hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game (状压+记忆化搜索)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝全店怎么托管 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/22 23:05
Fishhead’s Little Game
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 517 Accepted Submission(s): 124
Problem Description
There is a 3 by 3 grid and each vertex is assigned a number.
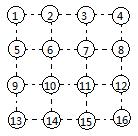
It looks like JiuGongGe, but they are different, for we are not going to fill the cell but the edge. For instance,
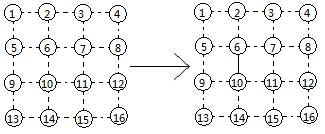
adding edge 6 –> 10
The rule of this game is that each player takes turns to add an edge. You will get one point if the edge you just added, together with edges already added before, forms a new square (only square of size 1 is considered). Of course, you get two points if that edge forms two squares. Notice that an edge can be added only once.
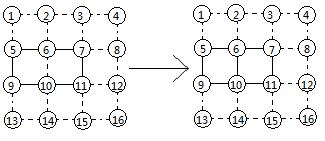
forming two squares to get two points
Tom200 and Jerry404 is playing this little game, and have played n rounds when Fishhead comes in. Fishhead wants to know who will be the winner. Can you help him? Assume that Tom200 and Jerry404 are clever enough to make optimal decisions in each round. Every Game starts from Tom200.

It looks like JiuGongGe, but they are different, for we are not going to fill the cell but the edge. For instance,

The rule of this game is that each player takes turns to add an edge. You will get one point if the edge you just added, together with edges already added before, forms a new square (only square of size 1 is considered). Of course, you get two points if that edge forms two squares. Notice that an edge can be added only once.

Tom200 and Jerry404 is playing this little game, and have played n rounds when Fishhead comes in. Fishhead wants to know who will be the winner. Can you help him? Assume that Tom200 and Jerry404 are clever enough to make optimal decisions in each round. Every Game starts from Tom200.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer T (T <= 100), the number of test cases.
For each case, the first line contains an integers n (12 <= n <= 24), which means they have taken total n rounds in turn. Next n lines each contains two integers a, b (a, b <= 16) representing the two endpoints of the edge.
For each case, the first line contains an integers n (12 <= n <= 24), which means they have taken total n rounds in turn. Next n lines each contains two integers a, b (a, b <= 16) representing the two endpoints of the edge.
Output
For each case output one line "Case #X: ", representing the Xth case, starting from 1. If Tom200 wins, print "Tom200" on one line, print "Jerry404" otherwise.
Sample Input
1151 21 52 65 96 109 105 62 33 77 1110 113 46 77 84 8
Sample Output
Case #1: Tom200HintIn case 1, Tom200 gets two points when she add edge 5 -> 6, two points in edge 6 -> 7, one point in 4 -> 8.
Source
2013 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Nanjing Online
题意:
在3*3的方格中,有4*4=16个点,标号分别为1~16,A、B两人轮流玩游戏,每次可以添加一条边(相邻节点),如果恰好能够凑成一个边长为1的正方形则得一分,两个的话得2分。给定两人放的n边后,求最终格局谁会胜。
思路:
状压+记忆化搜索。
将没有访问的边记录下来,用一个数表示这些边的状态实现状压。假设dfs(state)能生成一个该状态下的最优解,用dp[]保存下来就实现记忆化了。
一个state还剩sum分可加,对这个state进行加边(将其中一位 置为1),加这条边后能的 t 分,则
score=sum-dfs(newstate,sum-t);
取每种情况的score的最大值就够了。
代码:
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <map>#include <stack>#include <vector>#include <set>#include <queue>//#pragma comment (linker,"/STACK:102400000,102400000")#define maxn 30#define mod 1000000000#define INF 0x3f3f3f3fusing namespace std;int n,m,ans,cnt;int x[maxn],dp[10000];bool vis[maxn];int mp[maxn][maxn];int s[9][4]={ 1,4,5,8, 2,5,6,9, 3,6,7,10, 8,11,12,15, 9,12,13,16, 10,13,14,17, 15,18,19,22, 16,19,20,23, 17,20,21,24};int solve(){ int i,j,t=0; for(i=0;i<9;i++) { if(vis[s[i][0]]&&vis[s[i][1]]&&vis[s[i][2]]&&vis[s[i][3]]) t++; } return t;}int isok(int ste,int k){ int i,j,u,s1,s2; int vv[maxn]={0}; for(i=0;i<=cnt;i++) { u=1<<i; if(ste&u) vv[x[i]]=1; } s1=s2=0; for(i=0;i<9;i++) { if((vis[s[i][0]]||vv[s[i][0]])&&(vis[s[i][1]]||vv[s[i][1]])&&(vis[s[i][2]]||vv[s[i][2]])&&(vis[s[i][3]]||vv[s[i][3]])) s1++; } vv[x[k]]=1; for(i=0;i<9;i++) { if((vis[s[i][0]]||vv[s[i][0]])&&(vis[s[i][1]]||vv[s[i][1]])&&(vis[s[i][2]]||vv[s[i][2]])&&(vis[s[i][3]]||vv[s[i][3]])) s2++; } return s2-s1;}int dfs(int ste,int sum){ if(dp[ste]!=-1) return dp[ste]; int i,j,st,t,tmp,best=0; for(i=0;i<=cnt;i++) { st=1<<i; if((st&ste)==0) // 尚未访问这条边 { st=st|ste; tmp=isok(ste,i); t=dfs(st,sum-tmp); if(best<sum-t) best=sum-t; } } dp[ste]=best; return best;}int main(){ int i,j,t,u,v,s1,s2,T,J,test=0; memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp)); mp[1][2]=1,mp[2][3]=2,mp[3][4]=3; mp[1][5]=4,mp[2][6]=5,mp[3][7]=6,mp[4][8]=7; mp[5][6]=8,mp[6][7]=9,mp[7][8]=10; mp[5][9]=11,mp[6][10]=12,mp[7][11]=13,mp[8][12]=14; mp[9][10]=15,mp[10][11]=16,mp[11][12]=17; mp[9][13]=18,mp[10][14]=19,mp[11][15]=20,mp[12][16]=21; mp[13][14]=22,mp[14][15]=23,mp[15][16]=24; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d",&n); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); T=J=0; s1=0; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); vis[mp[u][v]]=vis[mp[v][u]]=1; s2=solve(); if(i&1) T+=s2-s1; else J+=s2-s1; s1=s2; } cnt=-1; for(i=1;i<=24;i++) { if(!vis[i]) x[++cnt]=i; } m=0; for(i=0;i<9;i++) { if(!vis[s[i][0]]||!vis[s[i][1]]||!vis[s[i][2]]||!vis[s[i][3]]) m++; } memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp)); u=dfs(0,m); printf("Case #%d: ",++test); if(n&1) { if(T+m-u>J+u) printf("Tom200\n"); else printf("Jerry404\n"); } else { if(T+u>J+m-u) printf("Tom200\n"); else printf("Jerry404\n"); } } return 0;}- hdu-4753-Fishhead’s Little Game-记忆化搜索
- hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game (状压+记忆化搜索)
- hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game (记忆化搜索+状态压缩)
- HDU 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game (博弈+记忆话搜索)
- hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game(状压dp)
- 对抗搜索/dp-hdu-4753-Fishhead’s Little Game
- HDU 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game (对抗搜索)
- HDU 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game(博弈搜索)
- hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game
- hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game
- Fishhead’s Little Game HDU 4753
- hdu4753Fishhead’s Little Game【状态压缩记忆化搜索+博弈】
- HDU 5024 Wang Xifeng's Little Plot 记忆化搜索
- Hdu-5024 Wang Xifeng's Little Plot(记忆化搜索)
- HDU 5024 (广州网络赛) Wang Xifeng's Little Plot 记忆化搜索+枚举
- HDU 5024 Wang Xifeng's Little Plot (枚举 + DFS记忆化搜索)
- ZOJ 3644 Kitty's Game(记忆化搜索+剪枝)
- hdu4753 Fishhead’s Little Game 状态压缩,总和一定的博弈
- 2013年完美世界校园招聘笔试题
- c算法100例
- c与c++ static函数的区别
- QiuQiu好好的
- Linux squid 安装配置
- hdu 4753 Fishhead’s Little Game (状压+记忆化搜索)
- sscanf,sscanf_s及其相关用法
- Linux时间子系统之一:clock source(时钟源)
- 风雨求职路
- HDU 4749 KMP + BIT HASH
- 向量计算器
- 单链表反转
- 归并排序
- ubuntu下缺省编译内核linux2.6.26


