cocos2d-x中几种存储数据的方式
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝开店阿里巴巴进货 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/07 14:40
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_82ca0a770101106d.html
- 先介绍CCUserDefault类
此类采用单例模式,可以通过sharedUserDefault()函数获取其唯一实例
CCUserDefault采用XML存储技术,就是一般的键值对,初学者也能容易的掌握
访问方式为CCUserDefault::sharedUserDefault()
这句话比较长,而且用的地方也比较多,所以建议采用宏定义简化代码
如下: #define userDefaultCCUserDefault::sharedUserDefault()
其实现的接口也比较简单实用,通过传统的get()、set()方法访问和修改值
如下:
//获取bool型值
//获取浮点数值
//获取字符串
//设置布尔型值
void
- 接下来是其一般存储与初始化流程
该存储文件名已经规定了为UserDefault.xml,当该文件不存在是会自动创建,存在之后直接存取就行了,不需要过多的操作
通过以下代码,以判断该文件是否存在,不存在就创建并写入记录,表明其已经存在。
当然这显得有些多余,因为直接写一条记录也会使其创建并且不会破坏其数据。
但对于程序员来说,这是一个好习惯
这样数据存储就初始化好了,之后直接调用get、set等方法就可以直接存取数据了
参考文档:http://4137613.blog.51cto.com/4127613/770754
2.CCFileUtils
转自:
http://blog.csdn.net/chiuan/article/details/8618411
为了保存自定义数据文件,需要保存文件和读取文件,也就是File的IO处理;
针对cocos2d-x我们可以通过CCFileUtils::sharedFileUtils()->getWriteablePath()获取到可读写的文件目录,其实是Caches目录。
关于file的操作,我们要明白几个概念:
File :文件对象,用于创建文件,操作文件
fopen:打开操作一个具体文件(文件路径,模式)模式有"w"\"r"读写等
fseek:移动文件指针
ftell:得到文件指针的位置,距离开头
rewind:文件指针重置
malloc:分配内存空间
fread:读一个文件的内容,需要输入buf储存空间,单位大小,长度,文件指针
fputs:写内容进去一个文件
摘录读取模式
r 以只读方式打开文件,该文件必须存在。
r+ 以可读写方式打开文件,该文件必须存在。
rb+ 读写打开一个二进制文件,允许读数据。
rt+ 读写打开一个文本文件,允许读和写。
w 打开只写文件,若文件存在则文件长度清为0,即该文件内容会消失。若文件不存在则建立该文件。
w+ 打开可读写文件,若文件存在则文件长度清为零,即该文件内容会消失。若文件不存在则建立该文件。
a 以附加的方式打开只写文件。若文件不存在,则会建立该文件,如果文件存在,写入的数据会被加到文件尾,即文件原先的内容会被保 留。(EOF符保留)
a+ 以附加方式打开可读写的文件。若文件不存在,则会建立该文件,如果文件存在,写入的数据会被加到文件尾后,即文件原先的内容会被保留。 (原来的EOF符不保留)
wb 只写打开或新建一个二进制文件;只允许写数据。
wb+ 读写打开或建立一个二进制文件,允许读和写。
wt+ 读写打开或着建立一个文本文件;允许读写。
at+ 读写打开一个文本文件,允许读或在文本末追加数据。
ab+ 读写打开一个二进制文件,允许读或在文件末追加数据。
以下是代码,2个静态方法,保存和读取:TDInvFileUtils.h
- //
- // TDInvFileUtils.h
- // MyCocoa2DTest
- //
- // Created by 韦 柱全 on 13-2-27.
- //
- //
- #ifndef __MyCocoa2DTest__TDInvFileUtils__
- #define __MyCocoa2DTest__TDInvFileUtils__
- #include <iostream>
- #include "cocos2d.h"
- using namespace cocos2d;
- using namespace std;
- /** 负责操作文件储存和读取
- */
- class TDInvFileUtils {
- public:
- /** 读取本地文件,返回数据 */
- static string getFileByName(string pFileName);
- /** 储存内容到文件 */
- static bool saveFile(char* pContent,string pFileName);
- };
- #endif /* defined(__MyCocoa2DTest__TDInvFileUtils__) */
其实现文件 TDInvFileUtils.cpp
- //
- // TDInvFileUtils.cpp
- // MyCocoa2DTest
- //
- // Created by 韦 柱全 on 13-2-27.
- //
- //
- #include "TDInvFileUtils.h"
- string TDInvFileUtils::getFileByName(string pFileName){
- //第一先获取文件的路径
- string path = CCFileUtils::sharedFileUtils()->getWriteablePath() + pFileName;
- CCLOG("path = %s",path.c_str());
- //创建一个文件指针
- FILE* file = fopen(path.c_str(), "r");
- if (file) {
- char* buf; //要获取的字符串
- int len; //获取的长度
- /*获取长度*/
- fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END); //移到尾部
- len = ftell(file); //提取长度
- rewind(file); //回归原位
- CCLOG("count the file content len = %d",len);
- //分配buf空间
- buf = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * len + 1);
- if (!buf) {
- CCLOG("malloc space is not enough.");
- return NULL;
- }
- //读取文件
- //读取进的buf,单位大小,长度,文件指针
- int rLen = fread(buf, sizeof(char), len, file);
- buf[rLen] = '\0';
- CCLOG("has read Length = %d",rLen);
- CCLOG("has read content = %s",buf);
- string result = buf;
- fclose(file);
- free(buf);
- return result;
- }
- else
- CCLOG("open file error.");
- return NULL;
- }
- bool TDInvFileUtils::saveFile(char *pContent, string pFileName){
- //第一获取储存的文件路径
- string path = CCFileUtils::sharedFileUtils()->getWriteablePath() + pFileName;
- CCLOG("wanna save file path = %s",path.c_str());
- //创建一个文件指针
- //路径、模式
- FILE* file = fopen(path.c_str(), "w");
- if (file) {
- fputs(pContent, file);
- fclose(file);
- }
- else
- CCLOG("save file error.");
- return false;
- }
3.SQLite
转自:
http://4137613.blog.51cto.com/4127613/772518
cocos2d-x学习笔记17:记录存储2:SQLite基本使用


- #include "sqlite3.h"
- sqlite3 *pDB = NULL;//数据库指针
- char * errMsg = NULL;//错误信息
- std::string sqlstr;//SQL指令
- int result;//sqlite3_exec返回值
- //打开一个数据库,如果该数据库不存在,则创建一个数据库文件
- result = sqlite3_open("save.db", &pDB);
- if( result != SQLITE_OK )
- CCLog( "打开数据库失败,错误码:%d ,错误原因:%s\n" , result, errMsg );
- //创建表,设置ID为主键,且自动增加
- result=sqlite3_exec( pDB, "create table MyTable_1( ID integer primary key autoincrement, name nvarchar(32) ) " , NULL, NULL, &errMsg );
- if( result != SQLITE_OK )
- CCLog( "创建表失败,错误码:%d ,错误原因:%s\n" , result, errMsg );
- //插入数据
- sqlstr=" insert into MyTable_1( name ) values ( '克塞' ) ";
- result = sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , NULL, NULL, &errMsg );
- if(result != SQLITE_OK )
- CCLog( "插入记录失败,错误码:%d ,错误原因:%s\n" , result, errMsg );
- //插入数据
- sqlstr=" insert into MyTable_1( name ) values ( '葫芦娃' ) ";
- result = sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , NULL, NULL, &errMsg );
- if(result != SQLITE_OK )
- CCLog( "插入记录失败,错误码:%d ,错误原因:%s\n" , result, errMsg );
- //插入数据
- sqlstr=" insert into MyTable_1( name ) values ( '擎天柱' ) ";
- result = sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , NULL, NULL, &errMsg );
- if(result != SQLITE_OK )
- CCLog( "插入记录失败,错误码:%d ,错误原因:%s\n" , result, errMsg );
- //关闭数据库
- sqlite3_close(pDB);
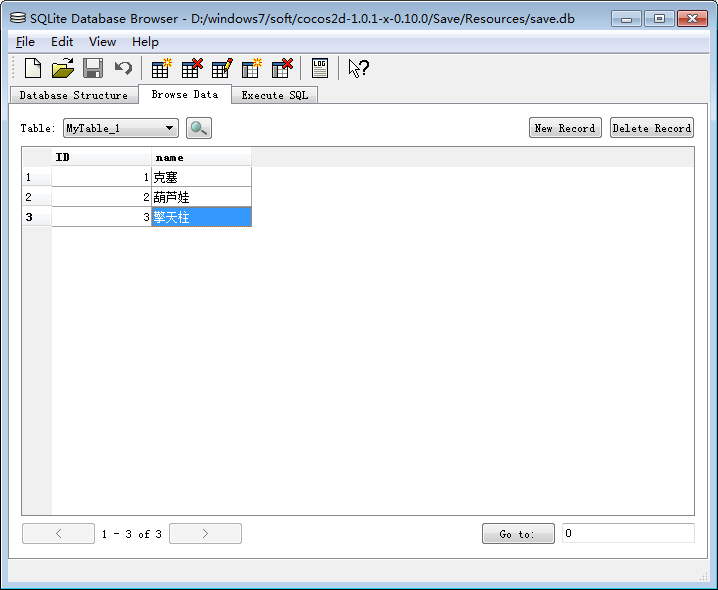
- sqlstr="update MyTable_1 set name='威震天' where ID = 3";
- sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , NULL, NULL, &errMsg );
- sqlstr="delete from MyTable_1 where ID = 2";
- sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , NULL, NULL, &errMsg );
- bool isExisted_;
- sqlstr="select count(type) from sqlite_master where type='table' and name='MyTable_1'";
- sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , isExisted, &isExisted_, &errMsg );
- int isExisted( void * para, int n_column, char ** column_value, char ** column_name )
- {
- bool *isExisted_=(bool*)para;
- *isExisted_=(**column_value)!='0';
- return 0;
- }
- bool isExisted_;
- sqlstr="select count(*) from MyTable_1 where ID = 2";
- sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , isExisted, &isExisted_, &errMsg );
- int count;
- sqlstr="select * from MyTable_1";
- sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , loadRecordCount, &count, &errMsg );
- int loadRecordCount( void * para, int n_column, char ** column_value, char ** column_name )
- {
- int *count=(int*)para;
- *count=n_column;
- return 0;
- }
- sqlstr="select * from MyTable_1 where ID=3";
- sqlite3_exec( pDB, sqlstr.c_str() , loadRecord, NULL, &errMsg );
- int loadRecord( void * para, int n_column, char ** column_value, char ** column_name )
- {
- CCLog("ID=%s,name=%s",column_value[0],column_value[1]);
- return 0;
- }
本文出自 “老G的小屋” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://4137613.blog.51cto.com/4127613/772518
- cocos2d-x中几种存储数据的方式
- cocos2d-x中几种存储数据的方式
- cocos2d-x中几种存储数据的方式
- cocos2d-x中几种存储数据的方式
- cocos2d-x 数据存储
- cocos2d-x中的简单的数据存储
- Cocos2d-x Sqlite3数据存储
- cocos2d-x 数据存储 CCUserDefault
- cocos2d-x 数据存储 CCFileUtils
- [寒江孤叶丶的Cocos2d-x之旅_10]Cocos2d-x中存储用户数据,如何存储数据。如何保存数据。
- Cocos2d-x教程(9)-简单的数据存储,CCUserDefault
- Cocos2d-x教程(9)-简单的数据存储,CCUserDefault
- cocos2d-x 浅谈数据存储-CCUserDefault
- cocos2d-x 使用TinyXML2存储数据:
- cocos2d-x 数据存储 Sqlite数据库
- cocos2d-x CCUserDefault 实现数据存储XML
- cocos2d-x 浅谈数据存储-CCUserDefault
- cocos2d-x lua table数据存储
- myeclipse快捷键手册大全
- Loadrunner添加服务器监控
- QT QGridLayout QHBoxLayout QVBoxLayout 布局管理器运用
- Selinux结合Apache使用
- IOS调试技巧:当程序崩溃的时候怎么办 iphone IOS
- cocos2d-x中几种存储数据的方式
- CWnd::OnHScroll
- NSAttributedString UIKit Additions 参考
- onSaveInstanceState和onRestoreInstanceState触发的时机
- Flash Builder4.7 在“查出出现”期间发生了内部错误。
- python telnetlib 模块的使用
- iPhone网络开发之如何使用NSURLConnection
- C++ 异常
- 随机函数原理


