android基础知识12:android自动化测试04—Robotium:实例(上)
来源:互联网 发布:gta4渣优化 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 17:29
前文已经对基于junit的android测试框架有了一个大概的介绍,下面我们对activity测试进行分析。
本文主要举两个基于Robotium的activity测试例子,一个是测试单个activity,一个测试多个activity。
1、Robotium概述
首先,我们来了解一下android的测试类的层次结构:
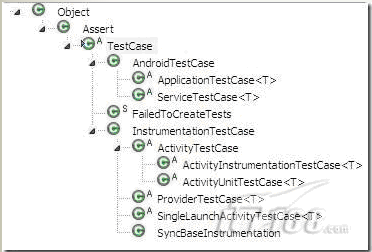
可以看出android中的测试方法主要有AndroidTextCase和InstrumentationTextCase。在这篇文章中,我将介绍Instrumentation这种测试方法,那么什么是Instrumentation?
Instrumentation和Activity有点类似,只不过Activity是需要一个界面的,而Instrumentation并不是这样的,我们可以将它理解为一种没有图形界面的,具有启动能力的,用于监控其他类(用Target Package声明)的工具类。
2、单个activity测试例子
2.1普通测试
我想大家在安装完robotium后,都会试试noteslist 这个例子吧。这个是官网提到的例子
首先打开noteslist 源码
\samples\android-7\NotePad
再打开noteslisttest 源码
可以从上面下载 http://code.google.com/p/robotium/downloads/list/ExampleTestProject_v2.3.zip
要做一点修改。 因为noteslist是在androidV21开发的,而我的测试代码是V23的。我们最好要改成一致的。
修改 noteslisttest 下的AndroidManifest.xml
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="9" />
改成<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
这两个数字表示什么意思呢?
7--androidV21,9--androidV23,最低版本是3--AndroidV15.
大家按顺序排就知道哪个数字对应的版本了
然后在 noteslisttest 右击选中Properties--Android,选中AndroidV21
这样noteslisttest 里带的android jar 由android2.3 变为android2.1
再说一个配置,我觉得也很重要
还是在AndroidManifest.xml 里
<instrumentation android:targetPackage="com.example.android.notepad" android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner" />
红色加粗的字符串表示我们要测试代码的package
OK,这样我们就弄好代码了。 我们只需要执行Run As--Android Junit test
下面我们看看 noteslisttest 里的具体代码,看看它是怎么测试的
- private Solo solo;
- // 告知系统我要测试的app是什么
- public NotePadTest() {
- super("com.example.android.notepad", NotesList.class);
- }
- //打开noteslist
- public void setUp() throws Exception {
- solo = new Solo(getInstrumentation(), getActivity());
- }
- @Smoke
- public void testAddNote() throws Exception {
- solo.clickOnMenuItem("Add note");
- solo.assertCurrentActivity("Expected NoteEditor activity", "NoteEditor"); //Assert that NoteEditor activity is opened
- solo.enterText(0, "Note 1"); //In text field 0, add Note 1
- solo.goBack(); //Go back
- solo.clickOnMenuItem("Add note"); //Clicks on menu item
- solo.enterText(0, "Note 2"); //In text field 0, add Note 2
- solo.goBackToActivity("NotesList"); //Go back to first activity named "NotesList"
- boolean expected = true;
- boolean actual = solo.searchText("Note 1") && solo.searchText("Note 2");
- assertEquals("Note 1 and/or Note 2 are not found", expected, actual); //Assert that Note 1 & Note 2 are found
- }
clickOnMenuItem(String)
功能是点击Menu按钮,选择文本描述为String的菜单,如我们的例子是"Add note"
assertCurrentActivity(String message,String name)
这个是判断当前的activity是否和我预期的一致
message是描述性的文字
name是指activity的名字
关于如何知道activity 名字,我找了半天的文档,目前的方法是得看源码中的 AndroidManifest.xml--Application label--Application Nodes,在那里我们可以看到所有的activity的name
enterText(int index,string text)
index用来标识写到哪个EditText中。如果当前只打开一个EditText,那index=0
text:就是我们要写入的内容
goBack()
相当于手机上的 返回键(back key)
goBackToActivity(String name)
返回到指定的activity
searchText(String text)
在当前的activity中搜索是否含有text的内容
- @Smoke
- public void testEditNote() throws Exception {
- solo.clickInList(2); // Clicks on the second list line
- solo.setActivityOrientation(Solo.LANDSCAPE); // Change orientation of activity
- solo.clickOnMenuItem("Edit title"); // Change title
- solo.enterText(0, " test"); //In first text field (0), add test.
- solo.goBackToActivity("NotesList");
- boolean expected = true;
- boolean actual = solo.searchText("(?i).*?note 1 test"); // (Regexp) case insensitive // insensitive
- assertEquals("Note 1 test is not found", expected, actual); //Assert that Note 1 test is found
- }
clickInList(int index)
点击list表的第index行,进入该文本界面
solo.setActivityOrientation(Solo.LANDSCAPE);
setActivityOrientation,设置手机屏幕显示方式
LANDSCAPE:横向显示
Portrait:竖向显示
- @Smoke
- public void testRemoveNote() throws Exception {
- solo.clickOnText("(?i).*?test.*"); //(Regexp) case insensitive/text that contains "test"
- solo.clickOnMenuItem("Delete"); //Delete Note 1 test
- boolean expected = false; //Note 1 test & Note 2 should not be found
- boolean actual = solo.searchText("Note 1 test");
- assertEquals("Note 1 Test is found", expected, actual); //Assert that Note 1 test is not found
- solo.clickLongOnText("Note 2");
- solo.clickOnText("(?i).*?Delete.*"); //Clicks on Delete in the context menu
- actual = solo.searchText("Note 2");
- assertEquals("Note 2 is found", expected, actual); //Assert that Note 2 is not found
- }
clickOnText(String text)
点击包含该文字的地方
其中text可以用正则表达式表示
(?i)----忽略大小写。默认情况是大小写敏感的。
正则表达式与java保持一致
clickLongOnText(String text)
长时间按住所选的文字
这里需要注意:被测apk和测试apk必须使用相同的签名。
2.2 数据驱动测试
本例与上一例子都是对于单个activity测试,不同的地方在于本例使用的测试数据来源于文件。
被测试代码是简易计算器,代码: /Files/morebetter/android code/AndroidCalculator.rar
1. 数据驱动测试架构
测试数据源:TestData.csv
第一个输入框从First Value中读数据
第二个输入框从Second Value中读数据
点击Multiply
比较测试结果和期望结果是否一致,将结果写到文件里
2. 创建数据源文件
格式如上图
3. 把数据源文件上传到Emulator上
在被测试代码中创建res/raw/files文件夹。这样files文件夹就能被上传到Emulator上了
用Eclipse—Run As—Android Application 运行被测试代码
在Eclipse上加载DDMS,点击File Exploer,浏览Emulator-5554的所有文件
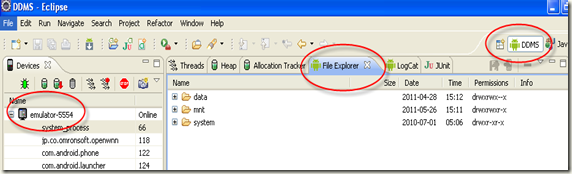
打开/data/data/com.calculator/files, 点击右侧上传到device的按钮,将csv文件上传到emulator上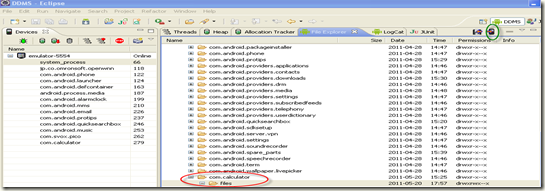
4. 编辑测试case, 代码为:/Files/morebetter/android code/AndroidCalculatorTestApk.rar
5. 运行测试case
6. 将测试结果写到文件里,该文件存放在/data/data/com.calculator/files 下面
7. 将测试结果导入到本地电脑中

3、多个activity测试
在Android SDK中“Resources”-“Tutorials”下有“Notepad Tutorial”和“Activity Testing”两个项目,一个示例是指导你如何快速开发一个Android小程序,一个是指导你如何对项目进行测试,两个项目都适合在入门的时候好好学习。
其中的“Activity Testing”是对“Samples”-“Spinner”项目进行测试,其中包含了UI测试、状态破坏和状态恢复测试。这个项目只有一个Activity,测试起来也不麻烦,细心阅读文档就可以完成。但是一个程序只有一个Activity应该是很难遇见的吧,那么应该对多活动(Multi Activities)的程序进行测试呢?
其实我这也是随便整整,大家随便看看。
在查看SDK关于测试的章节后,有疑问如下:
测试Activity、Service、Provider都是自动化的,那么我们如何控制运行过程?
如何在界面模拟操作,如点击按钮,输入文字内容等等。
新建一个项目,项目名为Login,包名为com.vruc.android.login,程序名为Login,活动名为AuthenticateActivity;同时添加一个项目名为LoginTest,包名为com.vruc.android.login.test,程序名为LoginTest的测试项目。
完整的Login项目:
1.更改main.xml文件名为login.xml,更改代码为下:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent">
- <EditText android:id="@+id/username_field"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="match_parent"></EditText>
- <EditText android:id="@+id/password_field"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="match_parent"></EditText>
- <Button android:text="Login" android:id="@+id/login_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
- </LinearLayout>
- public class AuthenticateActivity extends Activity {
- /** Called when the activity is first created. */
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.login);
- Button login = (Button) findViewById(R.id.login_button);
- login.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- Intent i = new Intent(AuthenticateActivity.this,WelcomeActivity.class);
- i.putExtra(ACCOUNT_SERVICE,((EditText) findViewById(R.id.username_field)).getText().toString());
- startActivity(i);
- finish();
- }
- });
- }
- }
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent">
- <TextView android:id="@+id/welcome_message"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:textSize="15pt"></TextView>
- </LinearLayout>
- public class WelcomeActivity extends Activity {
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.welcome);
- Intent i = this.getIntent();
- ((TextView)findViewById(R.id.welcome_message)).setText(i.getStringExtra(ACCOUNT_SERVICE));
- }
完整的LoginTest项目
1.添加LoginTest.java文件,继承类为android.test.InstrumentationTestCase
2.完整LoginTest.java中测试代码:
- public static final String TEST_USERNAME = "TEST_USERNAME";
- public static final String TEST_PASSWORD = "TEST_PASSWORD";
- public void testUserLogin() {
- // 注册最开始的活动并运行
- Instrumentation instrumentation = getInstrumentation();
- ActivityMonitor monitor = instrumentation.addMonitor(
- AuthenticateActivity.class.getName(), null, false);
- // 运行活动
- Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN);
- intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
- intent.setClassName(instrumentation.getTargetContext(), AuthenticateActivity.class.getName());
- instrumentation.startActivitySync(intent);
- // 等待Authenticate活动开始
- Activity currentActivity = getInstrumentation().waitForMonitorWithTimeout(monitor, 5);
- assertTrue(currentActivity != null);
- // 自动输入预定的用户名
- View currentView = currentActivity.findViewById(com.vruc.android.login.R.id.username_field);
- assertTrue(currentView != null);
- TouchUtils.clickView(this, currentView);
- instrumentation.sendStringSync(TEST_USERNAME);
- // 自动输入预定的密码
- currentView = currentActivity.findViewById(com.vruc.android.login.R.id.password_field);
- assertTrue(currentView != null);
- TouchUtils.clickView(this, currentView);
- instrumentation.sendStringSync(TEST_PASSWORD);
- // 移除当前活动监视,注册新的活动监视,要在还没有按下按钮前准备
- instrumentation.removeMonitor(monitor);
- monitor = instrumentation.addMonitor(WelcomeActivity.class.getName(), null, false);
- // 自动点击登陆按钮
- currentView = currentActivity.findViewById(com.vruc.android.login.R.id.login_button);
- assertTrue(currentView != null);
- TouchUtils.clickView(this, currentView);
- // 等待Welcome活动开始
- currentActivity = getInstrumentation().waitForMonitorWithTimeout(monitor, 5);
- currentView = currentActivity.findViewById(com.vruc.android.login.R.id.welcome_message);
- assertTrue(currentView != null);
- assertEquals(TEST_USERNAME, ((TextView) currentView).getText().toString());
- }
4、Activity 启动 Instrumentation 测试
和startActivity 及 startService类似
在activity中 启动Instrumentation 以便调用运行测试项目 ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2
可以尝试如下代码实现
startInstrumentation(new ComponentName("com.example.test", "android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner"), null, null);
5、从Intent中获取数据
大多数Activity在启动时,都会从Intent中获取一些数据。
在使用Robotium测试时,当然也会需要从Activity中获取数据。
可用的流程为
1。将setUp()方法中的
solo = new Solo(getInstrumentation(), getActivity());
转移到每一个testXXX方法中。
2.在该语句前,可以做Intent的注入,例如
- Intent intent=new Intent();
- Bundle b=new Bundle();
- b.putParcelable(Account.class.getName(), account);
- b.putParcelable(User.class.getName(), user);
- intent.putExtras(b);
- setActivityIntent(intent);
solo = new Solo(getInstrumentation(), getActivity());之后,例如
有操作本地Key-Value存储的,需要早solo= 之后执行。否则会引起Activity提前实例化。导致Intent注入失败
参考文献:
android单元测试初探——Instrumentation
Activity 启动 Instrumentation 测试
学习NotesList(Robotium自带的例子)
Android Test - Auto Test Multi Activities
Robotium 数据驱动测试框架
- android基础知识12:android自动化测试04—Robotium:实例(上)
- android基础知识12:android自动化测试04—Robotium:实例(下)
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(一)
- Android 自动化测试—robotium
- Android Robotium自动化测试
- android 自动化测试robotium
- ANDROID自动化测试 robotium
- Android Robotium自动化测试
- Robotium android自动化测试
- Android自动化测试工具——robotium
- Android 自动化测试(5)<robotium>
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(一)环境
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(二)初识
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(三)EditText控件
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(四)CheckBox控件
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(五)Spinner控件
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(六)只有APK存在
- Android 自动化测试—robotium(七)Ant 构建脚本
- 这两天遇到一个难题网页无法请求出现404页面提示
- 嘿,哥们儿,你应该再努力一些
- ERP系统容灾方案对ERP生产系统的影响
- ubuntu 制作USB启动盘
- linux如何查找文件或者目录的位置相关命令汇总
- android基础知识12:android自动化测试04—Robotium:实例(上)
- 如何用T-SQL判断SQL语法是否正确
- 【专题】单调队列/斜率优化DP
- Comparable排序(备忘)
- java.io.Serializable这个接口
- android基础知识12:android自动化测试03—基于junit的android测试框架03
- 如何使用jQuery ui 分享心得
- Triangle CrackMe
- POJ 3233 Matrix Power Series(矩阵快速幂+二分求和)


