SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝情趣用品 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 20:26
写在前面:本节是前一节内容的后续部分,这两节都是从全局的角度SQLite内核各个模块的设计和功能。只有从全局上把握SQLite,才会更容易的理解SQLite的实现。SQLite采用了层次化,模块化的设计,而这些使得它的可扩展性和可移植性非常强。而且SQLite的架构与通用DBMS的结构差别不是很大,所以它对于理解通用DBMS具有重要意义。好了,下面我们开始讨论SQLite剩余的两部分:Back-end(后端)和compiler(编译器)。
2、B-tree和Pager
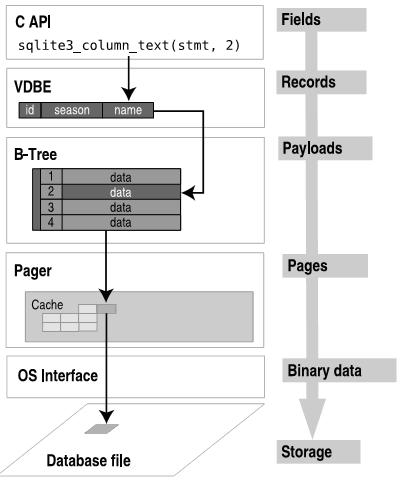
B-Tree使得VDBE可以在O(logN)下查询,插入和删除数据,以及O(1)下双向遍历结果集。B-Tree不会直接读写磁盘,它仅仅维护着页面(pages)之间的关系。当B-TREE需要页面或者修改页面时,它就会调用Pager。当修改页面时,pager保证原始页面首先写入日志文件,当它完成写操作时,pager根据事务状态决定如何做。B-tree不直接读写文件,而是通过page cache这个缓冲模块读写文件对于性能是有重要意义的(注:这和操作系统读写文件类似,在Linux中,操作系统的上层模块并不直接调用设备驱动读写设备,而是通过一个高速缓冲模块调用设备驱动读写文件,并将结果存到高速缓冲区)。
2.1、数据库文件格式(Database File Format)
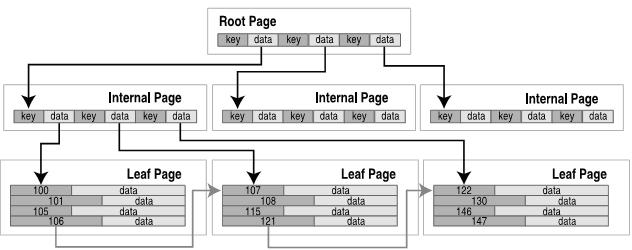
数据库中所有的页面都按从1开始顺序标记。一个数据库由许多B-tree构成——每一个表和索引都有一个B-tree(注:索引采用B-tree,而表采用B+tree,这主要是表和索引的需求不同以及B-tree和B+tree的结构不同决定的:B+tree的所有叶子节点包含了全部关键字信息,而且可以有两种顺序查找——具体参见《数据结构》,严蔚敏。而B-tree更适合用来作索引)。所有表和索引的根页面都存储在sqlite_master表中。
数据库中第一个页面(page 1)有点特殊,page 1的前100个字节包含一个描述数据库文件的特殊的文件头。它包括库的版本,模式的版本,页面大小,编码等所有创建数据库时设置的参数。这个特殊的文件头的内容在btree.c中定义,page 1也是sqlite_master表的根页面。
2.1、页面重用及回收(Page Reuse and Vacuum )
SQLite利用一个空闲列表(free list)进行页面回收。当一个页面的所有记录都被删除时,就被插入到该列表。当运行VACUUM命令时,会清除free list,所以数据库会缩小,本质上它是在新的文件重新建立数据库,而所有使用的页在都被拷贝过去,而free list却不会,结果就是一个新的,变小的数据库。当数据库的autovacuum开启时,SQLite不会使用free list,而且在每一次commit时自动压缩数据库。
2.2、B-Tree记录
B-tree中页面由B-tree记录组成,也叫做payloads。每一个B-tree记录,或者payload有两个域:关键字域(key field)和数据域(data field)。Key field就是ROWID的值,或者数据库中表的关键字的值。从B-tree的角度,data field可以是任何无结构的数据。数据库的记录就保存在这些data fields中。B-tree的任务就是排序和遍历,它最需要就是关键字。Payloads的大小是不定的,这与内部的关键字和数据域有关,当一个payload太大不能存在一个页面内进便保存到多个页面。
B+Tree按关键字排序,所有的关键字必须唯一。表采用B+tree,内部页面不包含数据,如下:
B+tree中根页面(root page)和内部页面(internal pages)都是用来导航的,这些页面的数据域都是指向下级页面的指针,仅仅包含关键字。所有的数据库记录都存储在叶子页面(leaf pages)内。在叶节点一级,记录和页面都是按照关键字的顺序的,所以B-tree可以水平方向遍历,时间复杂度为O(1)。
2.3、记录和域(Records and Fields)
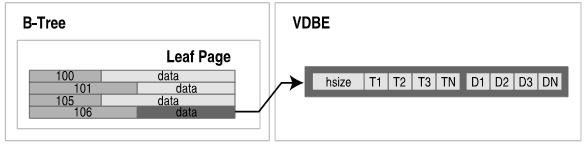
位于叶节点页面的数据域的记录由VDBE管理,数据库记录以二进制的形式存储,但有一定的数据格式。记录格式包括一个逻辑头(logical header)和一个数据区(data segment),header segment包括header的大小和一个数据类型数组,数据类型用来在data segment的数据的类型,如下:
2.4、层次数据组织(Hierarchical Data Organization)
从上往下,数据越来越无序,从下向上,数据越来越结构化.
2.5、B-Tree API
B-Tree模块有它自己的API,它可以独立于C API使用。另一个特点就是它支持事务。由pager处理的事务,锁和日志都是为B-tree服务的。根据功能可以分为以下几类:
2.5.1、访问和事务函数
sqlite3BtreeOpen: Opens a new database file. Returns a B-tree object.
sqlite3BtreeClose: Closes a database.
sqlite3BtreeBeginTrans: Starts a new transaction.
sqlite3BtreeCommit: Commits the current transaction.
sqlite3BtreeRollback: Rolls back the current transaction.
sqlite3BtreeBeginStmt: Starts a statement transaction.
sqlite3BtreeCommitStmt: Commits a statement transaction.
sqlite3BtreeRollbackStmt: Rolls back a statement transaction.
2.5.2、表函数
sqlite3BtreeCreateTable: Creates a new, empty B-tree in a database file.
sqlite3BtreeDropTable: Destroys a B-tree in a database file.
sqlite3BtreeClearTable: Removes all data from a B-tree, but keeps the B-tree intact.
2.5.3、游标函数(Cursor Functions)
sqlite3BtreeCursor: Creates a new cursor pointing to a particular B-tree.
sqlite3BtreeCloseCursor: Closes the B-tree cursor.
sqlite3BtreeFirst: Moves the cursor to the first element in a B-tree.
sqlite3BtreeLast: Moves the cursor to the last element in a B-tree.
sqlite3BtreeNext: Moves the cursor to the next element after the one it is currently
pointing to.
sqlite3BtreePrevious: Moves the cursor to the previous element before the one it is
currently pointing to.
sqlite3BtreeMoveto: Moves the cursor to an element that matches the key value passed in as a parameter.
2.5.4、记录函数(Record Functions)
sqlite3BtreeDelete: Deletes the record that the cursor is pointing to.
sqlite3BtreeInsert: Inserts a new element in the appropriate place of the B-tree.
sqlite3BtreeKeySize: Returns the number of bytes in the key of the record that the
cursor is pointing to.
sqlite3BtreeKey: Returns the key of the record the cursor is currently pointing to.
sqlite3BtreeDataSize: Returns the number of bytes in the data record that the cursor is
currently pointing to.
sqlite3BtreeData: Returns the data in the record the cursor is currently pointing to.
2.5.5、配置函数(Configuration Functions)
sqlite3BtreeSetCacheSize: Controls the page cache size as well as the synchronous
writes (as defined in the synchronous pragma).
sqlite3BtreeSetSafetyLevel: Changes the way data is synced to disk in order to increase
or decrease how well the database resists damage due to OS crashes and power failures.
Level 1 is the same as asynchronous (no syncs() occur and there is a high probability of
damage). This is the equivalent to pragma synchronous=OFF. Level 2 is the default. There
is a very low but non-zero probability of damage. This is the equivalent to pragma
synchronous=NORMAL. Level 3 reduces the probability of damage to near zero but with a
write performance reduction. This is the equivalent to pragma synchronous=FULL.
sqlite3BtreeSetPageSize: Sets the database page size.
sqlite3BtreeGetPageSize: Returns the database page size.
sqlite3BtreeSetAutoVacuum: Sets the autovacuum property of the database.
sqlite3BtreeGetAutoVacuum: Returns whether the database uses autovacuum.
sqlite3BtreeSetBusyHandler: Sets the busy handler
2.6、实例分析
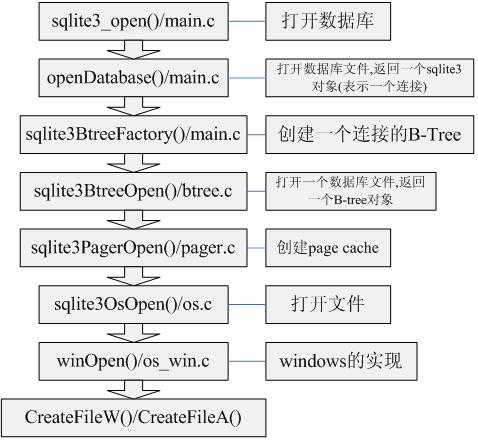
最后以sqlite3_open的具体实现结束本节的讨论(参见Version 3.6.10的源码):
由上图可以知道,SQLite的所有IO操作,最终都转化为操作系统的系统调用(一名话:DBMS建立在痛苦的OS之上)。同时也可以看到SQLite的实现非常的层次化,模块化,使得SQLite更易扩展,可移植性非常强。
3、编译器(Compiler)
3.1、分词器(Tokenizer)
接口把要执行的SQL语句传递给Tokenizer,Tokenizer按照SQL的词法定义把它切分一个一个的词,并传递给分析器(Parser)进行语法分析。分词器是手工写的,主要在Tokenizer.c中实现。
3.2、分析器(Parser)
SQLite的语法分析器是用Lemon——一个开源的LALR(1)语法分析器的生成器,生成的文件为parser.c。
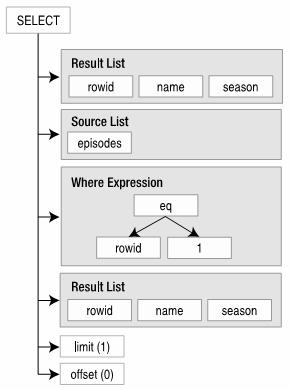
一个简单的语法树:
SELECT rowid, name, season FROM episodes WHERE rowid=1 LIMIT 1
3.3、代码生成器(Code Generator)
代码生成器是SQLite中取庞大,最复杂的部分。它与Parser关系紧密,根据语法分析树生成VDBE程序执行SQL语句的功能。由诸多文件构成:select.c,update.c,insert.c,delete.c,trigger.c,where.c等文件。这些文件生成相应的VDBE程序指令,比如SELECT语句就由select.c生成。下面是一个读操作中打开表的代码的生成实现:
/* Generate code that will open a table for reading.
*/
void sqlite3OpenTableForReading(
Vdbe *v, /* Generate code into this VDBE */
int iCur, /* The cursor number of the table */
Table *pTab /* The table to be opened */
){
sqlite3VdbeAddOp(v, OP_Integer, pTab->iDb, 0);
sqlite3VdbeAddOp(v, OP_OpenRead, iCur, pTab->tnum);
VdbeComment((v, "# %s", pTab->zName));
sqlite3VdbeAddOp(v, OP_SetNumColumns, iCur, pTab->nCol);
}
Sqlite3vdbeAddOp函数有三个参数:(1)VDBE实例(它将添加指令),(2)操作码(一条指令),(3)两个操作数。
3.4、查询优化
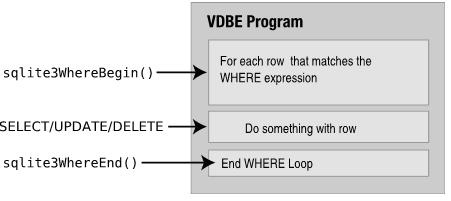
代码生成器不仅负责生成代码,也负责进行查询优化。主要的实现位于where.c中,生成的WHERE语句块通常被其它模块共享,比如select.c,update.c以及delete.c。这些模块调用sqlite3WhereBegin()开始WHERE语句块的指令生成,然后加入它们自己的VDBE代码返回,最后调用sqlite3WhereEnd()结束指令生成,如下:
SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1) 虚拟机(VM)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(1)
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2) Back-end(后端)和compiler(编译器)
- SQLite 内核概述(2)
- SQLite 入门与分析
- SQLite入门与分析
- poj 2409 Let it Bead
- 关于在ubuntu10.04版本(而且该版本安装了OPEN JDK时),安装SUN JAVA遇到了几个问题并且安装成功
- 求重复出现的自然数序列 C++实现
- ExtJS 案例
- pureftp+pureadmin安装配置
- SQLite入门与分析(三)---内核概述(2)
- 题目1172:哈夫曼树
- org.hibernate.HibernateException: No Session found for current thread
- 敏捷思维学习Ext.Net MVC--3.5Form表单组件之下拉菜单(ComboBox)
- 墙高万丈,挡的是不来的人
- JSON资料整理
- NYOJ589 糖果
- repeater行中的TextBox利用datepicker输入日期
- LNMP环境搭建