重要性不言而喻,但也比较复杂。Core Data 相关的类比较多,初学者往往不太容易弄懂。计划用三个教程来讲解这一部分:
框架详解:讲解
Core data应用程序示例:通过生成一个使用 Core data 的应用程序来讲解如何 在
手动创建Core data示例:不利用框架自动生成代码,完全自己编写所有的 Core data 相关代码的命令行应用程序来深入讲解 Core data的使用。
本文为第一部份:框架详解
一,概观
下面先给出一张类关系图,让我们对它有个总体的认识。
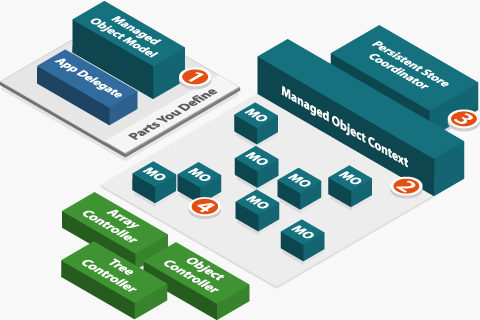
在上图中,我们可以看到有五个相关模块:
1, Managed Object Model
Managed Object Model 是描述应用程序的数据模型,这个模型包含实体(Entity),特性(Property),读取请求(Fetch Request)等。(下文都使用英文术语。)
2,Managed Object Context
Managed Object Context 参与对数据对象进行各种操作的全过程,并监测数据对象的变化,以提供对 undo/redo 的支持及更新绑定到数据的 UI。
3,Persistent Store Coordinator
Persistent Store Coordinator 相当于数据文件管理器,处理底层的对数据文件的读取与写入。一般我们无需与它打交道。
4,Managed Object
Managed Object 数据对象,与 Managed Object Context 相关联。
5,Controller
图中绿色的 Array Controller, Object Controller, Tree Controller 这些控制器,一般都是通过 control+drag 将 Managed Object Context 绑定到它们,这样我们就可以在 nib 中可视化地操作数据。
这写模块是怎样运作的呢?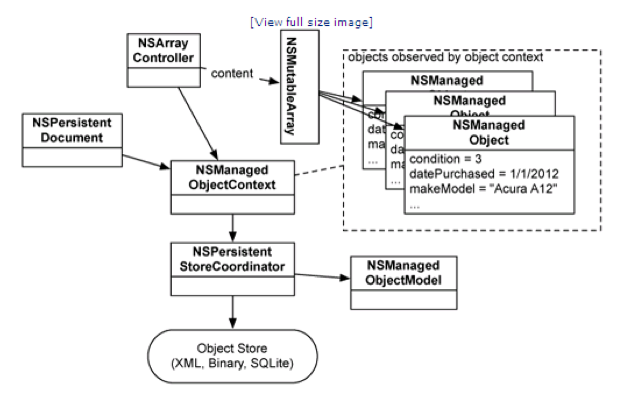
1,应用程序先创建或读取模型文件(后缀为xcdatamodeld)生成 NSManagedObjectModel 对象。Document应用程序是一般是通过 NSDocument 或其子类 NSPersistentDocument)从模型文件(后缀为 xcdatamodeld)读取。
2,然后生成 NSManagedObjectContext 和 NSPersistentStoreCoordin
3,NSPersistentStoreCoordin
4,NSManagedObjectContext 参与对数据进行各种操作的整个过程,它持有 Managed Object。我们通过它来监测 Managed Object。监测数据对象有两个作用:支持 undo/redo 以及数据绑定。这个类是最常被用到的。
5,Array Controller, Object Controller, Tree Controller 这些控制器一般与 NSManagedObjectContext 关联,因此我们可以通过它们在 nib 中可视化地操作数据对象。
二, Model class
模型有点像数据库的表结构,里面包含 Entry, 实体又包含三种 Property:Attribute(属性),RelationShip(关系), Fetched Property(读取属性)。Model class 的名字多以 "Description" 结尾。我们可以看出:模型就是描述数据类型以及其关系的。
主要的 Model class 有:
1)Entity - NSEntityDescription
Entity 相当于数据库中的一个表,它描述一种抽象数据类型,其对应的类为 NSManagedObject 或其子类。
NSEntityDescription 常用方法:
+insertNewObjectForEntity
-managedObjectClassName 返回映射到 Entity 的 NSManagedObject 类名
-attributesByName 以名字为 key, 返回 Entity 中对应的 Attributes
-relationshipsByName 以名字为 key, 返回 Entity 中对应的 Relationships
2)Property - NSPropertyDescription
Property 为 Entity 的特性,它相当于数据库表中的一列,或者 XML 文件中的 value-key 对中的 key。它可以描述实体数据(Attribute),Entity之间的关系(RelationShip),或查询属性(Fetched Property)。
Attribute 存储基本数据,如 NSString, NSNumber or NSDate 等。它可以有默认值,也可以使用正则表达式或其他条件对其值进行限定。一个属性可以是 optional 的。
Relationship 描述 Entity,Property 之间的关系,可以是一对一,也可以是一对多的关系。
Fetched Property 根据查询谓词返回指定 Entity 的符合条件的数据对象。
上面说的比较抽象,举个例子来说,见图:
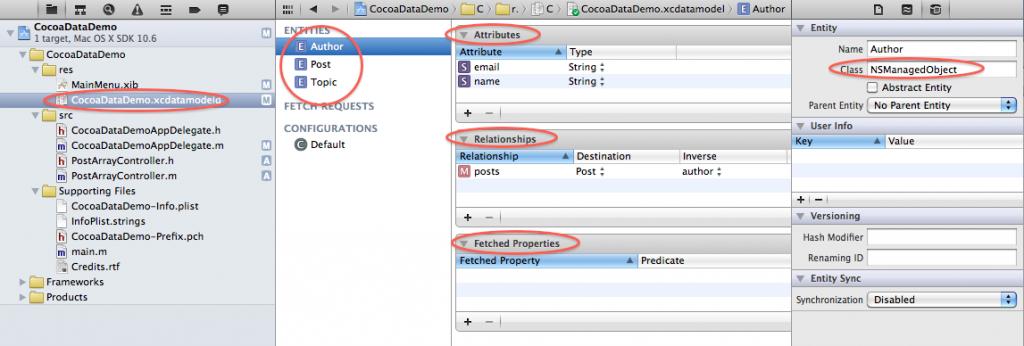
我们有一个
我们通常使用 KVC 机制来访问 Property。下面来看代码:
- NSManagedObjectContext
* context = [[NSApp delegate] managedObjectContext]; - NSManagedObject
* author = nil; -
- author
= [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntity ForName: @"Author" inManagedObjectContext: context]; - [author
setValue: @"nemo@pixar.com" forKey: "email"];@ -
- NSLog
(@"The Author's ,email is: %@" [author "email"]);valueForKey:@
在上面代码中,我们先取得 NSManagedObjectContext, 然后调用 NSEntityDescription 的方法,以 Author 为实体模型,生成对应的 NSManagedObject 对象,插入 NSManagedObjectContext 中,然后给这个对象设置特性 email 的值。
三,运行时类与对象
> Managed Object - NSManagedObject
Managed Object 表示数据文件中的一条记录,每一个 Managed Object 在内存中对应 Entity 的一个数据表示。Managed Object 的成员为 Entity 的 Property 所描述。
比如在上面的代码,author 这个 NSManagedObject,对应名为 Author 的 Entity。
每一个 Managed Object 都有一个全局 ID(类型为:NSManagedObjectID)。Managed Object 会附加到一个 Managed Object Context,我们可以通过这个全局 ID 在 Managed Object Context 查询对应的 Managed Object。
> Managed Object Context - NSManagedObjectContext
Managed Object Context 的作用相当重要,对数据对象进行的操作都与它有关。当创建一个数据对象并插入 Managed Object Context 中,Managed Object Context 就开始跟踪这个数据对象的一切变动,并在合适的时候提供对 undo/redo 的支持,或调用 Persistent Store Coordinato 将变化保存到数据文件中去。
通常我们将 controller 类(如:NSArrayController,NSTreeController)或其子类与 Managed Object Context 绑定,这样就方便我们动态地生成,获取数据对象等。
这个接口的作用就是指定数据对象的存储数据文件(通过指定 PersistantStore 实现)-executeFetchRequest: error:执行 Fetch Request 并返回所有匹配的数据对象
> Persistent Store Coordinator - NSPersistentStoreCoordin
使用 Core Data document 类型的应用程序,通常会从磁盘上的数据文中中读取或存储数据,这写底层的读写就由 Persistent Store Coordinator 来处理。一般我们无需与它直接打交道来读写文件,Managed Object Context 在背后已经为我们调用 Persistent Store Coordinator 做了这部分工作。
迁移前的数据存储不可再使用-managedObjectIDForURIRep
> Persistent Document - NSPersistentDocument
NSPersistentDocument 是 NSDocument 的子类。 multi-document Core Data 应用程序使用它来简化对 Core Data 的操作。通常使用 NSPersistentDocument 的默认实现就足够了,它从 Info.plist 中读取 Document types 信息来决定数据的存储格式(xml,sqlite, binary)。
四,Fetch Requests
Fetch Requests 相当于一个查询语句,你必须指定要查询的 Entity。我们通过 Fetch Requests 向 Managed Object Context 查询符合条件的数据对象,以 NSArray 形式返回查询结果,如果我们没有设置任何查询条件,则返回该 Entity 的所有数据对象。我们可以使用谓词来设置查询条件,通常会将常用的 Fetch Requests 保存到 dictionary 以重复利用。
示例:
- NSManagedObjectContext
* context = [[NSApp delegate] managedObjectContext]; - NSManagedObjectModel
* model = [[NSApp delegate] managedObjectModel]; - NSDictionary
* entities = [model entitiesByName]; - NSEntityDescription
* entity = [entities valueForKey:@"Post"]; -
- NSPredicate
* predicate; - predicate
= [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"creationDate > ,%@" date]; -
- NSSortDescriptor
* sort = [[NSortDescriptor alloc] initWithKey:@"title"]; - NSArray
* sortDescriptors = [NSArray arrayWithObject: sort]; -
- NSFetchRequest
* fetch = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init]; - [fetch
setEntity: entity]; - [fetch
setPredicate: predicate]; - [fetch
setSortDescriptors: sortDescriptors]; -
- NSArray
* results = [context executeFetchRequest:fetch error:nil]; - [sort
release]; - [fetch
release];
在上面代码中,我们查询在指定日期之后创建的 post,并将查询结果按照 title 排序返回。
参考资料:
Core Data Reference API listing for the Core Data classes
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Cocoa/Reference/CoreData_ObjC/index.html
NSPredicate Reference API listing for NSPredicate
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Cocoa/Reference/Foundation/ObjC_classic/Classes/NSPredicate.html
第二节 手动编写core data 代码
前面详细讲解了 Core Data 的框架以及设计的类,下面我们来讲解一个完全手动编写代码使用这些类的示例,这个例子来自苹果官方示例。在这个例子里面,我们打算做这样一件事情:记录程序运行记录(时间与 process id),并保存到xml文件中。我们使用 Core Data 来做这个事情。
示例代码下载:点击这里
一,建立一个新的 Mac
- int
main int( argc, constchar * argv[]) - {
-
NSLog(@" === );Core Data Tutorial ===" -
-
// Enable GC -
// -
objc_startCollectorThread(); -
-
return 0; - }
二,创建并设置模型类
在 main() 之前添加如下方法:
- NSManagedObjectModel
*managedObjectModel() - {
-
static NSManagedObjectModel *moModel = nil; -
-
if (moModel != nil) { -
return moModel; -
} -
-
moModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] init]; -
-
// Create the entity -
// -
NSEntityDescription *runEntity = [[NSEntityDescription alloc] init]; -
[runEntity setName:@"Run"]; -
[runEntity setManagedObjectClassNam e:@"Run"]; -
-
[moModel setEntities:[NSArray arrayWithObject:runEntity]]; -
-
// Add the Attributes -
// -
NSAttributeDescription *dateAttribute = [[NSAttributeDescription alloc] init]; -
[dateAttribute setName:@"date"]; -
[dateAttribute setAttributeType:NSDateAttributeType]; -
[dateAttribute setOptional:NO]; -
-
NSAttributeDescription *idAttribute = [[NSAttributeDescription alloc] init]; -
[idAttribute setName:@"processID"]; -
[idAttribute setAttributeType:NSInteger32AttributeType ]; -
[idAttribute setOptional:NO]; -
[idAttribute setDefaultValue:[NSNumber numberWithInteger:-1]]; -
-
// Create the validation predicate for the process ID. -
// The following code is equivalent to validationPredicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF > 0"] -
// -
NSExpression *lhs = [NSExpression expressionForEvaluatedOb ject]; -
NSExpression *rhs = [NSExpression expressionForConstantVal ue:[NSNumber numberWithInteger:0]]; -
-
NSPredicate *validationPredicate = [NSComparisonPredicate -
predicateWithLeftExpress ion:lhs -
rightExpression:rhs -
modifier:NSDirectPredicateModifie r -
type:NSGreaterThanPredicateOp eratorType -
options:0]; -
-
NSString *validationWarning = @"Process ID ;< 1" -
[idAttribute setValidationPredicates:[NSArray arrayWithObject:validationPredicate] -
withValidationWarnings:[NSArray arrayWithObject:validationWarning]]; -
-
// set the properties for the entity. -
// -
NSArray *properties = [NSArray arrayWithObjects: dateAttribute, idAttribute, nil]; -
[runEntity setProperties:properties]; -
-
// Add a Localization Dictionary -
// -
NSMutableDictionary *localizationDictionary = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary]; -
[localizationDictionary setObject:@"Date" forKey:@ "Property/date/Entity/Run"]; -
[localizationDictionary setObject:@"Process ID" forKey:@ "Property/processID/Entity/Run"]; -
[localizationDictionary setObject:@"Process ID must not be less than 1" forKey:@ "ErrorString/ProcessID ];< 1" -
-
[moModel setLocalizationDictionar y:localizationDictionary]; -
-
return moModel; - }
1)我们创建了一个全局模型
2)并在其中创建一个名为
3)给 Run Entity 添加了两个必须的 Property:date 和 processID,分别表示运行时间以及进程 ID;并设置默认的进程 ID 为 -1;
4)给 processID 特性设置检验条件:必须大于 0;
5)给模型设置本地化描述词典;
本地化描述提供对 Entity,Property,Error信息等的便于理解的描述,其可用的键值对如下表:
Key
Value
"Entity/NonLocalizedEntityName"
"LocalizedEntityName"
"Property/NonLocalizedPropertyName
"LocalizedPropertyName"
"Property/NonLocalizedPropertyName
"LocalizedPropertyName"
"ErrorString/NonLocalizedErrorString"
"LocalizedErrorString"
三,创建并设置运行时类和对象
由于要用到存储功能,所以我们必须定义持久化数据的存储路径。我们在 main() 之前添加如下方法设置存储路径:
- NSURL
*applicationLogDirectory() - {
-
NSString *LOG_DIRECTORY = @"CoreDataTutorial"; -
static NSURL *ald = nil; -
-
if (ald == nil) -
{ -
NSFileManager *fileManager = [[NSFileManager alloc] init]; -
NSError *error = nil; -
NSURL *libraryURL = [fileManager URLForDirectory:NSLibraryDirectory inDomain:NSUserDomainMask -
appropriateForURL:nil create:YES error:&error]; -
if (libraryURL == nil) { -
NSLog(@"Could not ,access Library directory\n%@" [error localizedDescription]); -
} -
else -
{ -
ald = [libraryURL URLByAppendingPathCompon ent:@"Logs"]; -
ald = [ald URLByAppendingPathCompon ent:LOG_DIRECTORY]; -
-
NSLog(@" >> ,log path %@" [ald path]); -
-
NSDictionary *properties = [ald resourceValuesForKeys:[NSArray arrayWithObject:NSURLIsDirectoryKey] error:&error]; -
if (properties == nil) -
{ -
if (![fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:[ald path] withIntermediateDirector ies:YES attributes:nil error:&error]) -
{ -
NSLog(@"Could not ,create directory %@\n%@" -
[ald path], [error localizedDescription]); -
ald = nil; -
} -
} -
} -
} -
-
return ald; - }
在上面的代码中,我们将持久化数据文件保存到路径:/Users/kesalin/Library/Logs/CoreDataTutorial 下。
下面,我们来创建运行时对象:ManagedObjectContext 和 PersistentStoreCoordinat
- NSManagedObjectContext
*managedObjectContext() - {
-
static NSManagedObjectContext *moContext = nil; -
if (moContext != nil) { -
return moContext; -
} -
-
moContext = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] init]; -
-
// Create a persistent store coordinator, then set the coordinator for the context. -
// -
NSManagedObjectModel *moModel = managedObjectModel(); -
NSPersistentStoreCoordin ator *coordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordin ator alloc] initWithManagedObjectMod el:moModel]; -
[moContext setPersistentStoreCoordi nator: coordinator]; -
-
// Create a new persistent store of the appropriate type. -
// -
NSString *STORE_TYPE = NSXMLStoreType; -
NSString *STORE_FILENAME = @"CoreDataTutorial.xml"; -
-
NSError *error = nil; -
NSURL *url = [applicationLogDirectory() URLByAppendingPathCompon ent:STORE_FILENAME]; -
-
NSPersistentStore *newStore = [coordinator addPersistentStoreWithTy pe:STORE_TYPE -
configuration:nil -
URL:url -
options:nil -
error:&error]; -
-
if (newStore == nil) { -
NSLog(@"Store Configuration ,Failure\n%@" ([error "UnknownlocalizedDescription] != nil) ? [error localizedDescription] : @ Error" ); -
} -
-
return moContext; - }
在上面的代码中:
1)我们创建了一个全局
2)并在设置其 persistent store coordinator,存储类型为 xml,保存文件名为:CoreDataTutorial.xml,并将其放到前面定义的存储路径下。
好,至此万事具备,只欠 ManagedObject 了!下面我们就来定义这个数据对象类。向工程添加 Core Data->NSManagedObject subclass 的类,名为 Run (模型中 Entity 定义的类名)
Run.h
- #import
<CoreData/NSManagedObject.h> -
- @interface
Run : NSManagedObject - {
-
NSInteger processID; - }
-
- @property
(retain) NSDate *date; - @property
(retain) NSDate *primitiveDate; - @property
NSInteger processID; -
- @end
Run.m
- //
- //
Run.m - //
CoreDataTutorial - //
- //
Created by kesalin on 8/29/11. - //
Copyright 2011 kesalin@gmail.com. All rights reserved. - //
-
- #import
"Run.h" -
- @implementation
Run -
- @dynamic
date; - @dynamic
primitiveDate; -
- -
(void) awakeFromInsert - {
-
[super awakeFromInsert]; -
-
self.primitiveDate = [NSDate date]; - }
-
- #pragma
mark - - #pragma
mark Getter and setter -
- -
(NSInteger)processID - {
-
[self willAccessValueForKey:@"processID"]; -
NSInteger pid = processID; -
[self didAccessValueForKey:@"processID"]; -
return pid; - }
-
- -
(void)setProcessID:(NSInteger)newProcessID - {
-
[self willChangeValueForKey:@"processID"]; -
processID = newProcessID; -
[self didChangeValueForKey:@"processID"]; - }
-
- //
Implement a setNilValueForKey: method. If the key is “processID” then set processID to 0. - //
- -
(void)setNilValueForKey:(NSString *)key { -
-
if ([key "processID"])isEqualToString:@ { -
self.processID = 0; -
} -
else { -
[super setNilValueForKey:key]; -
} - }
-
- @end
注意:
1)这个类中的 date 和
2)在这里我们演示了如何正确地手动实现 processID 的 setter 和 getter:为了让 ManagedObjecContext
3)当我们设置 nil 给数据对象 processID
4)当数据对象被插入到 ManagedObjectContext 时,我们在
三,创建或读取数据对象,设置其值,保存
好,至此真正的万事具备,我们可以创建或从持久化文件中读取数据对象,设置其值,并将其保存到持久化文件中。本例中持久化文件为 xml 文件。修改 main() 中代码如下:
- int
main int( argc, constchar * argv[]) - {
-
NSLog(@" === );Core Data Tutorial ===" -
-
// Enable GC -
// -
objc_startCollectorThread(); -
-
NSError *error = nil; -
-
NSManagedObjectModel *moModel = managedObjectModel(); -
NSLog(@"The managed ,object model is defined as follows:\n%@" moModel); -
-
if (applicationLogDirectory() == nil) { -
exit(1); -
} -
-
NSManagedObjectContext *moContext = managedObjectContext(); -
-
// Create an Instance of the Run Entity -
// -
NSEntityDescription *runEntity = [[moModel entitiesByName] objectForKey:@"Run"]; -
Run *run = [[Run alloc] initWithEntity:runEntity insertIntoManagedObjectC ontext:moContext]; -
NSProcessInfo *processInfo = [NSProcessInfo processInfo]; -
run.processID = [processInfo processIdentifier]; -
-
if (![moContext save: &error]) { -
NSLog(@"Error while ,saving\n%@" ([error "UnknownlocalizedDescription] != nil) ? [error localizedDescription] : @ Error" ); -
exit(1); -
} -
-
// Fetching Run Objects -
// -
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init]; -
[request setEntity:runEntity]; -
-
NSSortDescriptor *sortDescriptor = [[NSSortDescriptor alloc] initWithKey:@"date" ascending:YES]; -
[request setSortDescriptors:[NSArray arrayWithObject:sortDescriptor]]; -
-
error = nil; -
NSArray *array = [moContext executeFetchRequest:request error:&error]; -
if ((error != nil) || (array == nil)) -
{ -
NSLog(@"Error while ,fetching\n%@" ([error "UnknownlocalizedDescription] != nil) ? [error localizedDescription] : @ Error" ); -
exit(1); -
} -
-
// Display the Results -
// -
NSDateFormatter *formatter = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init]; -
[formatter setDateStyle:NSDateFormatterMediumSty le]; -
[formatter setTimeStyle:NSDateFormatterMediumSty le]; -
-
NSLog(@"%@ run ,history:" [processInfo processName]); -
-
for (run in array) -
{ -
NSLog(@"On %@ ,as process ID %ld" [formatter stringForObjectValue:run.date], run.processID); -
} -
-
return 0; - }
在上面的代码中:
1)我们先获得全局的
2)并创建一个Run Entity,设置其 Property
3)将该数据对象保存到持久化文件中:[moContext
4)然后我们创建一个
5)将查询结果打印输出;
大功告成!编译运行,我们可以得到如下显示:
- 2011-09-03
21:42:47.556 CoreDataTutorial[992:903] CoreDataTutorial run history: - 2011-09-03
21:42:47.557 CoreDataTutorial[992:903] On 2011-9-3 下午09:41:56 as process ID 940 - 2011-09-03
21:42:47.557 CoreDataTutorial[992:903] On 2011-9-3 下午09:42:16 as process ID 955 - 2011-09-03
21:42:47.558 CoreDataTutorial[992:903] On 2011-9-3 下午09:42:20 as process ID 965 - 2011-09-03
21:42:47.558 CoreDataTutorial[992:903] On 2011-9-3 下午09:42:24 as process ID 978 - 2011-09-03
21:42:47.559 CoreDataTutorial[992:903] On 2011-9-3 下午09:42:47 as process ID 992
通过这个例子,我们可以更好理解 Core Data
core data的基本操作
1. 插入
AppDelegate *app = [[UIApplication sharedApplication] delegate];
NSManagedObjectContext *context = [app managedObjectContext];
NSManagedObject *newManagedObject = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntity
[newManagedObject setValue:value forKey:@"propertyname"];
NSError *error; if (![context save:&error]) {
// Handle the error…
}
//查询
//删除
NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext = appDelegate.managedObjectContext;
[context deleteObject:[objecs
// Save the context.
NSError *error; if (![context save:&error]) {
// Update to handle the error appropriately.
NSLog(@”Unresolved error %@, %@”, error, [error userInfo]);
exit(-1); // Fail
}
//属性
NSManagedObject *managedObject;
NSString *keypath;
NSString *labelString;
NSString *currentValue = [self.managedObject valueForKeyPath:self.keypath];
NSEntityDescription *ed = [self.managedObject entity];
NSDictionary *properties = [ed propertiesByName];
NSAttributeDescription *ad = [properties objectForKey:self.keypath];
NSString *defaultValue = nil;
if (ad != nil)
defaultValue = [ad defaultValue];
//core data relation
NSManagedObject *child = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntity
NSMutableSet *children = [person mutableSetValueForKey:@"children"]; //查询,可修改
[children addObject:child];
[children removeObject:childToBeRemoved];
[[children
NSSet *children = [person valueForKey:@"children"]; //查询,不可修改
for (NSManagedObject *oneChild in children) {
// do something
}
补充:
1 是否将图片存储到Core Data中,以及NSData如何存储的一些规则
First, always store your images in a usable format such as PNG or JPEG instead of NSData. This will save you a lot of headaches.
Second, the rule for storing binary data is:
- < 100kb store in the same table as the relevant data
- < 1mb store in a separate table attached via a relationship to avoid loading unnecessarily
- > 1mb store on disk and reference it inside of Core Data
(1。图片尽量保存为文件 2。<100k 和相关数据保存在一张表中
- 由浅入深 Core Data 详解
- Core Data - 框架详解
- Core Data 详解
- Core Data 详解
- Core Data详解
- Core Data详解
- Core Data详解
- Core Data(1) - 框架详解
- Cocoa之Core Data 框架详解
- Cocoa之Core Data(1)框架详解
- Core Data- 框架详解(1)
- 深入浅出 Cocoa 之 Core Data- 框架详解
- IOS 数据存储之 Core Data详解
- iOS激情详解之Core Data
- iOS core Data 详解-<1>基本使用
- iOS core Data 详解-<2>多线程
- IOS 数据存储之 Core Data详解
- IOS 数据存储之 Core Data详解
- winform中配置Log4Net
- Ubuntu下以USB调试方式链接Android手机
- COL命令用法
- JQuery 禁用所有select标签的值
- Java程序设计(九)----模拟用户帐户的程序
- 由浅入深 Core Data 详解
- Qt Model/View Framework学习
- shorten URL
- hadoop伪分布式的配置
- 问心无愧的伤感爱情日志分享:我爱你,到底值不值得
- 使用/proc文件系统和内核打交道(2)-确定系统的CPU情况
- 使用MultiView 与View 单击不同的Linkbutton,显示不同领域的内容
- 方法中的内部类能不能访问方法中的局部变量,为什么
- 如何让google,baidu,Yahoo收录你的网站


