FFmpeg入门(4)-An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 2
来源:互联网 发布:oracle转mysql 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/29 19:17
An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 2 中将1中的保存图片改为用SDL显示,在显示之前要讲本地帧改为YUV420P格式。
对照1把2 的代码进行相应修改得到:
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>#include <libavformat/avformat.h>#include <libswscale/swscale.h>#include <SDL/SDL.h>#include <SDL/SDL_thread.h>#include <unistd.h>//slqstatic AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = NULL;int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {// AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx;// static AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = NULL; AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx; AVCodec *pCodec; AVFrame *pFrame; AVFrame *pFrameRGB; AVPacket packet; SDL_Surface *screen; SDL_Overlay *bmp; uint8_t *buffer; int numBytes; int i; av_register_all(); //slq//reads the file header and stores information about the file format in the AVFormatContext structure pFormatCtx if (avformat_open_input( &pFormatCtx, argv[1], NULL, NULL) < 0) //if (avformat_open_input( &input_fmt_ctx, input_file, NULL, NULL) < 0) { //if (av_open_input_file(&pFormatCtx, argv[1], NULL, 0, NULL) != 0) return -1;// Retrieve stream information if (av_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx) < 0) return -1;// Dump information about file onto standard error // dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, argv[1], 0); av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, argv[1], 0);// Find the first video stream int videoStream = -1; for (i = 0; i < pFormatCtx->nb_streams; ++i) { if (pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) { videoStream = i; break; } }// Get a pointer to the codec context for the video stream pCodecCtx = pFormatCtx->streams[videoStream]->codec; // Find the decoder for the video stream pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id); if (pCodec == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported codec@!\n"); } // Open codec //slq if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, NULL) < 0) //if (avcodec_open(pCodecCtx, pCodec) < 0) return -1; // Allocate video frame (native format) pFrame = avcodec_alloc_frame(); // Allocate an AVFrame structure ( RGB ) pFrameRGB = avcodec_alloc_frame(); if (pFrameRGB == NULL) return -1; // we still need a place to put the raw data when we convert it. //We use avpicture_get_size to get the size we need, //and allocate the space manually: // Determine required buffer size and allocate buffer numBytes = avpicture_get_size(PIX_FMT_RGB24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); //av_malloc is ffmpeg's malloc that is just a simple wrapper around malloc that makes sure the memory addresses are aligned and such. buffer = (uint8_t *) av_malloc(numBytes * sizeof(uint8_t)); // Assign appropriate parts of buffer to image planes n. 图像平面;映像平面 in pFrameRGB // Note that pFrameRGB is an AVFrame, but AVFrame is a superset // of AVPicture avpicture_fill((AVPicture *) pFrameRGB, buffer, PIX_FMT_RGB24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); /* * SDL */ //SDL_Init() essentially tells the library what features we're going to use if (SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO | SDL_INIT_AUDIO | SDL_INIT_TIMER)) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not initialize SDL - %s\n", SDL_GetError()); exit(1); } //This sets up a screen with the given width and height. //The next option is the bit depth of the screen - 0 is a special value that means "same as the current display". screen = SDL_SetVideoMode(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, 0, 0); if (!screen) { fprintf(stderr, "SDL: could not set video mode - exiting\n"); exit(1); } //using YV12 to display the image bmp = SDL_CreateYUVOverlay(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, SDL_YV12_OVERLAY, screen); i = 0; while (av_read_frame(pFormatCtx, &packet) >= 0) { // Is this a packet from the video stream? if (packet.stream_index == videoStream) { int frameFinished; /* avcodec_decode_video(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &frameFinished, packet.data, packet.size); */ avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &frameFinished, &packet); // Did we get a video frame? if (frameFinished) {#ifdef SAVEFILE /*保存到文件*/ /* *此函数已经不用 img_convert((AVPicture *)pFrameRGB, PIX_FMT_RGB24, (AVPicture*)pFrame, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); */ static struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx; img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height , pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, PIX_FMT_RGB24, SWS_BICUBIC , NULL, NULL, NULL); sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, (const uint8_t* const*)pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height, pFrameRGB->data, pFrameRGB->linesize); if(++i <= 5) SaveFrame(pFrameRGB, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, i);#else /*显示 */ AVPicture pict; static struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx; SDL_Rect rect; SDL_LockYUVOverlay(bmp); pict.data[0] = bmp->pixels[0]; pict.data[1] = bmp->pixels[2]; pict.data[2] = bmp->pixels[1]; pict.linesize[0] = bmp->pitches[0]; pict.linesize[1] = bmp->pitches[2]; pict.linesize[2] = bmp->pitches[1]; /* // Convert the image into YUV format that SDL uses img_convert(&pict, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, (AVPicture *) pFrame, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); */ img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, PIX_FMT_YUV420P, SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL); sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, (const uint8_t* const *) pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height, pict.data, pict.linesize); SDL_UnlockYUVOverlay(bmp); rect.x = 0; rect.y = 0; rect.w = pCodecCtx->width; rect.h = pCodecCtx->height; SDL_DisplayYUVOverlay(bmp, &rect);#endif usleep(25000); } } // Free the packet that was allocated by av_read_frame av_free_packet(&packet); } av_free(buffer); av_free(pFrameRGB); av_free(pFrame); avcodec_close(pCodecCtx); av_close_input_file(pFormatCtx); return 0;}程序2编译 运行
gcc -o tutorial02 tutorial02.1.c -lavutil -lavformat -lavcodec -lz -lm `sdl-config --cflags --libs`
gcc -g -o tutorial02 tutorial02.1.c -lavutil -lavformat -lavcodec -lswscale -lz -lm -lpthread `sdl-config --cflags --libs`

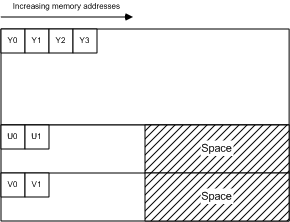
YUV420P格式分析
http://my.oschina.net/u/589963/blog/167766
0 0
- FFmpeg入门(4)-An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 2
- FFmpeg入门(3)-An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial
- FFmpeg入门(5)-An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 3
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial
- ffmpeg学习(2)--An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 01
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 02
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 00
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 03
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 04
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 05
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 07
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 06
- An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 08
- 【笔记】An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 00
- VS2010/MFC编程入门之二十三(常用控件:列表框控件ListBox)
- U-Mail邮件系统客户无需担心OpenSSL心脏出血漏洞
- 局部变量作为返回值问题
- VS2010/MFC编程入门之二十四(常用控件:组合框控件Combo Box)
- Java 程序员应该了解的10个面向对象设计原则
- FFmpeg入门(4)-An ffmpeg and SDL Tutorial 2
- PL/SQL Developer 远程连接Oracle数据库
- 寄送物品损坏-道歉信(英文电子邮件模板)
- Cookie工作过程& HTTP无状态协议分析与Cookie的关系
- VS2010/MFC编程入门之二十五(常用控件:滚动条控件Scroll Bar)
- Uva-116 Unidirectional TSP DP
- 错过会议-道歉信(英文电子邮件模板)
- Linux 开机启动过程分析
- phonegap3.4.0如何安装