YUV pixel formats
来源:互联网 发布:papership mac 破解 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 09:04
YUV pixel formats
做视频采集与处理,自然少不了要学会分析YUV数据。因为从采集的角度来说,一般的视频采集芯片输出的码流一般都是YUV数据流的形式,而从视频处理(例如H.264、MPEG视频编解码)的角度来说,也是在原始YUV码流进行编码和解析,所以,了解如何分析YUV数据流对于做视频领域的人而言,至关重要。本文就是根据我的学习和了解,简单地介绍如何分析YUV数据流。
YUV,分为三个分量,“Y”表示明亮度(Luminance或Luma),也就是灰度值;而“U”和“V” 表示的则是色度(Chrominance或Chroma),作用是描述影像色彩及饱和度,用于指定像素的颜色。
与我们熟知的RGB类似,YUV也是一种颜色编码方法,主要用于电视系统以及模拟视频领域,它将亮度信息(Y)与色彩信息(UV)分离,没有UV信息一样可以显示完整的图像,只不过是黑白的,这样的设计很好地解决了彩色电视机与黑白电视的兼容问题。并且,YUV不像RGB那样要求三个独立的视频信号同时传输,所以用YUV方式传送占用极少的频宽。
好了,言归正传,谈谈如何分析YUV码流吧。YUV码流有多种不同的格式,要分析YUV码流,就必须搞清楚你面对的到底是哪一种格式,并且必须搞清楚这种格式的YUV采样和分布情况。下面我将介绍几种常用的YUV码流格式,供大家参考。
1. 采样方式
YUV码流的存储格式其实与其采样的方式密切相关,主流的采样方式有三种,YUV4:4:4,YUV4:2:2,YUV4:2:0,关于其详细原理,可以通过网上其它文章了解,这里我想强调的是如何根据其采样格式来从码流中还原每个像素点的YUV值,因为只有正确地还原了每个像素点的YUV值,才能通过YUV与RGB的转换公式提取出每个像素点的RGB值,然后显示出来。
用三个图来直观地表示采集的方式吧,以黑点表示采样该像素点的Y分量,以空心圆圈表示采用该像素点的UV分量。

先记住下面这段话,以后提取每个像素的YUV分量会用到。
- YUV 4:4:4采样,每一个Y对应一组UV分量。
- YUV 4:2:2采样,每两个Y共用一组UV分量。
- YUV 4:2:0采样,每四个Y共用一组UV分量。
2. 存储方式
下面我用图的形式给出常见的YUV码流的存储方式,并在存储方式后面附有取样每个像素点的YUV数据的方法,其中,Cb、Cr的含义等同于U、V。
(1) YUVY 格式 (属于YUV422)

YUYV为YUV422采样的存储格式中的一种,相邻的两个Y共用其相邻的两个Cb、Cr,分析,对于像素点Y'00、Y'01 而言,其Cb、Cr的值均为 Cb00、Cr00,其他的像素点的YUV取值依次类推。
(2) UYVY 格式 (属于YUV422)

UYVY格式也是YUV422采样的存储格式中的一种,只不过与YUYV不同的是UV的排列顺序不一样而已,还原其每个像素点的YUV值的方法与上面一样。
(3) YUV422P(属于YUV422)
YUV422P也属于YUV422的一种,它是一种Plane模式,即打包模式,并不是将YUV数据交错存储,而是先存放所有的Y分量,然后存储所有的U(Cb)分量,最后存储所有的V(Cr)分量,如上图所示。其每一个像素点的YUV值提取方法也是遵循YUV422格式的最基本提取方法,即两个Y共用一个UV。比如,对于像素点Y'00、Y'01 而言,其Cb、Cr的值均为 Cb00、Cr00。
(4)YV12,YU12格式(属于YUV420)
YU12和YV12属于YUV420格式,也是一种Plane模式,将Y、U、V分量分别打包,依次存储。其每一个像素点的YUV数据提取遵循YUV420格式的提取方式,即4个Y分量共用一组UV。注意,上图中,Y'00、Y'01、Y'10、Y'11共用Cr00、Cb00,其他依次类推。
(5)NV12、NV21(属于YUV420)
NV12和NV21属于YUV420格式,是一种two-plane模式,即Y和UV分为两个Plane,但是UV(CbCr)为交错存储,而不是分为三个plane。其提取方式与上一种类似,即Y'00、Y'01、Y'10、Y'11共用Cr00、Cb00
3. 总结
几种常见的YUV码流格式就简单地列在上面了,大家在处理YUV码流前,先了解清楚自己的码流到底属于哪一种,然后对应进行处理。
最后,再回答一个疑问,即分析清楚YUV码流格式了,我们可以做什么?最常用的一点就是,提取出所有的Y分量,然后利用vc或者matlab把你采集的图像的灰度值(Y分量)显示处理,这样你就可以很快地知道你采集的图像是否有问题了。后面我将继续写一些文章讲述如何提取、转换、显示这些YUV原始码流,有兴趣可以继续关注,欢迎留言讨论。
http://www.fourcc.org/yuv.php
YUV formats fall into two distinct groups, the packed formats where Y, U (Cb) and V (Cr) samples are packed together into macropixels which are stored in a single array, and theplanar formats where each component is stored as a separate array, the final image being a fusing of the three separate planes.In the diagrams below, the numerical suffix attached to each Y, U or V sample indicates the sampling position across the image line, so, for example, V0 indicates the leftmost V sample and Yn indicates the Y sample at the (n+1)th pixel from the left.
Subsampling intervals in the horizontal and vertical directions may merit some explanation. The horizontal subsampling interval describes how frequently across a line a sample of that component is taken while the vertical interval describes on which lines samples are taken. For example, UYVY format has a horizontal subsampling period of 2 for both the U and V components indicating that U and V samples are taken for every second pixel across a line. Their vertical subsampling period is 1 indicating that U and V samples are taken on each line of the image.
For YVU9, though, the vertical subsampling interval is 4. This indicates that U and V samples are only taken on every fourth line of the original image. Since the horizontal sampling period is also 4, a single U and a single V sample are taken for each square block of 16 image pixels.
Also, if you are interested in YCrCb to RGB conversion, you may find this page helpful.
People reading this page may be interested in a freeware codec from Drastic Technologies which allegedly handles the vast majority of YUV formats listed here. I've not tried it but you can find ithere.
Packed YUV Formats
LabelFOURCC in HexBits per pixelDescriptionAYUV0x5655594132Combined YUV and alphaCLJR0x524A4C438Cirrus Logic format with 4 pixels packed into a u_int32. A form of YUV 4:1:1 wiht less than 8 bits per Y, U and V sample.cyuv0x7675796316Essentially a copy of UYVY except that the sense of the height is reversed - the image is upside down with respect to the UYVY version.GREY0x594552478Apparently a duplicate of Y800 (and also, presumably, "Y8 ")IRAW0x57615349?Intel uncompressed YUV. I have no information on this format - can you help?IUYV0x5659554916Interlaced version of UYVY (line order 0, 2, 4,....,1, 3, 5....) registered by Silviu Brinzei ofLEAD Technologies.IY410x3134594912Interlaced version of Y41P (line order 0, 2, 4,....,1, 3, 5....) registered by Silviu Brinzei ofLEAD Technologies.IYU10x315559491212 bit format used in mode 2 of the IEEE 1394 Digital Camera 1.04 spec. This is equivalent toY411IYU20x325559492424 bit format used in mode 0 of the IEEE 1394 Digital Camera 1.04 specHDYC0x4359444816YUV 4:2:2 (Y sample at every pixel, U and V sampled at every second pixel horizontally on each line). A macropixel contains 2 pixels in 1 u_int32. This is a suplicate ofUYVY except that the color components use the BT709 color space (as used in HD video).UYNV0x564E595516A direct copy of UYVY registered by NVidia to work around problems in some old codecs which did not like hardware which offered more than 2 UYVY surfaces.UYVP0x5056595524?YCbCr 4:2:2 extended precision 10-bits per component in U0Y0V0Y1 order. Registered byRich Ehlers of Evans & Sutherland.(Awaiting confirmation of component packing structure)UYVY0x5956595516YUV 4:2:2 (Y sample at every pixel, U and V sampled at every second pixel horizontally on each line). A macropixel contains 2 pixels in 1 u_int32.V2100x303132563210-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb equivalent to the Quicktime format of the same name.V4220x3232345616I am told that this is an upside down version of UYVY.V6550x3535365616?16 bit YUV 4:2:2 format registered by Vitec Multimedia. I have no information on the component ordering or packing.VYUY0x59555956?ATI Packed YUV Data (format unknown but you can get hold of a codec supporting ithere)Y4220x3232345916Direct copy of UYVY as used by ADS Technologies Pyro WebCam firewire camera.YUY20x3259555916YUV 4:2:2 as for UYVY but with different component ordering within the u_int32 macropixel.YUYV0x5659555916Duplicate of YUY2YUNV0x564E555916A direct copy of YUY2 registered by NVidia to work around problems in some old codecs which did not like hardware which offered more than 2 YUY2 surfaces.YVYU0x5559565916YUV 4:2:2 as for UYVY but with different component ordering within the u_int32 macropixel.Y41P0x5031345912YUV 4:1:1 (Y sample at every pixel, U and V sampled at every fourth pixel horizontally on each line). A macropixel contains 8 pixels in 3 u_int32s.Y4110x3131345912YUV 4:1:1 with a packed, 6 byte/4 pixel macroblock structure.Y2110x313132598Packed YUV format with Y sampled at every second pixel across each line and U and V sampled at every fourth pixel.Y41T0x5431345912Format as for Y41P but the lsb of each Y component is used to signal pixel transparency .Y42T0x5432345916Format as for UYVY but the lsb of each Y component is used to signal pixel transparency .YUVP0x5056555924?YCbCr 4:2:2 extended precision 10-bits per component in Y0U0Y1V0 order. Registered byRich Ehlers of Evans & Sutherland.Y8000x303038598Simple, single Y plane for monochrome images.Y80x202038598Duplicate of Y800 as far as I can see.Y160x203631591616-bit uncompressed greyscale image.AYUV
This is a 4:4:4 YUV format with 8 bit samples for each component along with an 8 bit alpha blend value per pixel. Component ordering is A Y U V (as the name suggests).
UYVY (and Y422 and UYNV and HDYC)
UYVY is probably the most popular of the various YUV 4:2:2 formats. It is output as the format of choice by the Radius Cinepak codec and is often the second choice of software MPEG codecs after YV12.
Y422 and UYNV appear to be direct equivalents to the original UYVY.
HDYC is equivalent in layout but pixels are described using the BT709 color space as used in HD video systems rather than the BT470 SD video color space typically used. Apparently there is a description in the DeckLink DirectShow SDK documentation athttp://blackmagic-design.com/support/software/archive/, find DeckLink SDK 5.6.2 for Windows XPand downloadhttp://blackmagic-design.com/support/software/register.asp?softID=108, set product to None, serial no is not required), see "Video Formats" section.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period21U Sample Period21Effective bits per pixel : 16
Positive biHeight implies top-down imge (top line first)

IUYV
IUYV is basically the same as UYVY with the exception that the data is interlaced. Lines are ordered 0,2,4,....,1,3,5.... instead of 0,1,2,3,4,5,....
cyuv
This FOURCC, allegedly registered by Creative Labs, is essentially a duplicate of UYVY. The only difference is that the image is flipped vertically, the first u_int16 in the buffer representing the bottom line of the viewed image. Note that the FOURCC is comprised of lower case characters (so much for the upper case convention !)
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period21U Sample Period21Effective bits per pixel : 16
Positive biHeight implies bottom-up image (botton line first)

YUY2 (and YUNV and V422 andYUYV)
YUY2 is another in the family of YUV 4:2:2 formats and appears to be used by all the same codecs as UYVY.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period21U Sample Period21Effective bits per pixel : 16
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
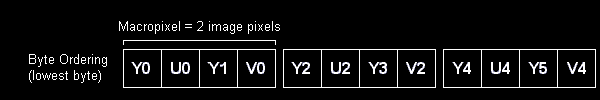
There is a help page here which contains information on playing AVIs which include video stored in YUY2 format.
YVYU
Despite being a simple byte ordering change from YUY2 or UYVY, YVYU seems to be seen somewhat less often than the other two formats defined above.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period21U Sample Period21Effective bits per pixel : 16
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
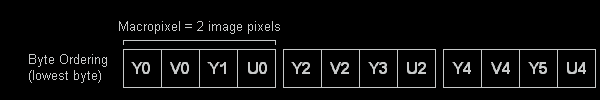
Y41P
This YUV 4:1:1 format is registered as a PCI standard format. Mediamatics MPEG 1 engine is the only codec (other than a Brooktree internal one) that I know of that can generate it.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period41U Sample Period41Effective bits per pixel : 12
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)

Y411
I was originally told that this was a duplicate of Y41P however it seems that this is not the case after all. Y411 is a packed YUV 4:1:1 format with a 6 pixel macroblock structure containing 4 pixels. Component packing order is:
U2 Y0 Y1 V2 Y2 Y3
I have not been able to find 100% confirmation of the position for the U and V samples. I suspect that the chroma samples are probably both taken at the position of Y2 but this is a guess just now.
I have recently been informed that this format is identical to IYU1.
Effective bits per pixel : 12
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
IY41
IY41 is basically the same as Y41P with the exception that the data is interlaced. Lines are ordered 0,2,4,....,1,3,5.... instead of 0,1,2,3,4,5,....
Y211
I have yet to find anything that will output Y211 ! The format looks very much like the missing YUV 4:2:2 ordering but Y samples are only taken on every second pixel. Think of it as a half width 4:2:2 image and double the width on display.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period21V Sample Period41U Sample Period41Effective bits per pixel : 8
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)

Y41T
This format is identical to Y41P except for the fact that the least significant bit of each Y component forms a chromakey channel. If this bit is set, the YUV image pixel is displayed, if cleared, the pixel is transparent (and the underlying graphics pixel is shown).
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
Y42T
This format is identical to UYVY except for the fact that the least significant bit of each Y component forms a chromakey channel. If this bit is set, the YUV image pixel is displayed, if cleared, the pixel is transparent (and the underlying graphics pixel is shown).
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
CLJR
Cirrus Logic's format packs 4 pixel samples into a single u_int32 by sacrificing precision on each sample. Y samples are truncated to 5 bits each, U and V have 6 bits per sample.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period41U Sample Period41Effective bits per pixel : 8
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
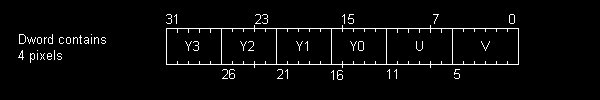
IYU1
The IYU1 format is a 12 bit format used in mode 2 of the IEEE 1394 Digital Camera 1.04 spec ("1394-based Digital Camera Specification, Version 1.04, August 9, 1996", page 14.). The format, a duplicate ofY411, is YUV (4:1:1) according to the following pattern:
IYU2
The IYU2 format is a 24 bit format used in mode 0 of the IEEE 1394 Digital Camera 1.04 spec (ibid.) The format is YUV (4:4:4) according to the following pattern:
YUVP
This is another format similar to YUY2 and it's aliases. The difference here is that each Y, U and V samples is 10 bits rather than 8. I am still waiting to hear how the samples are packed - is a macropixel just 5 bytes long with all the samples packed together or is there more to it than this?
V210
AJA Video Systems have implemented this Quicktime format for Windows. It is a 10 bit per component, YCrCb 4:2:2 format in which samples for 5 pixels are packed into 4 4-byte little endian words. Rather than repeat the details here, I suggest looking at the original definition on the Quicktime web site.
Supposedly there are images described as "YUV10" that are formatted similarly to this aside from the bit ordering (the correspondent mentioned having to run ntoh on the pixel data to reformat from YUV10 to V210. Despite 20 years of C, I've not heard of ntoh but I suspect it performs big-endian to little-endian conversion).
Planar YUV Formats
LabelFOURCC in HexBits per pixelDescription
YVU90x3955565998 bit Y plane followed by 8 bit 4x4 subsampled V and U planes. Registered by Intel.YUV90x395655599?Registered by Intel., this is the format used internally by Indeo video codeIF090x393046499.5As YVU9 but an additional 4x4 subsampled plane is appended containing delta information relative to the last frame. (Bpp is reported as 9)YV160x36315659168 bit Y plane followed by 8 bit 2x1 subsampled V and U planes.YV120x32315659128 bit Y plane followed by 8 bit 2x2 subsampled V and U planes.I4200x30323449128 bit Y plane followed by 8 bit 2x2 subsampled U and V planes.IYUV0x5655594912Duplicate FOURCC, identical to I420.NV120x3231564E128-bit Y plane followed by an interleaved U/V plane with 2x2 subsamplingNV210x3132564E12As NV12 with U and V reversed in the interleaved planeIMC10x31434D4912As YV12 except the U and V planes each have the same stride as the Y planeIMC20x32434D4912Similar to IMC1 except that the U and V lines are interleaved at half stride boundariesIMC30x33434D4912As IMC1 except that U and V are swappedIMC40x34434D4912As IMC2 except that U and V are swappedCLPL0x4C504C4312Format similar to YV12 but including a level of indirection.Y41B0x4231345912?Weitek format listed as "YUV 4:1:1 planar". I have no other information on this format.Y42B0x4232345916?Weitek format listed as "YUV 4:2:2 planar". I have no other information on this format.Y8000x303038598Simple, single Y plane for monochrome images.Y80x202038598Duplicate of Y800 as far as I can see.CXY10x3159584312Awaiting clarification of format.CXY20x3259584216Awaiting clarification of format.YVU9
This format dates back to the days of the ActionMedia II adapter and comprises an NxN plane of Y samples, 8 bits each, followed by (N/4)x(N/4) V and U planes.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period44U Sample Period44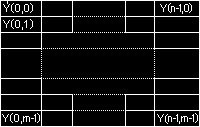
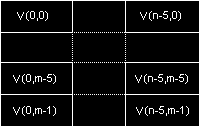
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
ATI has a codec supporting this format that you can download from here.
YUV9
Intel's web site states that YUV9 is "the color encoding scheme used in Indeo video technology. The YUV9 format stores information in 4x4 pixel blocks. Sixteen bytes of luminance are stored for every 1 byte of chrominance. For example, a 640x480 image will have 307,200 bytes of luminance and 19,200 bytes of chrominance." This sounds exactly the same asYVU9 to me. Anyone know if there is any difference?
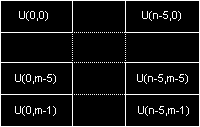
IF09
A derivative of YVU9, IF09 contains the basic 3 planes for Y, V and U followed by an additional (N/4)x(N/4) plane of "skip blocks". This final plane forms a basic delta encoding scheme which can be used by a displayer to decide which pixels in the image are unchanged from the previous displayed frame. The strange number of bits per pixel listed for the format results from the fact that an NxN image is described using N2+3(N/4)2 bytes.
This format is generated by Intel's Indeo codecs though users should beware - the original 32 bit Indeo 3.2 shipped with Windows 95 and the beta levels of Indeo 4.1 contain bugs which cause them to generate protection faults when using IF09. Fixed versions of these codecs are available from Intel.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period44U Sample Period44
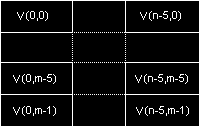

Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
Delta plane definition
To be completed...
YV12
This is the format of choice for many software MPEG codecs. It comprises an NxM Y plane followed by (N/2)x(M/2) V and U planes.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period22U Sample Period22
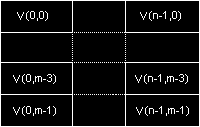
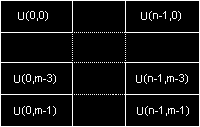
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
ATI says they have a download which contains this codec but I can't find it on their site. If you would like something similar for Quicktime,try here.
YV16
This format is basically a version of YV12 with higher chroma resolution. It comprises an NxM Y plane followed by (N/2)xM U and V planes.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period21U Sample Period21IYUV and I420
These formats are identical to YV12 except that the U and V plane order is reversed. They comprise an NxN Y plane followed by (N/2)x(N/2) U and V planes. Full marks to Intel for registering the same format twice and full marks to Microsoft for not picking up on this and rejecting the second registration.
(Note: There is some confusion over these formats thanks to the definitions onMicrosoft's site which tend to suggest that the two FOURCCs are different. One is described as a 4:2:0 format while the other is described as 4:1:1. Later, however, the same page states that YV12 is the same as both of these with the U and V plane order reversed. I would consider 4:2:0 to imply 1 chroma sample for every 2x2 luma block and 4:1:1 to imply 1 chroma sample for every 4x1 luma block but it seems as if the Microsoft writer may have been using the terms interchangeably. If you know these formats, please could youlet me know whether the definition here is correct or whether I need to update one or other?)
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period22U Sample Period22

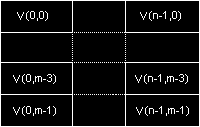
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
CLPL
This format introduces an extra level of indirection in the process of accessing YUV pixels in the surface. Locking the DirectDraw or DCI CLPL surface returns a pointer which itself points to three other pointers. These pointers respectively point to an NxN Y plane, an (N/2)x(N/2) U plane and an (N/2)x(N/2) V plane. The Y plane pointer retrieved is (allegedly) valid even when the surface is subsequently unlocked but the U and V pointers can only be used with a lock held (as you should be doing anyway if adhereing to the DirectDraw/DCI spec).
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample Period22U Sample Period22

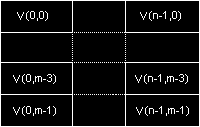
Positive biHeight implies top-down image (top line first)
Y800
This format contains only a single, 8 bit Y plane for monochrome images. Apparent duplicate FOURCCs are "Y8" and "GREY".
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample PeriodN/AN/AU Sample PeriodN/AN/A
Y16
This format contains only a single, 16 bit Y plane for monochrome images. Each pixel is represented by a 16 bit, little endian luminance sample.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V Sample PeriodN/AN/AU Sample PeriodN/AN/A
NV12
YUV 4:2:0 image with a plane of 8 bit Y samples followed by an interleaved U/V plane containing 8 bit 2x2 subsampled colour difference samples.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V (Cr) Sample Period22U (Cb) Sample Period22Microsoft defines this format as follows:
"A format in which all Y samples are found first in memory as an array of unsigned char with an even number of lines (possibly with a larger stride for memory alignment), followed immediately by an array of unsigned char containing interleaved Cb and Cr samples (such that if addressed as a little-endian WORD type, Cb would be in the LSBs and Cr would be in the MSBs) with the same total stride as the Y samples. This is the preferred 4:2:0 pixel format."
NV21
YUV 4:2:0 image with a plane of 8 bit Y samples followed by an interleaved V/U plane containing 8 bit 2x2 subsampled chroma samples. The same asNV12 except the interleave order of U and V is reversed.
HorizontalVerticalY Sample Period11V (Cr) Sample Period22U (Cb) Sample Period22Microsoft defines this format as follows:
"The same as NV12, except that Cb and Cr samples are swapped so that the chroma array of unsigned char would have Cr followed by Cb for each sample (such that if addressed as a little-endian WORD type, Cr would be in the LSBs and Cb would be in the MSBs)."
IMC1
 Similar toYV12, this format comprises an NxN Y plane followed by (N/2)x(N/2) U and V planes. The U and V planes have the same stride as the Y plane and are restricted to start on 16 line boundaries.
Similar toYV12, this format comprises an NxN Y plane followed by (N/2)x(N/2) U and V planes. The U and V planes have the same stride as the Y plane and are restricted to start on 16 line boundaries.
Microsoft defines this format as follows:
"The same as YV12, except that the stride of the Cb and Cr planes is the same as the stride in the Y plane. The Cb and Cr planes are also restricted to fall on memory boundaries that are a multiple of 16 lines (a restriction that has no effect on usage for the standard formats, since the standards all use 16×16 macroblocks)."
IMC2
 Similar toYV12, this format comprises an NxN Y plane followed by "rectangularly adjacent" (N/2)x(N/2) U and V planes. Lines of U and V pixels are interleaved at half stride boundaries below the Y plane.
Similar toYV12, this format comprises an NxN Y plane followed by "rectangularly adjacent" (N/2)x(N/2) U and V planes. Lines of U and V pixels are interleaved at half stride boundaries below the Y plane.
Microsoft defines this format as follows:
"The same as IMC1, except that Cb and Cr lines are interleaved at half-stride boundaries. In other words, each full-stride line in the chrominance area starts with a line of Cr, followed by a line of Cb that starts at the next half-stride boundary. (This is a more address-space-efficient format thanIMC1, cutting the chrominance address space in half, and thus cutting the total address space by 25%.) This runs a close second in preference relative toNV12, butNV12 appears to be more popular."
IMC3
The same as IMC1 except for swapping the U and V order.
IMC4
The same as IMC2 except for swapping the U and V order.
CXY1
Planar YUV 4:1:1 format registered by Conexant. Awaiting clarification of pixel component ordering.
CXY2
Planar YUV 4:2:2 format registered by Conexant. Awaiting clarification of pixel component ordering.
YUV主要的采样格式
主要的采样格式有YCbCr 4:2:0、YCbCr 4:2:2、YCbCr 4:1:1和 YCbCr 4:4:4。其中YCbCr 4:1:1比较常用,其含义为:每个点保存一个 8bit的亮度值(也就是Y值),每 2x2 个点保存一个 Cr和Cb值,图像在肉眼中的感觉不会起太大的变化。所以,原来用 RGB(R,G,B都是8bit unsigned)模型, 4 个点需要 8x3=24 bites(如下图第一个图).而现在仅需要 8+(8/4)+(8/4)=12bites,平均每个点占12bites(如下图第二个图)。这样就把图像的数据压缩了一半。
上边仅给出了理论上的示例,在实际数据存储中是有可能是不同的,下面给出几种具体的存储形式:
(1)YUV 4:4:4
YUV三个信道的抽样率相同,因此在生成的图像里,每个象素的三个分量信息完整(每个分量通常8比特),经过8比特量化之后,未经压缩的每个像素占用3个字节。
下面的四个像素为: [Y0 U0 V0] [Y1 U1 V1] [Y2 U2 V2] [Y3 U3 V3]
存放的码流为: Y0 U0 V0 Y1 U1 V1 Y2 U2 V2 Y3 U3 V3
(2) YUV 4:2:2
每个色差信道的抽样率是亮度信道的一半,所以水平方向的色度抽样率只是4:4:4的一半。对非压缩的8比特量化的图像来说,每个由两个水平方向相邻的像素组成的宏像素需要占用4字节内存。
下面的四个像素为: [Y0 U0 V0] [Y1 U1 V1] [Y2 U2 V2] [Y3 U3 V3]
存放的码流为: Y0 U0 Y1 V1 Y2 U2 Y3 V3
映射出像素点为:[Y0 U0 V1] [Y1 U0 V1] [Y2 U2 V3] [Y3 U2 V3]
(3) YUV 4:1:1
4:1:1的色度抽样,是在水平方向上对色度进行4:1抽样。对于低端用户和消费类产品这仍然是可以接受的。对非压缩的8比特量化的视频来说,每个由4个水平方向相邻的像素组成的宏像素需要占用6字节内存
下面的四个像素为: [Y0 U0 V0] [Y1 U1 V1] [Y2 U2 V2] [Y3 U3 V3]
存放的码流为: Y0 U0 Y1 Y2 V2 Y3
映射出像素点为:[Y0 U0 V2] [Y1 U0 V2] [Y2 U0 V2] [Y3 U0 V2]
(4)YUV4:2:0
4:2:0并不意味着只有Y,Cb而没有Cr分量。它指得是对每行扫描线来说,只有一种色度分量以2:1的抽样率存储。相邻的扫描行存储不同的色度分量,也就是说,如果一行是4:2:0的话,下一行就是4:0:2,再下一行是4:2:0...以此类推。对每个色度分量来说,水平方向和竖直方向的抽样率都是2:1,所以可以说色度的抽样率是4:1。对非压缩的8比特量化的视频来说,每个由2x2个2行2列相邻的像素组成的宏像素需要占用6字节内存。
下面八个像素为:[Y0 U0 V0] [Y1 U1 V1] [Y2 U2 V2] [Y3 U3 V3]
[Y5 U5 V5] [Y6 U6 V6] [Y7U7 V7] [Y8 U8 V8]
存放的码流为:Y0 U0 Y1 Y2 U2 Y3
Y5 V5 Y6 Y7 V7 Y8
映射出的像素点为:[Y0 U0 V5] [Y1 U0 V5] [Y2 U2 V7] [Y3 U2 V7]
[Y5 U0 V5] [Y6 U0 V5] [Y7U2 V7] [Y8 U2 V7]
- YUV pixel formats
- YUV pixel formats
- YUV pixel formats
- YUV pixel formats
- YUV pixel formats
- YUV pixel formats
- yuv pixel formats
- YUV Formats
- YUV Formats
- YUV Formats
- YUV Formats
- YUV pixel formats 每个像素占多少位里面都有介绍
- RGB pixel formats
- [zz]YUV Formats
- Understanding YUV data formats
- RGB/YUV Pixel Conversion
- 4:2:0 Video Pixel Formats
- Video Rendering with 8-Bit YUV Formats
- POJ 2594 Treasure Exploration
- TP4056大电流1A使用注意事项
- JavaScript绘图库 Raphael
- ARM常用汇编指令
- POJ 2060 Taxi Cab Scheme
- YUV pixel formats
- Trie树
- Oracle数据库启动与停止
- QQ空间伤感日志_我爱你_但,那只是曾经
- Oracle的文件系统
- JAVA获取每个月的天数
- speex源码分析-2-lsp量化
- DataSet、DataTable、DataView格式转换成XML字符串、XML文件
- POJ3273 Monthly Expense (二分统计)+二分查找基础例子


