POJ1518、 UVA1531 - Problem Bee(几何+贪心)
来源:互联网 发布:sql在线格式化工具 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/17 06:41
Imagine a perfectly formed honeycomb, spanning the infinite Cartesian plane. It is an interlocking grid composed of congruent equilateral hexagons. One hexagon is located so that its center is at the origin and has two corners on the X-axis. A bee must be very careful about how it travels in order not to get lost in the infinite plane. To get from an arbitrary point A to another arbitrary point B, it will first head from A to the exact center of the hexagon in which A is located. Then, it will travel in a straight line to the exact center of an adjacent hexagon. It will move from center to adjacent center until it has reached the hexagon containing point B. At the destination hexagon, it will move from the center to point B. In all cases, the bee will take a path of minimal distance that obeys the rules. The figure below demonstrates one possible minimal path from point A to point B.
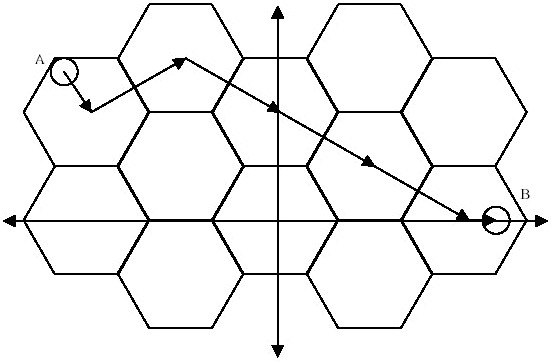
Input
Input will be in the form of 5 floating point numbers per line. The first number will be the length, in centimeters, of the sides of the hexagons. The next two numbers will be the x and y coordinates of point A, followed by the x and y coordinates of point B. The input will be terminated by a line containing five zeroes. Neither point A nor point B will ever be exactly on a border between hexagons.
Output
For each line of the input, output the minimum length of a path from point A to point B, to the nearest 0.001 centimeters.
Sample Input
1.0 -3.2 2.2 3.3 09 1 4 5 10.1 0.09 0 0.21 00 0 0 0 0
Sample Output
7.7375.0000.526
题意:给定蜂窝长度,起点A和起点B,蜜蜂移动要从A移动到对应的六边形中心,然后从一个六边形中心移动到另一个六边形中心,最后在从六边形中心移动到B,注意如果AB在同一中心,直接A移动到B。
思路:竖直方向和水平方向多的肯定是要移动的段数,那么问题就变成找A和B的中心,直接找点对应的X,Y坐标是第几个六边形,注意如果在边上要处理一下,最后判断周围6个是否有比它距离更近的六边形中心,确定中心后,路径就很好计算了,
代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <math.h>#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))const double pi = acos(-1.0);const int d[6][2] = {{0, 2}, {0, -2}, {1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}};double l, xa, ya, xb, yb, hd, wd;int xan, yan, xbn, ybn;double dis(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { return sqrt((x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1));}void tra(int &x, int &y, double xa, double ya) { if (x % 2) {if (y % 2 == 0) { y++;} } else {if (y % 2) { y++;} } int minx = x, miny = y; double mind = dis(x * wd, y * hd, xa, ya); for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {double xx = (d[i][0] + x) * wd;double yy = (d[i][1] + y) * hd;if (mind > dis(xx, yy, xa, ya)) { minx = d[i][0] + x; miny = d[i][1] + y; mind = dis(xx, yy, xa, ya);} } x = minx; y = miny;}void init() { hd = sin(pi/3) * l; wd = l + l / 2; xan = xa / wd; yan = ya / hd; xbn = xb / wd; ybn = yb / hd; tra(xan, yan, xa, ya); tra(xbn, ybn, xb, yb);}double solve() { if (xan == xbn && yan == ybn)return dis(xa, ya, xb, yb); int xx = abs(xbn - xan), yy = abs(ybn - yan); double ans = dis(xa, ya, xan * wd, yan * hd) + dis(xb, yb, xbn * wd, ybn * hd) + xx * sin(pi/3) * 2 * l; if (yy > xx)ans += (yy - xx) * l * sqrt(3) / 2; return ans;}int main() { while (~scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &l, &xa, &ya, &xb, &yb) && l || xa || ya || xb || yb) {init();printf("%.3lf\n", solve()); } return 0;}- POJ1518、 UVA1531 - Problem Bee(几何+贪心)
- UVa1531 - Problem Bee
- uva 1531 & poj 1518 Problem Bee(几何计算+贪心)
- poj 1518 Problem Bee
- UVa 1531 - Problem Bee
- UVa Problem 10182 Bee Maja (蜜蜂 Maja)
- POJ 1518 Problem Bee 笔记
- POJ 1518 Problem Bee 笔记
- TopCoder SRM 652 Div2 Problem 1000 - NoRightTurnDiv2 (几何 + 贪心)
- 1.13 Codeforces 30D Kings Problem 贪心 计算几何
- bee
- bee
- Bee
- UVA 11106 - Rectilinear Polygon(几何+贪心)
- FZU 2144(几何+贪心区间覆盖)
- (一般)POJ-1328 区间贪心,几何
- HDU 5858 Hard problem (几何)
- hdu5858 Hard problem (计算几何)
- UItableview编辑模式
- SVN中trunk,branches,tags用法详解
- SVN的标准目录结构:trunk、branches、tags
- 浙大ACM 1003 Crashing Balloon
- svn之trunk、branches、tags
- POJ1518、 UVA1531 - Problem Bee(几何+贪心)
- Linux服务器下用svn创建多个项目
- cocos2d-x创建工程批处理
- 创建多个svn仓库并通过http访问
- DIY
- SVN 多项目管理(强烈建议每个项目建一个库)
- poj 2484 博弈--对称思想 15行代码以内解决
- Navicat for MySQL中文乱码问题
- 【Unity3D自学记录】获取WWW下载的进度


