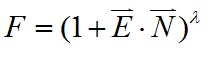Specular Reflection Models
来源:互联网 发布:seo的优化 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/01 09:52
From Wiki
Specular Reflection Models
A number of different models exist to predict the distribution of microfacets. Most assume that the microfacet normals are distributed evenly around the normal; these models are called ISOTROPIC. If microfacets are distributed with a preference for a certain direction along the surface, the distribution isANISOTROPIC.
1. Phong Distribution
In the Phong reflection model, the intensity of the specular highlight is calculated as:
Where R is the mirror reflection of the light vector off the surface, andV is the viewpoint vector.
In the Blinn–Phong shading model, the intensity of a specular highlight is calculated as:

Where N is the smooth surface normal andH is the half-angle direction (the direction vector midway betweenL, the vector to the light, and V, the viewpoint vector).
The number shininessis called the Phong exponent, and is a user-chosen value that controls the apparent smoothness of the surface. These equations imply that the distribution of microfacet normals is an approximately Gaussian distribution (for largeshininess), or approximately Pearson type II distribution, of the corresponding angle. While this is a useful heuristic and produces believable results, it isNOT a physically based model.
Another similar formula, but only calculated differently:
where R is an eye reflection vector,E is an eye vector (view vector),N is surface normal vector. All vectors arenormalized. L is a light vector.
2. Gaussian distribution
A slightly better model of microfacet distribution can be created using a Gaussian distribution. The usual function calculates specular highlight intensity as
where m is a constant between 0 and 1 that controls the apparent smoothness of the surface.
3. Beckmann distribution
A physically based model of microfacet distribution is the Beckmann distribution:
where m is the rms slope of the surface microfacets (the roughness of the material). Compare to the empirical models above, this function "gives the absolute magnitude of the reflectance without introducing arbitrary constants; the disadvantage is that it requires more computation".However, this model can be simplified since
Also note that the product of cos(α) and a surface distribution function is normalized over the half-sphere which is obeyed by this function.
4. Heidrich–Seidel anisotropic distribution
The Heidrich–Seidel distribution is a simple anisotropic distribution, based on the Phong model. It can be used to model surfaces that have small parallel grooves or fibers, such as brushed metal, satin, and hair. The specular highlight intensity for this distribution is:
where n is the anisotropic exponent,V is the viewing direction, L is the direction of incoming light, andT is the direction parallel to the grooves or fibers at this point on the surface. If you have a unit vectorD which specifies the global direction of the anisotropic distribution, you can compute the vectorT at a given point by the following:
where N is the unit normal vector at that point on the surface. You can also easily compute the cosine of the angle between the vectors by using a property of the dot product and the sine of the angle by using the trigonometric identities.
The anisotropic kspec should be used in conjunction with a non-anisotropic distribution like a Phong distribution to produce the correct specular highlight.
5. Ward anisotropic distribution
The specular term is 0 if N·L < 0 orN·R < 0. All vectors are unit vectors. The vectorR is the mirror reflection of the light vector off the surface,L is the direction from the surface point to the light,H is the half-angle direction, N is the surface normal, and X andY are two orthogonal vectors in the normal plane which specify the anisotropic directions.
6. Cook–Torrance model
The Cook–Torrance model uses a specular term of the form:
Here D is the Beckmann distribution factor as above andF is the Fresnel term,
For performance reasons in real-time 3D graphics Schlick's approximation is often used to approximate Fresnel term.
G is the geometric attenuation term, describing selfshadowing due to the microfacets, and is of the form
In these formulas E is the vector to the camera or eye,H is the half-angle vector,L is the vector to the light source andN is the normal vector, andα is the angle between H and N.
- Specular Reflection Models
- <PhysicallyBasedRendering>chap8 REFLECTION MODELS
- diffuse/glossy/specular reflection and transmission
- 【Ray Tracing from Ground Up】Specular Reflection
- DSOJ Specular reflection of a tree(树的镜面映射)
- Q117:PBRT-V3反射模型(Reflection Models)笔记
- 问题六十八:着色模型(shading model)(1)——反射模型(reflection model)(2.2)——高光反射(specular reflection)
- Specular Offset
- Specular IBL
- specular BRDF
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Reflection
- Why doesn't this simple RegEx work with sed?
- hdu 3833 YY's new problem(hash表)
- STL系列之四 heap 堆
- matlab小波分析工具箱常用函数
- RMAN恢复目录(Recovery Catalog)
- Specular Reflection Models
- Vm虚拟机中Linux扩展磁盘空间
- STL系列之五 priority_queue 优先级队列
- 广播接收器—Broadcast Receiver(一)
- “马航客机失联”请多点克制少点猜想!
- http://www.regular-expressions.info/gnu.html
- mfc-菜单-学习笔记
- linux/videodev.h:没有那个文件或目录
- chrome浏览器频繁崩溃